What Is PCI Express (PCIe)?
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, computers necessitate an assortment of supplementary parts and components, alongside the customary motherboard constituents, to attain the desired level of functionality. This blog elucidates the significance of Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe), various crucial components, and their pivotal role in augmenting a computer’s capabilities to optimize efficiency at the edge. Discover the essence of PCIe, explore its diverse components, and unravel its potential for unleashing unparalleled computational prowess in the realm of edge computing.
ad
What is PCIe?
PCIe, or peripherals component interconnect express, is a standardized interface for establishing connections with high-speed input-output (HSIO) components. Numerous PCIe slots are available on high-performance computer motherboards, allowing the integration of various upgrades such as GPUs, RAID cards, WiFi cards, and SSD add-on cards. PCIe’s main advantages include increased bandwidth, faster speed, lower latency, and increased utility. The number of PCIe slots available vary depending on the model of motherboard acquired.
How Do PCIe Slots Work?
PCIe slots are labeled as x1, x4, x8, and x16, with the numerical value denoting the number of lanes available for data transmission to and from the PCIe card. Each lane indicates the path that data takes, and the more lanes there are, the bigger the data capacity. Let’s look at the various types of PCIe slots to have a better understanding:
ad
- PCIe x1: These compact slots are typically utilized for a wide range of cards, including average network adapters and USB expansion cards. They possess a single lane, enabling data movement at a rate of one bit per cycle.
- PCIe x4: Featuring four PCIe lanes, these slots can also be inserted into an x16 slot. They are commonly employed for single M.2 NVMe SSD expansion cards, as well as SATA 3 expansion cards and high-speed network adapters.
- PCIe x8: These slots can also fit into an x16 slot, but with half the number of PCIe lanes. They find widespread usage in applications such as GPUs or M.2 NVMe SSD expansion cards.
- PCIe x16: Representing the largest slots on the motherboard, these are designed to accommodate cards that demand high bandwidth, notably GPUs.
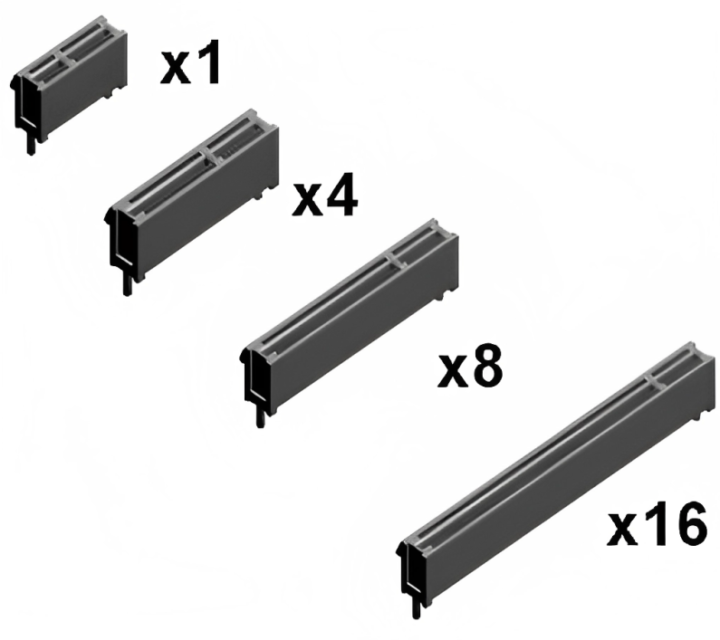
Among these configurations, PCIe x16 is very popular since it meets the needs of most GPUs, allowing them to operate at their full capability.
A PCIe slot has two main components: the mechanical aspect, which includes the physical card slot, and the electrical aspect, which includes the lanes. It is conceivable to come across a slot that is mechanically x16 but electrically x8, suggesting that it can physically contain 16 cards but only supports 8 lanes, resulting in lower performance.
Furthermore, an x8 mechanical card can be inserted into an x8 mechanical slot with just x4 electrical lanes, resulting in half the performance capabilities.
What is a PCIe Card?
A PCIe card, often known as an expansion card, is a versatile component that may be smoothly connected into your system via PCIe slots in the field of hardware expansion for devices. These cards allow you to improve and expand the capabilities of your device by adding specialized functionalities or features.
What is a PCIe lane?
The PCIe lanes serve as the primary link between a PCIe-supported device and the processor/chipset. These lanes function as physical routes, consisting of two pairs of copper wires known as traces, that traverse the motherboard and connect the device to either the processor or the motherboard chipset.

