What Is RFID Technology And How It Works?
RFID is an acronym for “radio-frequency identification” and refers to a technology whereby digital data encoded in RFID tags or smart labels (defined below) are captured by an RFID Tag reader via radio waves. RFID is similar to barcoding in that data from a tag or label are captured by a device that stores the data in a database. RFID, however, has several advantages over systems that use barcode asset tracking software. The most notable is that RFID tag data can be read outside the line-of-sight, whereas barcodes must be aligned with an optical scanner. If you are considering implementing an RFID solution,
How RFID works?![how RFID works]()
ad
RFID belongs to a group of technologies referred to as Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC). AIDC methods automatically identify objects, collect data about them, and enter those data directly into computer systems with little or no human intervention. RFID methods utilize radio waves to accomplish this. At a simple level, RFID systems consist of three components: an RFID tag or smart label, an RFID reader, and an antenna. RFID tags contain an integrated circuit and an antenna, which are used to transmit data to the RFID reader (also called an interrogator). The reader then converts the radio waves to a more usable form of data. Information collected from the tags is then transferred through a communications interface to a host computer system, where the data can be stored in a database and analyzed at a later time.
Types of RFID
Within the Electromagnetic Spectrum, there are three primary frequency ranges used for RFID transmissions – Low Frequency, High Frequency, and Ultra-High Frequency.
Low-Frequency RFID
- General Frequency Range: 30 – 300 kHz
- Primary Frequency Range: 125 – 134 kHz
- Read Range: Contact – 10 Centimeters
- Applications: Animal Tracking, Access Control, Car Key-Fob, Applications with High Volumes of Liquids and Metals
- Pros: Works well near Liquids & Metals, Global Standards
- Cons: Very Short Read Range, Limited Quantity of Memory, Low Data Transmission Rate, High Production Cost
High-Frequency RFID
- Primary Frequency Range: 13.56 MHz
- Read Range: Near Contact – 30 Centimeters
- Applications: DVD Kiosks, Library Books, Personal ID Cards, Poker/Gaming Chips, NFC Applications
- Pros: NFC Global Protocols, Larger Memory Options, Global Standards
- Cons: Short Read Range, Low Data Transmission Rate
Ultra High-Frequency RFID
- General Frequency Range: 300 – 3000 MHz
- Primary Frequency Ranges: 433 MHz, 860 – 960 MHz
There are two types of RFID that reside within the Ultra High-Frequency range: Active RFID and Passive RFID.
Active RFID
- Primary Frequency Range: 433 MHz, (Can use 2.45 GHz – under the Extremely High-Frequency Range)
- Read Range: 30 – 100+ Meters
- Average Cost Per Tag: $25.00 – $50.00
- Applications: Vehicle Tracking, Auto Manufacturing, Mining, Construction, Asset Tracking
- Pros: Very Long Read Range, Lower Infrastructure Cost (vs. Passive RFID), Large Memory Capacity, High Data Transmission Rates
- Cons: High Per Tag Cost, Shipping Restrictions (due to batteries), Complex Software may be Required, High Interference from Metal and Liquids; Few Global Standards
Passive RFID
- Primary Frequency Ranges: 860 – 960 MHz
- Read Range: Near Contact – 25 Meters
- Average Cost Per Tag: $0.09 – $20.00
- Applications: Supply Chain Tracking, Manufacturing, Pharmaceuticals, Electronic Tolling, Inventory Tracking, Race Timing, Asset Tracking
- Pros: Long Read Range, Low Cost Per Tag, Wide Variety of Tag Sizes and Shapes, Global Standards, High Data Transmission Rates
- Cons: High Equipment Costs, Moderate Memory Capacity, High Interference from Metal and Liquids
RFID Smart tags and labels
As stated above, an RFID tag consists of an integrated circuit and an antenna. The tag is also composed of a protective material that holds the pieces together and shields them from various environmental conditions. The protective material depends on the application. For example, employee ID badges containing RFID tags are typically made from durable plastic, and the tag is embedded between the layers of plastic. RFID tags come in a variety of shapes and sizes and are either passive or active. Passive tags are the most widely used, as they are smaller and less expensive to implement. Passive tags must be “powered up” by the RFID reader before they can transmit data. Unlike passive tags, active RFID tags have an onboard power supply (e.g., a battery), thereby enabling them to transmit data at all times.
Smart labels differ from RFID tags in that they incorporate both RFID and barcode technologies. They’re made of an adhesive label embedded with an RFID tag inlay, and they may also feature a barcode and/or other printed information. Smart labels can be encoded and printed on-demand using desktop label printers, whereas programming RFID tags are more time consuming and require more advanced equipment.
RFID Technology in our everyday life![RFID]()
In our everyday life, everybody uses RFID technology, most of the times without knowing it. Today in this article we are going to see some examples of where we find it. Maybe you will be surprised about how many times you use RFID in your everyday life.
As you know, the initials RFID mean Radio Frequency Identification. The basic concept of operation is:
- An antenna sends out and receives radio signals.
- These signals are received and returned by an RFID tag with information added.
- A reader that is integrated with a system accepts and stores these data called events and finally, they trigger actions.
