What is WiFi and How Does It Work?
A WiFi Network is a wireless (no-wires) network that connects to your Internet router and wireless-enabled devices in your home via a radio signal.
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that connects computers, mobile devices, and other equipment (printers, video cameras) to the Internet. A WiFi is what you use when you connect your laptop to a hotspot at a coffee shop or hotel, or when you set up a wireless network at home. Wi-Fi is the radio signal transmitted from a wireless router to a nearby device, which converts the signal into usable data. The gadget delivers a radio signal back to the router, which is wired or cabled to the internet.
So, what is Wi-Fi exactly? Wireless Fidelity means that a device works with the 802.11 standard, which is the established standard for wireless networks. This type of network does not require any wires to function. You can access your shared files, your Internet connection, and other wireless devices from any point within your network’s service area if it is a WiFi network, and it is simple to set up. This gives you the convenience of mobility as well as access to your shared files.
However, Local area wireless technology is implied by the phrase Wi-Fi, albeit it does not stand for anything in particular. In this article we will get informed everything about Wi-Fi, catch it up till the last word!
What is Wi-Fi?

We all know about Wi-Fi. It works on our phones, laptops, and everywhere else. Wi-Fi is a technology for wireless networking that lets us connect to networks or connect with other computers or mobile devices. In Wi-Fi, information is sent around in a circle using radio waves.
Wi-Fi is a brand name given by the Wi-Fi Alliance, which used to be called the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance. The term “Wi-Fi” is also a generic term for the communication standard for a wireless network that works as a Local Area Network without using cables or wires. It is called WLAN. IEEE 802.11 is the standard for how to talk. Physical Data Link Layer is what makes Wi-Fi work.
Wi-Fi is now built into all mobile computing devices, such as laptops, cell phones, digital cameras, and smart TVs. The Wi-Fi connection is made from the access point or base station to the client connection or any client-to-client connection within a certain range. The range depends on the router, which provides the radio frequency through Wi-Fi. At the moment, these frequencies work on two types of bandwidth: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
Both bandwidths can be used on modern laptops and phones, but it depends on the Wi-Fi adapter inside the device to pick up the Wi-Fi signal. All devices work with a default bandwidth of 2.4 GHz. With 2.4 GHz, the Wi-Fi signal can reach a large area, but the frequency is low, so the speed of the internet is slower. With 5 GHz, the signal can reach a smaller area, but the frequency is high, so the speed is very high.
Let’s say there is an internet connection with a bandwidth of 60 MB/s. For 2.4 GHz bandwidth, it gives about 30 to 45 MB/s, and for 5 GHz bandwidth, it gives about 50 to 57 MB/s.
READ MORE:
- Difference between modem and router
- What Is Good Internet Speed And How Much You Really Need
- Which Types Of Internet Connection Is Good For You
Wi-Fi History
Did you know that WiFi was discovered by chance? John O’Sullivan, an Australian scientist, wanted to prove that one of Stephen Hawking’s ideas about black holes was right. He and his team were working on a tool that could find and block certain radio waves. Unfortunately, the tool they made didn’t help them find radio waves coming from black holes. Several years later, John O’Sullivan worked for the CSIRO (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization). His job was to find a way for computers to talk to each other without wires. He went back to his “failed invention” and made some small changes to it. WiFi was finally made possible by John O’Sullivan and his team.
In the 1990s, WiFi was made. After all these years, many people still don’t know what WiFi is or how it works. Most of us just think of it as being the internet, but that isn’t quite right. WiFi devices do let you connect to the internet, but they are not the internet.
We’ll talk about everything to do with Wi-Fi, from what it is and how it works to the different Wi-Fi devices you can use in places where regular internet isn’t available. The idea of Wi-Fi has been around for a long time, but the way it’s used is relatively new. At first, the ALOHA System was a wireless network that was used to link the islands of Hawaii together in 1971. The ALOHA protocol was used for this, and packet transfer was used on the network. Later, the protocol is changed to IEEE 802.11.
