What Is DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) In Networking
Learn more about the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, its operation, and its essential components. Also, explore the benefits and drawbacks of DHCP.
DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a network management protocol used to automate the process of setting devices on IP networks, allowing them to utilise network services such as DNS, NTP, and any communication protocol based on UDP or TCP. A DHCP server assigns an IP address and other network configuration parameters dynamically to each device on a network so that it can communicate with other IP networks. DHCP is an upgrade of the previous BOOTP protocol. DHCP is a crucial component of the DDI solution (DNS-DHCP-IPAM).
A Brief Overview of DHCP
DHCP is an expansion of the Bootstrap Protocol, a network IP management protocol developed in 1985. (BOOTP). If BOOTP clients exist on a network segment, DHCP servers can process BOOTP client requests. BOOTP introduced the concept of a relay agent that allowed BOOTP packets to be relayed across networks using a central BOOTP server to serve hosts on several IP subnets. However, BOOTP needed a laborious process to upload configuration information for each client and lacked a means for reclaiming IP addresses that were no longer in use.
How DHCP works?
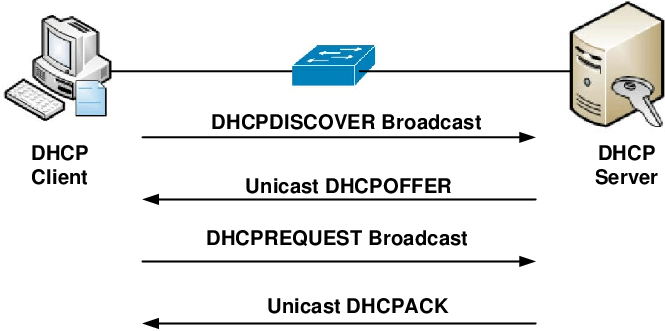
DHCP operates at the application layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack to allocate TCP/IP configuration information to DHCP clients and dynamically assign IP addresses to DHCP clients/nodes. The data consists of subnet mask information, the default gateway, IP addresses, and domain name system addresses.
DHCP is a client-server protocol in which servers manage a pool of unique IP addresses and information about client configuration parameters, and allocate IP addresses from those address pools.
This is how the DHCP lease procedure operates:
- A client (network device) must initially be linked to the internet.
DHCP clients seek an IP address. The client typically broadcasts a query for this information. - In response to a client’s request, the DHCP server provides the IP server address and other configuration information. This configuration information also consists of the lease period for which the allocation is valid.
- DHCP clients request the same settings while refreshing an assignment, however the DHCP server may assign a new IP address. This is determined by the administrator’s policies.
Elements of DHCP
When working with DHCP, it is essential to comprehend each component. The following are the components:
DHCP Server: A DHCP server is a networked device that runs the DCHP service and stores IP addresses and configuration data. This is often a server or a router, but it might also be an SD-WAN appliance or anything else that operates as a host.
DHCP client: is the entity that gets configuration information from a DHCP server. This could be a computer, laptop, IoT endpoint, or any other device that requires network connectivity. By default, the majority of devices are configured to receive DHCP information.
IP addresses Pool: The pool of IP addresses is the range of IP addresses available to DHCP clients. IP addresses are normally assigned in descending order from lowest to highest.
Default gateway address: A default gateway, commonly known as the gateway address, is the node that forwards data between local networks and the internet.
DHCP options: DHCP has several configurations, which are referred to as options. Among the most typical DHCP options are:
- Option 3 (router option)
- Option 6 (DNS server option)
- Choice 33 (static route option)
- Choice 51 (IP address lease option)
Subnet: Subnet is the segmentation of IP networks into subnets. Subnet is used to keep networks manageable.
DHCP relay: A host or router that listens for client messages broadcast on a network and relays them to a configured server. The server then returns responses to the relay agent, which forwards them to the client. Instead of having a server on each subnet, DHCP relay can be used to centralise DHCP servers.
Lease: Lease refers to the period of time a DHCP client maintains the IP address information. When a client’s lease expires, it must be renewed.
What exactly is DHCP lease?
When a DHCP server assigns a newly joined device a new IP address, the IP address is only valid for a limited amount of time. This period of time is known as the DHCP lease, as you now know.