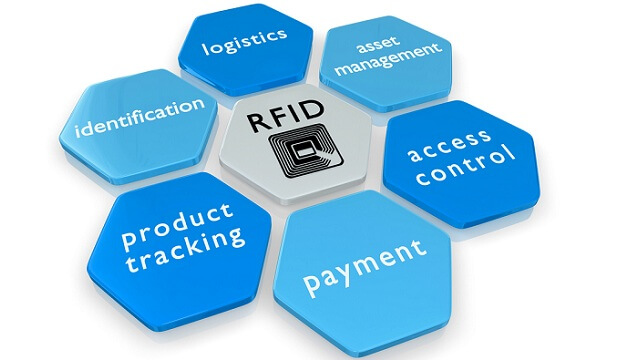
Application of RFID
Examples of applications that benefit from RFID are endless. Applications extend from broad areas like inventory tracking to supply chain management and can become more specialized depending on the company or industry. Types of RFID applications can span from IT asset tracking to textile tracking and even into specifics like rental item tracking.
Payments in means of transport: public transports and tolls
In order to eliminate the delays on road tolls, Electronic Tolls Collection (ETC) collects tolls electronically. With an RFID tag on a car don’t need to stop when they pass through tolls, the payment is automatic if the car is enrolled in the program and if it’s not, the system sends an event that triggers an action like don’t let the car pass or it takes a photo.
If you don’t drive, when you are traveling around the city you also use RFID in public transport, because of the entrance payment and the exit control can be done thanks to RFID tags in the prepaid transport passes.
Asset management: Location, identification and transport trace
Nowadays, the most modern and effective organizations are using RFID technology to automate assets tracking. Systems based on RFID solutions avoid many problems caused by manual tracking. With RFID they increase security and accuracy of the information which the company has about the goods in a constant and instantly way.
So, when you’re in a hotel, the tools, machines, and other items and disposable consumables may be controlled by RFID tags.
Logistics
Tagging goods and pallets, you can instantly know what goods you have, how many they are and how much space they occupy in your warehouse or back store just when they are entered.
Can you imagine what would happen if huge food companies didn’t have constant and instant control of the products they have in stock? When you shop at the supermarket you are not aware of how much the product has traveled, but thanks to RFID technology there is a trace of its movements.
Inventories and warehouses
The main objective to use RFID is to increase the efficiency of warehouses by reducing work and logistic costs. Likewise, to get instantly an accurate inventory of goods with all kinds of details, like size, quality, country, and so on. Physical inventory counts which are expensive and inaccurate are not necessary anymore. This way you save money and time.
Identification of animals
Tagging animals with RFID is an important tool for a farmer, in order to identify each animal with its information like origin, pedigree, medical details, etc. As well as with the help of software, to keep updated the information by uploading new information like veterinary visits.
Surgeries
The RFID technology in hospitals is present in many forms, from tracking surgical tools to tracking persons –patients, visitors, and staff. There are several important reasons to use the RFID system in the healthcare industry from reducing medical errors like to lost essential surgery tools or forget surgery sponges within patients, as well as reduce economic costs or increase the security at healthcare buildings.
The most common RFID applications in hospitals are inventory tracking, control access, staff and patients tracking, tracking tools, tracking disposable consumables, tracking large/expensive equipment, laundry tracking, etc.
Access control: sports facilities, buildings, tourism
The RFID access control systems work to identify whose, where and when it’s entering a building or a room. It’s useful to have information about individuals in an organization or event like a sports match or music festival, as well as to allow or deny the entry of individuals in particular places.
The same function can be fulfilled in a company to have control over the schedules of employees, to what places they access inside the company and the control of people who are visiting the company offices.
Passports
Passports with an embedded chip are called biometric passport, ePassport or digital passport. This chip has biometric information that is used to authenticate the identity of the passport holder. The information stored in the RFID chips of ePassports depends on the country’s policy. Data usually stored are name, date, and place of birth, sex, nationality and a digital version of the photograph. Data about the passport are in the chip too, such as the number, issue date and place, and the expiration date. The standardized biometrics used for the identification system are facial recognition, fingerprint recognition or iris recognition.
Fuel Pumps
A Radio-frequency Identification (RFID) reader on the fuel nozzle finds out how much petrol or diesel you want to buy, the attendant refills your car tank and you drive out without waiting to pay the bill. This is the scene across several HPCL petrol pumps in Indian top cities.
Every Fastlane user is provided with an RFID sticker linked to Fastlane mobile app. This enables the user to pre-set the fueling amount before reaching the petrol pump. After you reach the fuel outlet, the Fastlane RFID sticker pasted on the car windshield provides vehicle identification and fuel type, as well as billing and payment information to the petrol pump attendant. After the fueling is complete, you get an instant notification and you can simply drive away without having to stay and make the payments.
📚 Also Read: What is RFID blocking, and do you need it?
Some other popular utilities of RFID Technology
- Race Timing
- Supply Chain Management
- Pharmaceutical Tracking
- Inventory Tracking
- IT Asset Tracking
- Laundry & Textile Tracking
- File Tracking
- Returnable Transit Item (RTI) Tracking
- Event & Attendee Tracking
- Access Control
- Vehicle Tracking
- Tolling
- Hospital Infant Tracking
- Retail Inventory Tracking
- Pipe and Spool Tracking
- DVD Kiosks
- Library Materials Tracking
- Marketing Campaigns
- Real-Time Location Systems
Conclusion: The RFID technology has a long journey to cover, to be an integral part of the human body. People still feel more comfortable with their plastic cards. It is not much far when the RFID technology will replace the conventional payment methods and will be used to find missing persons, detecting explosives or tracking a deceased aircraft’s BlackBox sank in the deep ocean to unfold the causes of the catastrophe.
ad



Comments are closed.