Then, in 1985, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) put out a new network for general use that works on 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5.8 GHz bandwidth. It’s called the ISM band. Also, IBM made a Token Ring LAN network that can connect several computers and move data at a speed of 4 Mb/s. Then, in 1988, someone came up with waveLAN, a wireless cashier system based on the Token Ring LAN network. It works on the 900MHz or 2.4 GHz band and has speeds of 1 to 2 Mbps. Then, in 1989, it was changed to meet IEEE 802.11LAN/MAN standards. ? Then, in 1990, Vic Hayes, who was known as the “Father of WiFi,” started the IEEE 802.11 Working Group for Wireless LANs.
- Then, in 1994, Dr. Alex Hills started a project to study the wireless network. The project covered 7 buildings wirelessly with the network.
- In the year 1996, the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) created a wireless network based on the same 802.11 protocol. This network later became known as IEEE 802.11a standards.
- In 1997, the first official version of Wi-Fi came out. It was called 802.11, and it could support a link speed of up to 2 Mb/s. The link speed was then increased to 11 Mb/s on the 2.4 GHz frequency band in 1999. This version is called 802.11b.
- Then, a month later, the IEEE 802.11a standard is officially approved. It has a link speed of up to 54 Mb/s on the 5 GHz band, but the signal range is shorter than on the 2.4 GHz band.
- During 2003, a new version called 802.11g makes the speed faster. Over 2.4 GHz, the speed ranges from 54 to 108 Mb/s.
- The next two versions, 802.11i and 802.11e, came out after this. In 802.11i, the security mechanism was improved, and in 802.11e, Voice over Wireless LAN and multimedia streaming were added.
- Then, in 2009, 802.11n is made, which works with both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. And dual-band routers use both of these at the same time to reach speeds of up to 600 Mbps.
- Then, in 2014, a new version came out that could go as fast as 1733 Mb/s in the 5 GHz band. This type is called 802.11ac. The most recent version of Wi-Fi is this one.
Continue Reading:
- Read more on Wireless networking protocols
- Learn more on Wi-Fi mesh network
- Download Wi-Fi hotspot software for Windows Pc
- Learn how to get rid of error -Wi-Fi connect but not internet’
How does Wi-Fi work?
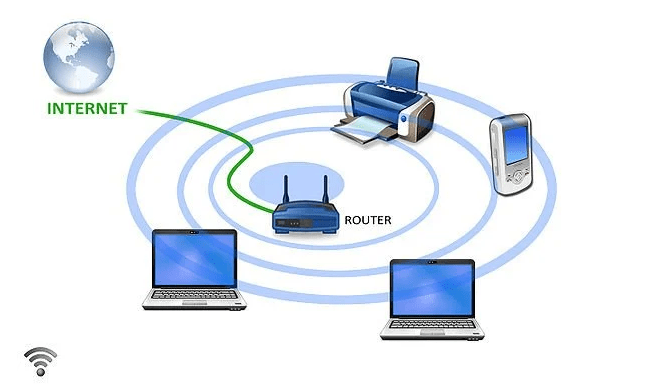
Wi-Fi is able to send data from your wireless router to your Wi-Fi-enabled devices, such as your TV, smartphone, tablet, and computer. This is accomplished through the use of radio waves. Your devices and the personal information they store can become subject to hackers, cyberattacks, and other types of dangers due to the fact that they connect with each other over airways. This is especially important to keep in mind whenever you connect to a public Wi-Fi network at a location such as a coffee shop or airport. Connecting to a personal hotspot or a wireless network that requires a password whenever it is an option is preferable to connecting to a public network.
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology, so it sends networks through electromagnetic waves. We know that electromagnetic waves can be divided into groups based on their frequency, such as X-rays, Gamma-rays, radio waves, microwaves, etc. Radio frequency is used in Wi-Fi. There are three ways that Wi-Fi signals can be sent,
- Base station network or an Ethernet(802.3) connection: It is the main host network from which the router gets its network connection.
- Access point or router: That connects a wired network to a wireless network. It takes a wired Ethernet connection and turns it into a wireless connection, which it then sends out as a radio wave.
- Accessing devices: We use Wi-Fi and surf the web on our phones, computers, and other devices.
All electronic devices, including routers and our devices, read data in binary form. In this case, routers send out radio waves, which our devices pick up and read in binary form. We all know what a wave looks like. In binary, the top point of the wave is called a 1 and the bottom point is called a 0.
Wireless network types
Wireless PAN, Wireless LAN, Wireless MAN, and Wireless WAN are the four most common types of wireless networks.
