What is VoIP And How Does A VoIP Phone System Work?
VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. It is also called IP telephony, internet telephony, and internet calling.
Voice over Internet Protocol, or VoIP, is a group of hardware and software that lets people make and receive voice calls over the internet. VoIP lets people send and receive voice calls over the internet, instead of using traditional phones or circuit transmission. Instead, VoIP sends voice data as data packets that are sent over a packet-switched network with media delivery protocols that let callers speak and listen as if they were talking over a PSTN connection.
What is VoIP?
ad
VoIP, which stands for “Voice over Internet Protocol” or “Voice over IP,” is a technology that lets you send voice calls and other forms of communication, like text and video, over the internet.
Instead of using the phone company’s wiring, IP telephony, internet telephony, or web calling turns voice and other multimedia content into digital data. This data can then be sent over the internet, enterprise local area networks (LANs), or wide area networks (WANs) (WANs). In this way, VoIP technology lets users make voice and video calls or send different kinds of messages from a computer, mobile device, VoIP phone handset, or any web browser that supports WebRTC.
A VoIP phone system first turns the sound waves of a speaker’s voice into digital data, which is then sent through a network connection to its destination. If the destination is a regular telephone network, the signal is changed back to a telephone signal before it gets there.
A VoIP phone system is, at its most basic, a way to send voice calls over IP networks. It is a way to make phone calls instead of using a landline. Recent changes and improvements are quickly making it the standard way for businesses to talk to each other if they want a reliable and future-proof way to talk. VoIP is now reliable and consistent at the top level.
ad

VoIP phone system is very popular in call centers because it is cheaper than other options and works well with CRM systems. Hard phones with VoIP capabilities have been used in call centers for a long time. However, most contact centers now just use a headset with a microphone to connect the agent and the caller. It’s called a “soft” phone.
VoIP is also more functional than traditional phone calls. Incoming calls can easily be sent to a VoIP phone, no matter where in the network it is physically plugged in. This means that “phones” can be anywhere with a stable internet connection. Calls can be routed using any number of digital protocols, and agents in a contact center can work from anywhere in the world using a VoIP phone. This makes it much easier to expand a call center than if it only used traditional phone lines.
A service provider gives a regular phone call a specific path in the real world (usually a dedicated phone company). This route is between you and the number you call. This system also uses the traditional telephone infrastructure, which is the network of phone lines that spans the country.
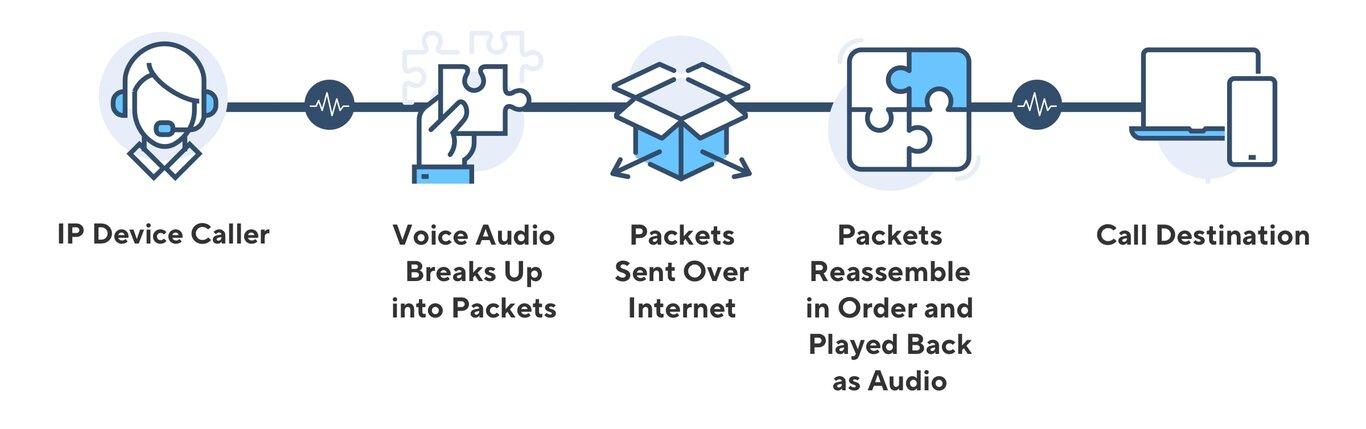
Calls are sent in a different way with a VoIP phone service. The voice you hear on the other end of a call is turned into digital packets. The best way to think of them is as data envelopes, just like how traditional envelopes hold what you’ve written on them.