PCIe lanes, like a busy highway, enable bidirectional data transfer, allowing data to travel in both directions at the same time. This arrangement ensures that communication between the device and the system is efficient and seamless.
A single device can be assigned up to 32 of these adaptable PCIe lanes, offering adequate capacity for high-bandwidth, low-latency data transfers. This allocation enables devices to fully utilize the capabilities of PCIe technology, allowing for the quick and reliable transmission of data.
The Different Variations of PCIe
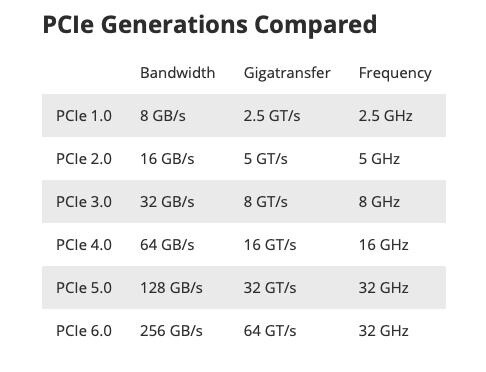
The PCIe standard encompasses five distinct generations: PCIe 1.0, PCIe 2.0, PCIe 3.0, PCIe 4.0, and PCIe 5.0, with each subsequent generation doubling the available bandwidth compared to its predecessor.
Excitingly, the anticipated release of PCIe 6.0 is expected to occur either by the end of 2022 or in the early months of 2023.
To provide a comprehensive overview of the capabilities across different PCIe generations, refer to the chart below:
What can you plug into PCIe Slots?
There are many devices that can be plugged into PCIe slots:
GPUs (Graphics Processing Units)
When it comes to components installed into PCIe slots, GPUs are one of the most common options. These strong computers are crucial in generating all of the visual aspects, and they also have advanced artificial intelligence capabilities.

To accommodate a GPU, the sole option is to utilize a PCIe x16 slot. As previously mentioned, the majority of GPUs are designed to leverage 16 PCIe lanes, necessitating the use of a full PCIe x16 slot to ensure optimal functionality and performance.
SATA Expansion Cards
Another practical application of PCIe slots is to increase storage capacity. When your motherboard only has a restricted number of SATA ports, PCIe SATA expansion cards come in handy for successfully addressing this issue.
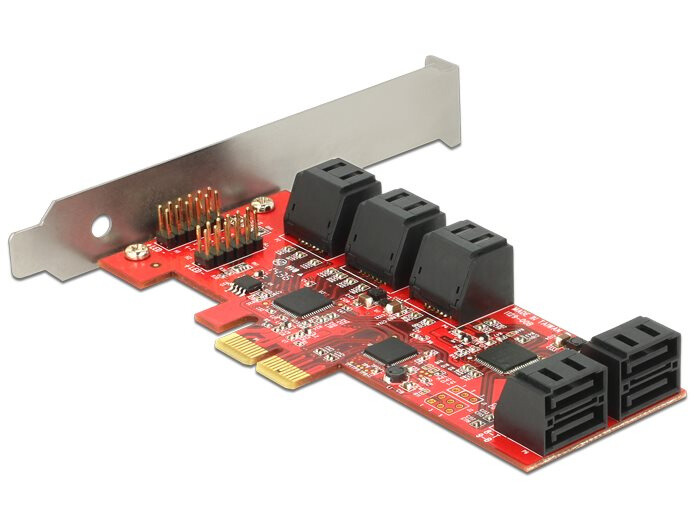
The size and slot requirements of a SATA expansion card are determined by various factors, such as the number of SATA slots it offers and the inclusion of a RAID controller. This variability allows for customization based on specific storage requirements.
SATA extension cards are designed to fit into PCIe slots, and depending on the model and specs, they are compatible with PCIe x1, x4, and x8 slots. Users can greatly enhance their storage capacities by using these expansion cards, which go beyond the constraints set by the motherboard’s native SATA ports.
Ethernet Network Cards (NIC cards)
While Ethernet functionality is usually integrated into most new motherboards, older motherboard models may not have this feature. In such instances, purchasing Ethernet network cards, also known as NIC cards, can be a wise decision.