1. Wi-Fi PAN (Wireless personal area networks)
Wireless personal area networks (WPANs) connect Internet devices in a small area that a person can usually reach. When it comes to these wireless networks, radio is usually the best way to talk. WPAN applications can also be used with ZigBee.
2. Wi-Fi LAN (Wireless local area network)
Using a wireless distribution method, a wireless local area network (WLAN) connects two or more devices over a short distance. Usually, an access point is used to connect to the internet. Spread-spectrum or OFDM technologies may let users move around within a local coverage area and still stay connected to the network.
3. Wi-Fi MAN (Wireless metropolitan area network)
Wireless metropolitan area networks are a kind of wireless network that connects several wireless LANs.
4. Wi-Fi WAN (Wireless wide area network)
Wireless wide area networks are wireless networks that cover large areas, like between cities or suburbs that are close to each other. These networks can be used to connect business branches or as a way for the public to connect to the Internet. Most of the time, microwave links using parabolic dishes on the 2.4 GHz band are used to connect access points instead of the omnidirectional antennas used in smaller networks.
Wi-Fi applications
Wi-Fi has a lot of uses. It is used everywhere a computer or digital media is used, and it is also used for entertainment. Some of the ways it can be used are listed below:
- Accessing the Internet, Any device that can use Wi-Fi can connect to the internet wirelessly.
- We can use Wi-Fi to stream or cast audio or video wirelessly to any device for fun.
- We can also print any document with a Wi-Fi printer, which is used a lot these days.
- Wi-Fi can also be used as HOTSPOTS, which provide wireless Internet access to a certain area. Using Hotspot, the owner of the main network connection can give temporary network access to Wi-Fi-enabled devices so that users can use the network without knowing anything about the main network connection. Wi-Fi adapters mostly use the owner’s network connection to send out radio signals and create a hotspot.
- Point-to-point networks are simple wireless connections that can be made from one place to another using Wi-Fi or WLAN. This can be useful if you want to connect two places that are hard to reach by wire, like two business buildings.
- VoWi-Fi, which stands for “voice over Wi-Fi,” is another important use. VoLTE was introduced by phone companies a few years ago (Voice over Long-Term Evolution ). VoWi-Fi, which lets us call anyone using our home Wi-Fi network, is now available. The only catch is that the phone needs to connect to the Wi-Fi. Then, the voice is sent over the Wi-Fi network instead of the SIM network, so the quality of the call is very good. VoWi-Fi is already being added to a lot of cell phones.
- Wi-Fi in offices, All of the computers in an office are linked together by Wi-Fi. For Wi-Fi, there are no complicated wiring issues. Also, the network speed is good. For Wi-Fi, a project can be shown to all the members at once in the form of an Excel sheet, a PowerPoint presentation, or something else. With Wi-Fi, a broken cable doesn’t affect the network like it does with cable.
- Also, a whole city can use W-Fi to connect to the internet by setting up routers in a specific area. Wi-Fi networks are already being used in schools, colleges, and universities because of how flexible they are.
- Wi-Fi can also be used to figure out where a device is by using the locations of Wi-Fi hotspots to figure out where it is.
Different kinds of Wi-Fi Standards:
Wi-Fi has a number of standards, which we’ve already talked about. Here, we’ll just talk about their names.
| Standards | Year of Release | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi-1 (802.11b) | 1999 | This version has a link speed from 2Mb/s to 11 Mb/s over a 2.4 GHz frequency band |
| Wi-Fi-2 (802.11a) | 1999 | After a month of release previous version, 802.11a was released and it provide up to 54 Mb/s link speed over 5 Ghz band |
| Wi-Fi-3 (802.11g) | 2003 | In this version the speed was increased up to 54 to 108 Mb/s over 2.4 GHz |
| 802.11i | 2004 | This is the same as 802.11g but only the security mechanism was increased in this version |
| 802.11e | 2004 | This is also the same as 802.11g, only Voice over Wireless LAN and multimedia streaming are involved |
| Wi-Fi-4 (802.11n) | 2009 | This version supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz radio frequency and it offers up to 72 to 600 Mb/s speed |
| Wi-Fi-5 (802.11ac) | 2014 | It supports a speed of 1733 Mb/s in the 5 GHz band |
In 2022, a new version called 802.11ax (Wifi-6) has been introduced. It was made by Huawei and can support up to 3.5 Gb/s. Wi-Fi 6 will be known to it.
