What Is A Dynamic IP Address – Definition, Uses And Benefits Explained
When a static IP address is assigned to a device, the address does not change. Most devices have IP addresses that change over time and are given to them by the network when they connect.
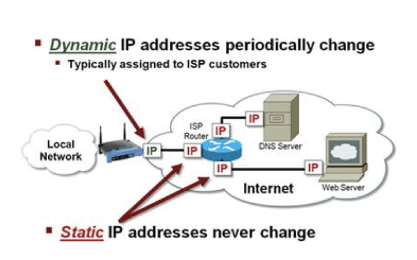
A dynamic IP address is one that changes often. It is used for most home networks because it is cheap and gives the ISP a lot of freedom in how it is given out.
Instead of giving the home network a fixed IP address, the Internet service provider gives it an IP address from a pool of addresses. After a few weeks or days, your IP address goes back into the pool, and you get a new one.
What Is a Dynamic IP Address?
A node or connection in a network, like your computer, laptop, or phone, is automatically given a dynamic IP address. It is given automatically by a DHCP server.
Most devices with a private IP address that are part of a local network (like one used in an office or home) are set up for DHCP. Without DHCP, every device on your home network would have to be set up manually with network information.
Since dynamic IP addresses change all the time, it’s hard to access your computer, webcam, or DVR from another location. So, the IP address could change at any time while the device is being used. If you want to access your computer from another location and the IP address changes in the next five minutes, you won’t be able to connect to it.
Differences between dynamic and static IP addresses
Static and dynamic IP addresses differ mostly in terminology. A literary character is either static or dynamic. The difference between static and dynamic IP addresses—changing and unchanging behavior—is the same. Static IP addresses have unchanging numbers, while dynamic IP addresses change.
ISPs or router/modem restarts can change a dynamic IP address, which can last days, weeks, or longer. The end user is unaffected by address changes, even while browsing the web. For residential use, an ISP assigns a device a dynamic IP address.
The ISP charges more for a static IP address. Static IP addresses are limited, thus they must be reserved. Static IP addresses can only be changed by ISPs. Businesses can streamline operations with static IP addresses. Dynamic IP addresses are cheaper than static IP.
Why Do We Need Dynamic IP Address?
Dynamic IP addresses are the addresses that internet service providers give to their customers by default. They are great for people who use the internet often because they are easy to set up.
Static IP addresses are always the same and cost more to set up and pay for. Also, they don’t have as many addresses as a dynamic IP, which has a fixed range.
One of the best things about dynamic IP addresses is that they are easier to change and manage. So, ISPs can set up dynamic IP addresses quickly and cheaply, and they can change on their own.
For example, when a computer is connected to a network, it is given a unique IP address. The same IP address is given to a different device that connects to the same network after it is disconnected. In this way, only a certain number of devices can connect to the network, because the ones that aren’t being used can be turned off to give the IP address to another device.
Another benefit of dynamic IP addresses is that, unlike static IPs, they don’t need to be set up by hand. All they have to do to get an IP address is turn on DHCP on the router. By default, almost all network devices with dynamic IP addresses are set up to choose an address from a pool of addresses.
How to Use Dynamic IP Address?
In the early days of the Internet, web designers didn’t see the need for an unlimited number of IP addresses. Until IPv6 came along, there were only a limited number of IP addresses available. Internet service providers limited the number of static IP addresses and began giving out temporary dynamic IP addresses to fix this problem. Using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, dynamic IP addresses sped up the process and let ISPs choose addresses from a pool of addresses (DHCP).
When a device is connected to the Internet, it is given a dynamic IP address. After the user disconnects, the IP address is either given to a new device or moved back to the pool.
When a user connects to the Internet and signs up for a DNS service, the device starts talking to the DNS to let the user know what IP address they have been given. The DNS service then sends the correct IP address to the DNS server by talking to it. So, when you use a dynamic IP address, a dynamic DNS service is more competitive than a static IP service.
Use of Dynamic IP Address In Businesses
There are some benefits to having a dynamic IP address, but privacy and security of data are two of the most important ones. Since dynamic IP addresses change all the time, it is hard for hackers to target or break into the device.
Dynamic IP addresses also take less time, money, and work to maintain because they are automatically set up with available IP addresses. By getting rid of manual setup and extra tools, organizations can save a lot of money. Companies can use more than one device with a dynamic IP address without having to set it up manually.
But there are a few things that can go wrong when businesses use dynamic IP addresses. With a dynamic IP address, there is a lot more downtime, and the device is more likely to lose connection while hosting servers. If geolocation is important to your business, you might not want to use dynamic IP addresses because they make geolocation less accurate.