“Codecs” handle the process of turning audio voice signals into digital packets. Codecs can be either pieces of hardware or processes that run on software. The voice signals are squished together and then turned into digital signals. To continue our analogy, they take what you say and put it in the digital envelopes.
So, what do users get out of VoIP? One of the best things about VoIP phone system is that it works over the internet and other data networks. By using the power of the cloud, VoIP providers make it possible to have intelligent conversations with customers, suppliers, collaborators, and employees no matter where they are or what device they prefer to use.
📚Also Read: How VoIP Is Reshaping Modern Communication
How Does a VoIP Phone System Work?
IP is then used to send the data packets. This can be done online or over a Local Area Network (LAN). The Real-Time Transport Protocol is often used to send them (RTP). Or, if not, through the Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP). The second is just a scrambled version of the first. This step is like when the postman picks up your letters and takes them to their final destination.
The data packets get where they need to go almost right away. The next step is to decode and unpack them. Codecs take care of this. They take the digital data and turn it back into signals that represent sound. The person you were talking to heard your voice just like they would over a regular phone line. At their end of the transmission, the codecs open the envelopes so they can read what’s inside.
Aside from the technical details, making a VoIP call shouldn’t be too different from making a regular phone call. You can use a hardware VoIP phone or a software-based VoIP phone to make the calls.
The first one looks and works a lot like a regular desk phone or handset. It will almost look the same and can be used the same way. That doesn’t just mean talking on the phone. Most VoIP phones also let you use voicemail, make internal calls, use auto-attendants or call routing systems, and transfer calls. Some even have screens that let people talk to each other through video. You might not know you weren’t using a regular phone if no one told you.
Softphones are what most people call VoIP phones that run on software. They are apps or programs that can be put on a computer or phone. The interfaces of these apps or programs are like a phone handset. They usually look the same and can be used with a touchscreen or a keyboard. Most of the time, a headset and microphone are used for calls on these phones. They can also use the mic and speakers that come with a computer.
How do VoIP calls work?
How does a VoIP call work? In real life, a VoIP call means that your voice is turned into a digital signal and sent over a data network. The IP call data is turned into a regular phone signal when it gets to its destination.
In general, you can make a phone call over the internet in three main ways:
1. An analog telephone adapter (ATA) is a converter that lets you connect a regular phone to your computer or internet connection. IP telephony is possible when you connect your phone to the ATA with a cable and, depending on the manufacturer, install some software.
2. IP phones with an RJ-45 Ethernet connector look and feel like regular phones, but they connect directly to your network router and come with all the hardware and software you need to make IP calls.
3. Peer-to-peer connections, or connections between two computers, use software to make phone calls over the internet. The necessary hardware is an internet connection, a sound card, a microphone, and speakers.
How Much Does a VoIP Call Cost?
Prices for VoIP phone systems vary by provider, but it’s usually safe to assume that you get what you pay for.
It’s easy to get excited when you see “free” or a single-digit price for a service that has a lot of hidden costs and/or few features.
When it comes to enterprise solutions, common price ranges are around $30 per user. When comparing one service provider to another, try to use a range instead of a single number if you can.
You should do this because, in addition to the base price, which is the main number you see, there may be other costs related to the installation, set-up, and after-installation stages. (More on this in a minute.)