By 2024, 802.11be, also called WiFi 7, is expected to be the standard. It should have even better range, more connections, and faster data rates than any of the previous versions.
📚 Also Read: WiFi 7 Vs WiFi 6: More Speed & Capacity
Wifi terminologies
Gigahertz
The unit of Gigahertz is GHz, which is also used to measure other frequencies. GHz is used to show frequencies as billions of cycles per second and to measure them. It is used with WiFi wireless networks and radio frequencies to improve computer performance. Gigahertz is also used to measure the speed of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). S-band Satellite is used by new technologies like Bluetooth and others.
WiBro (Wireless Broadband)
WiFi has nothing to do with WiBro, so WiBro is the extended version of WiFi. It is a great and very new type of mobile broadband technology. WiFi works on the 802-11. WiBro was made so that people could stay connected while on the go.
WiFi Hotspot
People can connect to the internet in public places using Hotspot. There are a lot of things, like notebooks, laptops, phones, etc., that are set up with wireless network cards. All of these devices are made to connect to WiFi networks in the area. Hotspots are places where people can connect to the Internet for free. It is available in café, restaurant, airport, universities, libraries, ground etc.
WiFi finder
WiFi Finder is a helpful tool that can be used to find a public network in certain places. Now, your laptop’s battery will never die because WiFi Finder makes it easy to find a network. WiFi Finder is very small, about the size of a mouse. When a user turns on WiFi Finder, it automatically starts looking for a wireless network. If it finds one, it turns on its LED and asks to connect. There are different versions of WiFi Finder, each with its own features and ways to improve range and connection.
Access point
Access Point and Hotspot are almost the same thing. Access points are used to link together devices that can communicate. Most of the time, WAP is used to link wired networks. It also lets both wired and wireless devices talk to each other.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is an important term for a wifi network because it describes how much information can be sent over the connection, which is measured in bits per second or megabits per second.
Analogue phone
Wifi analog phones were used to send signals from voice phones. It also makes images and videos with their own signal.
Antenna-Directional
Antenna-Directional is a type of antenna that is used to send and receive radio waves.
Antenna-Omni-directional
Antennas that can point in any direction are used to send and receive radio waves. It is used to get waves from everywhere, and the area around the center antenna is shaped like a sphere.
Changing the circuits
Only with circuit switching is it possible to set up open circuit switching between users. So, a user can use the full circuit while waiting for the connection to become unrestricted.
Interoperability
Through interoperability, all kinds of software and hardware can work well together, even in places where hardware and software are mixed. IEEE 802.11 makes it possible.
GSM
GSM is the system that is used everywhere for mobile communications over wireless networks.
This is the norm in Europe’s mobile phone industry.
ISDN
ISDN is a digital network that brings together services. ISDN is used to build on the network knowledge and voice processing system that local phone companies offer.
ISM Band
ISM Band has different radio frequencies that are used in medicine, science, and instruments.
Switching packets
Packet switching is a way to send data in small pieces from remote sites through a wireless network. There is no circuit that doesn’t end with a happy release.
Pocket PC
Microsoft came up with the useful term “Pocket PC” to describe hand-held computers.
There are a lot of other terms for WiFi, like chipset, which changes the background task. Fire-wire is used as a small DVD camera and an external storage device for transferring data and other things.
SSID (Service Set Identifier)
It is a 32-character name that identifies a Wi-Fi network and tells it apart from other Wi-Fi networks. All of the devices try to connect to a certain SSID. The name of the wireless network is the SSID.
WPA-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access- Pre-Shared Key)
This is a program made by the Wi-Fi Alliance Authority to protect wireless networks using Pre-Shared Key (PSK) authentication. WPA has three kinds, like WPA. WPA2, WPA3. It is a way to protect the Wi-Fi signal from people who don’t want to use it.
Wi-Fi sends data through Ad-Hoc networks. It is a point-to-point network that doesn’t have any kind of interface.
Advantages of Wi-Fi
- It is a flexible way to connect to a network, and the wiring is simple. Can be used from anywhere where Wi-Fi is available.