In the same way, if your organization needs limited remote access to your system, dynamic IPs are not a good choice. They can make it hard to work from home or keep an eye on assignments that are far away.
Different companies use and benefit from dynamic IP addresses in different ways. Talk to your Internet service provider about which of the two is best for what you want to do.
For devices connected to a network, a dynamic IP address is a temporary address that changes over time. Computers use an Internet Protocol (IP) address, which is a number, to identify hosts, network interfaces, and various points on a network.
Dynamic IP addresses change between a few days and a few months and are selected from a pool of other IP addresses. Static IP addresses, on the other hand, give a home network a single, permanent IP address.
When using a dynamic IP address
The most prevalent type of IP address is dynamic, and internet service providers typically provide them by default (ISPs). Additionally, because they are simple to manage and don’t call for users to go through any additional setup or network configuration, dynamic IP addresses are perfect for regular internet users. A dynamic IP address should almost always be used for a company or home network.
Static IP addresses, or IP addresses that never change, call for additional setup and cost. However, there are no additional costs associated with dynamic IP addresses. The number of static IP addresses is also fixed because they are 32-bit numbers. This problem is mitigated by dynamic IP addresses, which draw new addresses from a pool of existing, shifting IP addresses.
Dynamic IP addresses are easy to use and don’t cost extra. Since they change frequently, they can also be seen as being more secure.
What functions do a dynamic IP address?
The need for an infinite number of IP addresses was not anticipated by the creators of the internet. So, until the later introduction of IPv6, there weren’t enough IP numbers to go around. Many ISPs use temporary IP address assignments from a pool of available IP addresses to temporarily assign an IP address to a requesting Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) computer in order to circumvent this issue and conserve the remaining number of static IP addresses they have available. A dynamic IP address is used for this temporary IP address.
requesting that DHCP assign computers a dynamic IP address, which functions as a temporary phone number for the duration of the current internet session or for a different period of time. Users’ dynamic IP addresses return to the IP address pool after they disconnect from the internet so that they can be assigned to another user. Users are unlikely to receive the same IP address from the pool even if they immediately reconnect.
The user’s computer contacts the DNS service after registering with a domain name system (DNS) service and connecting to the internet using a dynamic IP address to find out what IP address it has been given from the pool. The correct address is then forwarded to the requesting DHCP computer by the service in coordination with the DNS server. The next best thing to having a static IP address is using a dynamic DNS service to make arrangements for computers to locate a user even though they are using a dynamic IP address.
Dynamic IP address Pros And Cons
Pros
- They don’t need to be maintained, which makes them perfect for use at home where users might not have a lot of technical know-how.
- Users don’t have to worry about configuring their IP address because network configuration is done automatically.
- Given that there are only a certain number of static IPs available, dynamic IPs are more cost-effective.
- Static IPs are less economical than dynamic IPs.
- Since a device receives a new IP address each time a user logs on, they pose fewer security risks.
Despite their widespread use, dynamic IP addresses still have a few drawbacks that users should be aware of, including the following:
Cons
- The potential for a network failure, such as the failure of a DHCP server, to result in prolonged downtimes exists.
- DHCP automation may pose security risks; for instance, if control of a
- DHCP server is lost, users who connect to it may be intercepted and their personal data may be stolen.
- For activities like using a virtual private network (VPN), voice over IP (VoIP), or playing online games, dynamic IPs are less dependable because the service might stop working.
- The precise location of a device will be harder for geolocation services to determine.
- For the sake of ensuring secure access to the servers on their network, businesses with dynamic IP addresses may prefer employees to work locally.
- A program is required to assign and modify IP addresses for dynamic addresses.
Security
Because they alter with each session or login, dynamic IP addresses are fundamentally more secure than static IP addresses. A hacker will find it more challenging to locate and compromise a person’s data as a result. On a dynamic IP address, a hacker will have a harder time focusing on networked equipment.
Although dynamic IP addresses may be more secure, there are some security issues with them. There are, specifically, security concerns with DHCP automation. Users who connect to a DHCP server may have their communications intercepted and their data accessed if the server’s control is lost. For the sake of ensuring secure access to the servers on their network, businesses with dynamic IP addresses may prefer employees to work locally. Additionally, connecting to a dynamic IP address from remote access controls may be more difficult, which may deter employees from working off-site.
However, by using a router firewall, security suite, or VPN, security flaws in dynamic IP addresses can be mitigated. By hiding a user’s network address, a VPN, for instance, can make it more challenging to determine where a device is physically located. It is a good idea to implement additive security processes even though these measures cannot absolutely ensure that all data will be secure at all times.
ad


Comments are closed.