Even so, this is still less expensive than regular landline phones:

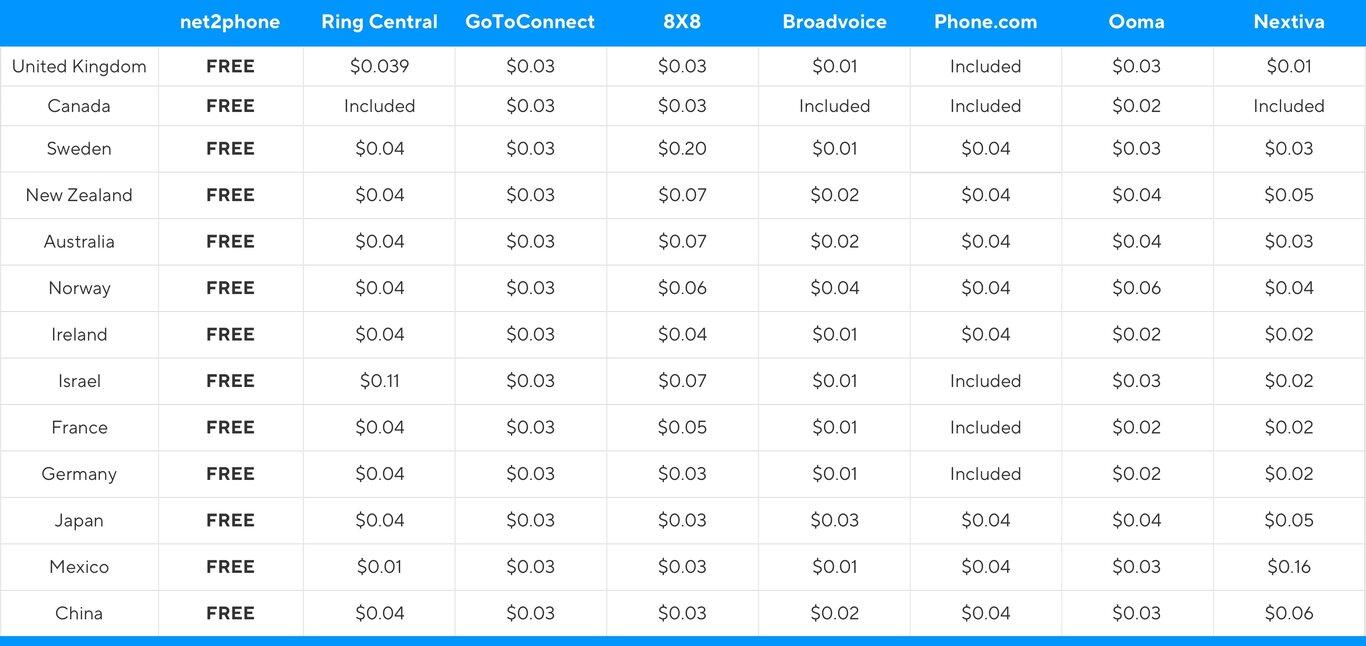
The following table provides a comparison of the costs of making international VoIP calls to a variety of countries, with all prices listed in US dollars per minute:
VoIP features
Voice over IP calls usually have a lot of useful features when they are made with a business-class VoIP system. Most of the time, but not always, the following are the main features of IP-based calling:
- Auto-Attendant: “Electronic receptionist” with advanced call handling and routing.
- Video Conferencing
- Voicemail to Text Transcription
- Instant Messaging (IM)
- SMS Text Messaging
- Mobile and Local Number Portability
- Presence Panel: Displays who is available to take a call, who is busy, etc.
- Call Forwarding
- Ring Groups: Allows all extensions in a group to ring simultaneously.
- Incoming Call Queues: Allows calls to be distributed and routed accordingly.
- Music On Hold
- Call Recording
- Call Analytics
Cloud PBX, which stands for “Cloud-based Private Branch Exchange,” is a virtual phone system that works over the internet. It automatically answers all calls and sends them to the right department or user extension.
Is VoIP worth it?
The cost savings you get with VoIP come with the substantial bonus of getting all the advanced features and analytics that you wouldn’t find in a traditional phone system.
Not only that, you also don’t need expensive telephony hardware or equipment—and you don’t have to worry about upgrades or maintenance, and you have the freedom to work from anywhere.
There’s just so much that VoIP gives you that PBX systems can’t match, along with the transparency in the cost of a VoIP service that’s hard to get with a traditional phone company.