The DHCP client must make a DHCP request to the server in order to extend its IP lease. If not, the server executes an IP address release procedure at the conclusion of the lease term.
DHCP operates as follows:
- DHCP oversees the provisioning of all network nodes and devices that are added or removed.
- Using a DHCP server, DHCP maintains the unique IP address of the host.
- When a client/node/device configured to work with DHCP connects to a network, a request is sent to the DHCP server. The server acknowledges by providing the client/node/device with an IP address.
DHCP is also used to configure the node or device with the correct subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server information.
IPV4 (Internet Protocol Version 4) and IPV6 support a variety of DHCP versions (Internet Protocol Version 6).
DHCP functions and uses
DHCP is utilised to distribute IP addresses inside a network and setup the device with the correct subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server information.
DHCP, including RFC (Request for Comments) 8415 — the November 2018 draught version — can also be utilised by regular electronic products whose manufacturers wish them to be connected to the internet of things (IoT). DHCP is one technique of connecting a device to the internet using a Manufacturer Usage Description (MUD), as specified by the Internet Engineering Task Force. Examples include refrigerators and sprinkler systems (IETF).
A person may potentially mistake DNS for Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) servers. A WINS server is used to achieve the same objective, albeit in a different manner and with a different protocol. WINS is a component of Microsoft’s networking architecture, however it is no longer widely used — DNS has superseded WINS.
DHCP Advantages And Disadvantages
DHCP Advantages
Centralized administration of IP configuration: DHCP IP configuration information can be maintained in a single location, allowing administrators to centrally manage all IP configuration information.
Dynamic host configuration: DHCP automates the process of configuring hosts and eliminates the need to manually setup each server. When TCP/IP (Transmission control protocol/Internet protocol) is introduced for the first time or when IP infrastructure modifications are required.
Seamless IP host configuration: The usage of DHCP ensures that IP configuration parameters such as IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, IP address of DND server, and so forth are automatically configured on DHCP clients without user intervention.
Scalability and Flexibility: Using DHCP provides the administrator with additional flexibility, enabling the administrator to alter the IP configuration simply as the infrastructure evolves.
DHCP Disadvantages
DHCP automates IP network setting. DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to computers without human interaction. This protocol tracks networked computers and prevents duplicate IP addresses. DHCP has drawbacks despite its benefits.
Security Concerns
If a malicious DHCP server is deployed to a network, DHCP automation poses a significant security concern. Uncontrolled by the network staff, a rogue server can supply IP addresses to users connected to the network. If a user connects to the malicious DHCP, information exchanged over that connection can be intercepted and viewed, compromising user privacy and network security. This is known as a man-in-the-middle attack, and it can have severe repercussions if sensitive data is transferred across a malicious DHCP server.
Failure
If there is only a single DHCP server in existence, it produces a single critical junction where a single fault can escalate into a system-wide issue. If the server dies, connected computers without an IP address will be unable to obtain one. Computers that had an IP address prior to the failure of the server will attempt to renew it, resulting in the loss of their IP address. Until the server is restored, there would be no access to the network, which could cause problems for individuals who rely on the network for communication.
Additional Configuration
A single DHCP server may be insufficient if the network contains numerous subnetworks or segments. Compensating for this deficiency needs more configuration, which necessitates additional time and resources to put everything up. Each segment of a network may need its own DHCP server or a DHCP relay agent. If neither alternative is practicable, it may be necessary to configure all connected routers for Bootstrap Protocol (BootP) broadcasts. BootP is an older and less sophisticated protocol than DHCP, and not all computers may support it.
2003 Windows Server
If your network uses Windows Server 2003, an older Microsoft server operating system, your DHCP client may experience issues. When connected to Windows Server 2003, not all DHCP clients function properly; however, this issue may or may not occur depending on the client.
Conclusion
DHCP minimizes the likelihood of frequent problems occurring while manually assigning IP addresses. Additionally, it assures that no two hosts can have identical IP addresses. DHCP serves a vital role in the management of small networks when mobile devices require temporary IP addresses.
Related Articles:
- What Is DNS And How It Works
- Statis vs Dynamic IP Address
- What Is Dynamic IP Address
- Types Of Servers And How It Works
ad


Comments are closed.