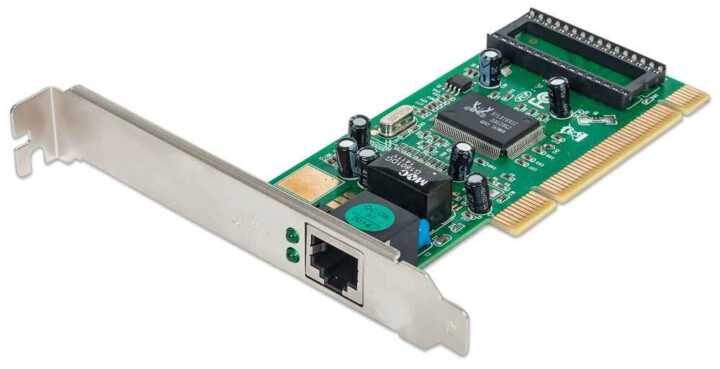
Users can improve their networking capability by putting NIC cards on older motherboards. Gigabit network speeds are often provided by mainstream motherboards. However, with the addition of NIC cards, users can achieve network speeds of 10G or faster, resulting in a huge improvement in network performance.
Riser Cards
Riser cards function as efficient PCIe port splitters, allowing PCIe slots on your motherboard to be expanded. PCIe riser cards, like port expansion cards, are essential for adding additional ports to your system, specifically PCIe slots.
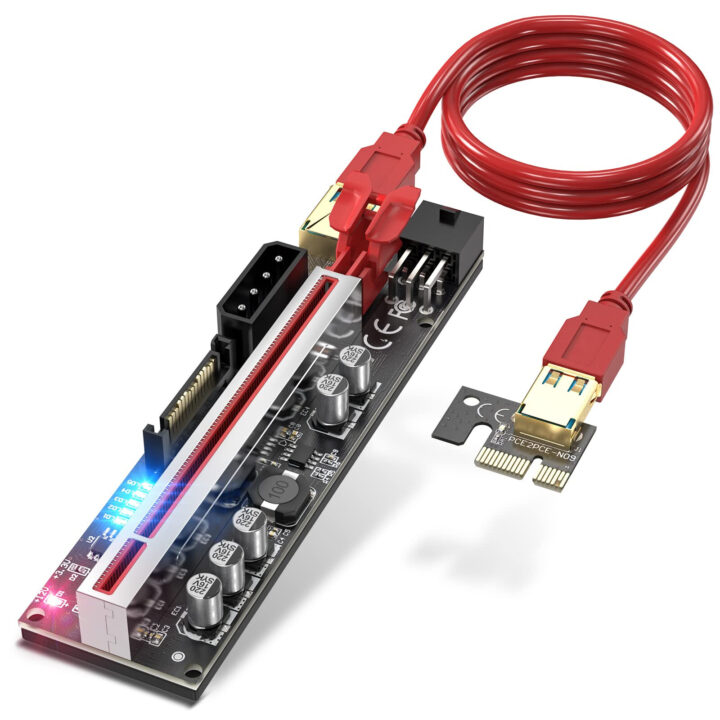

These cards are a practical solution for boosting the number of accessible PCIe slots in your system design, providing you increased flexibility and expandability.
M.2 NVMe Expansion Cards
When it comes to speed, PCIe NVMe SSDs are the pinnacle of high-performance storage solutions. They are the quickest hard drives currently available and are known for their excellent data transfer rates.
While many newer motherboards are equipped with at least one NVMe M.2 slot, there may be instances where either the M.2 slot is absent on the motherboard or there’s a desire to add an additional NVMe SSD to the system. In such cases, an NVMe SSD expansion card can serve as the ideal solution.
It’s vital to note that each M.2 NVMe slot requires the allocation of 4 PCIe lanes, which means that even the smallest M.2 NVMe SSD requires an x4 PCIe slot to function properly. As a result, when selecting an NVMe SSD extension card, confirm compatibility with the proper PCIe slot to accommodate the needed storage expansion.
PCIe and Trenton Systems
Trenton’s devoted team of engineers works tirelessly to design customized motherboards that use the latest PCIe technology to provide flawless interaction with a computer’s vital components. With PCIe as the foundation of our motherboard designs, we can provide our customers with a plethora of customization and upgrade possibilities.
Our motherboard choices have PCIe x16 slots, allowing you to integrate powerful NVIDIA GPUs. For example, our 3U BAM model features double-spaced x16 slots, allowing for the best inclusion of double-wide GPUs for improved performance.
Furthermore, we use PCIe to integrate NIC cards into our products, boosting networking, storage, and computing capabilities. We enable our customers to maximize the potential of their systems by leveraging PCIe.