The Most Important VoIP Terms
When updating your company communications system, you’ll encounter lingo. The telecoms industry has its own jargon. This tutorial may have some technical terms. Let’s define and explain as many as we can so you understand.
The most frequent terms, acronyms, and terms are covered in the glossary that follows. It has to do with VoIP services and the conventional alternatives that it can take the place of.
Bandwidth
The speed at which a network can transport data. 1000 bits per second (kbps). Additional VoIP calls can be supported with more bandwidth. With a slow internet connection, call quality will suffer.
Codecs
Hardware or software might be codecs. Data compression, encoding, and decompression. Codecs turn VoIP audio into digital data packets. They compress digital signals for transmission and re-convert them at the call’s end.
Latency
Higher latency means longer time between transmission commencement and data reception. VoIP latency might be a concern for video conferencing. Above 150 milliseconds, voice delay is noticeable. Conversation becomes difficult with more. Read about the Differnce between bandwidth and latency.
DSL
Digital Subscriber Line – It’s the standard phone technology that allows broadband over existing phone lines. Still permitting analogue phone signals to use copper lines.
IVR
IVR is a traditional telecommunication function. It’s an enhanced auto-attendant that lets callers access menus and handles call forwarding and transfers. “Press 1 for accounts” etc.
IP
Voice over IP uses Internet Protocol (IP). The IP standardizes online data transmission and reception. These guidelines let devices on different platforms communicate. IP provides rules for sending data packets. It doesn’t create the connection or organize the packets. Transport protocols handle this.
PBX
Private Branch Exchange (PBX) It’s a private business phone network. Your PBX allows you dial a coworker from a desk phone.
RTP
The RTTP. A protocol that transports VoIP data packets. It carries audio and video for multimodal communication. SRT Protocol – Secure, encrypted RTP.
SIP Trunking
Voice over internet. It’s a VoIP substitute. PBX internet connectivity is common. This gives users more control but requires more technology than VoIP.
Softphone
VoIP apps or software. Using a computer, mobile device, or tablet instead of a VoIP phone. Most softphones’ have a screen interface that resembles a phone. It will have a keypad, display, and touchscreen/keyboard.
VoIP Advantages and Disadvantages
What is a benefit of making calls over VoIP? As we already know, one of the best things about voice over IP calling is that you can use a data network or the internet to send and receive calls. VoIP users can have smart conversations thanks to the cloud, which makes it easy for people to talk to each other all over the world, no matter where they are or what device they use.
But that’s not the only good thing about it. In this section, we’ll talk about some of the pros and cons of VoIP.
Advantages of a VoIP
- Cost savings: Savings are one of the best things about VoIP phone system. Users don’t have to deal with the hardware and wires that come with a traditional phone system, so they don’t have to pay to install or maintain it. When you connect to the internet, the cost of phone calls is also much lower than when you use a regular phone.
- Flexibility and scalability: With cloud-based VoIP phone systems, businesses can give full communication capabilities to remote workers and sites in different parts of the world. Voice over IP services make it easy for businesses to quickly add or remove users and communication features in response to changing circumstances.
- Number portability: Most reliable VoIP providers will let users keep their current phone numbers, even if they switch to a different service. People who use Voice over IP usually have access to more phone numbers than people who use the public switched telephone network, or PSTN.
- A lot of features: In the next section, we’ll talk about how VoIP systems offer a lot of enterprise-class communication features.
- SIP Trunking: The SIP Trunking solution lets you take advantage of everything the cloud has to offer. With SIP Trunking, you don’t even have to replace your current equipment, because you can send bits of multimedia data instead of just voice data, as you can with VoIP.
Disadvantages of a VoIP
- Reliance on Power and Internet: VoIP technology needs a steady supply of electricity and a fast, stable connection to the Internet. If either of these utilities goes down or gets messed up, voice over the internet might not work as well or might not work at all.
- Potential Connectivity Issues: Even though super-fast broadband and leased line connections are common in many parts of the world, there are still places where the internet isn’t reliable or doesn’t exist at all. In these places, problems with latency (delays in data transfer) and packet loss can make it harder to make calls and send data.
How to Pick the Best VoIP Provider in 2022?
Which VoIP provider is the best? The answer will depend on what you want, how much money you have, and where you live.
Here are some general tips for choosing the best business voice over IP providers:
- Identify the communications features that you need most.
- Take future expansion or business growth into account.
- Establish the size of your budget.
- Make a comparative assessment of voice over internet providers, and what they have to offer.
- Look for testimonials, reviews, and customer referrals for the providers on your shortlist.
- Don’t forget to factor in what kind of technical support they have available.
FAQ
Do I need a Voice-over-IP phone system?
Look at your phone system now and ask yourself these important questions:
1. Will I have to keep all of my current equipment and just use adapters or converters to get voice over IP?
2. Can I change out some of the parts?
3. Do I need to buy a whole new set-up?
In 2022, if you run a small or medium-sized business, you will need VoIP to improve your communication skills and be able to compete with businesses of the same size and even ones that are bigger than yours.
- The small business phone system is made to help your business grow with every call.
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a way for businesses to communicate that is both affordable and scalable. It can be used from anywhere with internet access, whether you work from home or the office.
- PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) phone systems are being phased out in many places, so you’ll also need VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) phone systems to keep up with new technology and business practices.
How do I start using VoIP phone system?
To switch to VoIP, you’ll need to do the following:
- Make sure that your Information and Communications Technology (ICT) infrastructure is strong enough to handle internet telephony. You might need to upgrade to a faster internet service, preferably a wired broadband connection with at least 100 kilobits per second (kbps) per line.
- Connect your VoIP phone system directly to your office or workspace’s router or switch. Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) configuration may need to be done by IT staff in larger offices.
- Choose a service provider you can trust and who can do the job. The best business VoIP phone system for business communications have lot of useful features to offer. They should also have a variety of hardware and software options for IP telephony and be able to help you set up your system with their knowledge and help.
- Switching to VoIP unified communications platform is more than just a phone system for businesses. Ready to learn more about these and other ways to save money with voice over IP communications?
What is a VoIP Caller?
A VoIP caller is just someone who calls you over the internet instead of through a traditional phone network.
Your phone’s caller ID can tell you who is calling you over VoIP. You can also use a service that does a reverse phone lookup. If you use a VoIP phone with a packet analyzer, you can see the IP details of each call and look up the IP address that goes with it.
What is a VoIP phone?
A VoIP phone is a piece of hardware or software that uses voice over internet protocol technology to make and receive phone calls over an IP network.
A hardware voice-over-IP phone usually looks like a traditional hard-wired or cordless phone. It has a microphone or speaker, a touchpad, and displays that show user input and caller ID. Dedicated VoIP phone hardware usually lets you transfer calls, talk to more than one person at once, and use more than one VoIP account.
A software-based voice-over IP phone, also called a softphone, uses virtual phone software to let a user make IP phone calls from their computer or mobile device. Most of the time, the software uses a display that looks like a phone handset, with a touchpad and caller ID.
How is the sound quality in a VoIP call?
Recently, there has been a significant improvement in service quality. VoIP calls frequently have a similar sound to conventional phone calls. The quality of your internet connection is the one factor that really affects quality. If your connection’s latency is significant, you might experience call breakup and poorer voice quality.
What is a VoIP phone number?
A VoIP number is a phone number that is given to a user instead of a phone line. It is also called a “virtual phone number.”
We have already seen that voice-over-IP doesn’t depend much on where it is used. VoIP phone numbers have nothing to do with area codes. In fact, VoIP phone users can choose any area code for their phone number. This lets businesses set up shop in different parts of the country, which can be very profitable for business.
Contact us to find out how powerful VoIP communications can improve your business conversations right now.
Do I need to change my existing number when I use VoIP phone system?
When you switch to VoIP, the majority of companies let you keep your current number. The ability to make and receive calls from many locations using the same phone number is one of the VoIP phone system’s key benefits.
Do I need to change my handset while using VoIP?
Physical phones for VoIP calls must be compatible with the technology if you plan to use them. Your current mobile devices might not be, but it is not a given. But you’ll need new ones if you discover they’re not.
ad


Comments are closed.