Additionally, our PCIe Expansion Kit provides customers with the opportunity to expand their system’s capabilities by adding an additional 18 PCIe slots to any available PCIe x16 slot. This expansion opens up possibilities beyond the preloaded features, such as graphics and storage, allowing for versatile functionality.
PCIe enhances a computer’s capabilities by boosting bandwidth and lowering latency through a wide range of configurations and compatible add-ons. This offers optimal real-time performance, allowing customers to easily fulfill their demanding processing requirements.
Future of PCIe
The future of PCIe (PCI Express) looks promising, with ongoing developments aimed at pushing the boundaries of speed, bandwidth, and capabilities. Here are some key aspects to consider for the future of PCIe:
- Increased Bandwidth: PCIe is expected to continue evolving to provide higher bandwidth capabilities. This will facilitate faster data transfers and accommodate the growing demand for high-performance applications, such as AI, virtual reality, and data-intensive tasks.
- Advanced Generations: PCIe has already witnessed several generations, and the trend is likely to continue. Future iterations, such as PCIe 6.0 and beyond, will offer even greater bandwidth and improved efficiency, enabling more robust and demanding workloads.
- Enhanced Power Efficiency: PCIe is also expected to focus on optimizing power consumption and efficiency. Energy-efficient designs will enable devices to deliver improved performance while minimizing power requirements, addressing the growing concern for sustainability and energy conservation.
- Support for Emerging Technologies: PCIe will very certainly include support for emerging technologies like Gen-Z and CXL (Compute Express Link). These technologies are aimed at delivering scalable, high-speed interconnects for advanced computer systems and data center applications.
- Expansion of Use Cases: PCIe will expand its applications outside traditional domains as it evolves. This includes sectors such as edge computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), driverless vehicles, and machine learning, where PCIe’s fast and reliable communication may drive innovation and enable new possibilities.
- Backward Compatibility: PCIe’s backward compatibility means that future iterations will be compatible with prior generations. This allows for the smooth integration of new devices and components with current systems, protecting investment and eliminating the need for large infrastructure overhauls.
FAQ’s
What is the purpose of PCIe slots in a computer?
PCIe slots are used to connect various high-speed input-output (HSIO) components to the computer’s motherboard, such as graphics cards, network adapters, storage devices, and expansion cards. They allow for faster data transfer and improve the computer’s operation and performance.
Can I add a GPU to my motherboard without a PCIe x16 slot?
No, most GPUs require a PCIe x16 slot to function properly. A motherboard with at least one PCIe x16 slot is recommended for GPU installation. Other slot sizes, such as PCIe x8 or PCIe x4, may also be compatible depending on the GPU and motherboard combo.
How can I increase storage capacity using PCIe slots?
PCIe NVMe SSDs or SATA expansion cards can be used to increase storage capacity utilizing PCIe slots. PCIe NVMe SSDs offer the fastest storage performance, whereas SATA extension cards add more SATA ports for attaching more SATA drives.
What are the advantages of using PCIe riser cards?
PCIe riser cards act as port splitters, allowing the expansion of PCIe slots on a motherboard. The advantages of using PCIe riser cards include enhanced system design flexibility, the ability to add more PCIe slots, and the capacity to accept larger or specialized components, such as double-wide GPUs.
How does PCIe technology enhance a computer’s capabilities?
PCIe technology enhances a computer’s capabilities by providing higher bandwidth, faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, and increased connectivity options. It allows for seamless integration of critical components like GPUs, NIC cards, and storage devices, enabling improved performance, customization, and upgradeability.
What is the PCIe Expansion Kit mentioned in the article?
Trenton’s PCIe Expansion Kit allows users to add an additional 18 PCIe slots to any accessible PCIe x16 slot on their motherboard. This expansion kit provides more area for adding functions beyond the preloaded features, allowing for greater customization and flexibility in system setup.
Conclusion
PCI Express (PCIe) is a vital technology that facilitates high-speed communication between a computer’s motherboard and peripheral devices. With its ability to provide higher bandwidth, faster data transfer speeds, and increased connectivity options, PCIe enables users to maximize their system’s capabilities. Whether it’s integrating powerful GPUs, expanding storage, or enhancing networking, PCIe plays a crucial role in achieving optimal performance and adaptability. As PCIe continues to evolve, it remains a cornerstone of modern computing, empowering users to unleash the full potential of their devices.
ad


Comments are closed.