- Individual users do not need permission from the government to use it.
- It can be sold, and you can use Wi-Fi Extenders to make it bigger.
- It is simple and quick to set up. You only have to set up the SSID and password.
- WPA encryption is used to hide radio signals in a high-security Wi-Fi network.
- It costs less as well.
- It can also offer Hotspots.
- It also works with roaming.
Disadvantages of Wi-Fi
- Any device with a battery, like a cell phone, laptop, etc., will use a lot of power when using Wi-Fi.
- Even if encryption is used, there may still be security problems. Wi-Fi can be hacked in the same way that known devices can sometimes become unknown to the router.
- The speed is slower than when you connect directly to a cable.
- It has less radiation than a cell phone, but it can still hurt people.
- Weather conditions like thunderstorms can mess with Wi-Fi signals.
- Because it doesn’t have a firewall, Wi-Fi can be used by people who shouldn’t be able to.
- We need a router to use Wi-Fi, and routers need power, so if the power goes out, we can’t get on the internet.
FAQ
1. What is Wi-Fi network?
A Wi-Fi network is an internet connection shared with several devices via a wireless router. The router connects directly to your internet modem and broadcasts the internet signal to all your Wi-Fi devices. This allows you to stay online inside your network’s coverage region.
2. What is Wi-Fi calling?
Wi-Fi calling lets customers make and receive calls through a wireless internet connection instead of a cellular signal. Wi-Fi calling lets smartphone users talk and text from places with weak cellular signals. Cellular calls are usually meant, not texting. The service is available on Android and iOS smartphones and works like a phone call.
3. What is wifi6?
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) improves efficiency, adaptability, and scalability over preceding standards. These upgrades increase network speed and capacity for next-generation apps. Wi-Fi 6 combines Gigabit Ethernet wireless speed with licensed radio reliability and predictability.
4. What is mesh wifi?
Mesh WiFi eliminates dead zones and provides uninterrupted WiFi throughout your home.
Mesh systems improve network speed, coverage, and reliability. Mesh WiFi systems have many access points, unlike standard routers.
When a device connects to a modem, it becomes the hub. “Nodes” will rebroadcast the router’s signal. The outcome is a strong, efficient wireless network.
5. What is Wi-Fi router?
Wi-Fi router forward and route wireless network packets and function as LAN access points. It works like a wired router but uses wireless radio signals to communicate internally and externally. It’s a switch, router, and access point.
6. What is Wi-Fi modem?
A modem is a device that links your home to your Internet service provider (ISP), such as Xfinity, through coaxial cable. The modem transforms signals from your ISP into signals that your local devices can understand, and vice versa.
7. Is a modem required for Wi-Fi?
A wireless router can function without a modem. The router is there to provide IP addresses and a Wi-Fi connectivity to the devices. This allows you to effortlessly move files from one computer to another, stream videos from your phone to your television or Chromecast, and print files.
8. What’s the Difference Between a Modem and a Router?
A modem is a piece of hardware that establishes a connection between your home network and your internet service provider, also known as an ISP. A router is a little box that connects all of your wired and wireless devices to the internet at the same time and enables them to communicate with one another without going via your computer.
9. What is the difference between WiFi and the internet?
Wi-Fi refers to wireless networks. Previously, network cables were used to build a local area network. Inconvenient. Wi-Fi connects devices wirelessly. The network works without a physical link. Routers control these connections. Routers connect devices.
WAN describes the internet. It connects computers worldwide. You’ll join a global network after connecting your wireless network. Internet.
10. What is Wi-Fi hotspot?
A Wi-Fi hotspot is a physical site where individuals may access the Internet, generally via Wi-Fi, using a wireless local area network (WLAN) with a router that is connected to an Internet service provider.
12. What is SSID for Wi-Fi?
Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name of your network. If you open the Wi-Fi networks list on your laptop or mobile device, you will see a list of SSIDs. Access points and wireless routers broadcast SSIDs so that neighboring devices may discover and display accessible networks.
13. What is good Wi-Fi speed?
For more than four devices, 25 Mbps is suggested. For two or more users who routinely stream high-definition or 4K video, use videoconferencing, engage in online gaming, or work from home, 12 to 25 Mbps is the optimal internet speed.
14. What is my Wi-Fi speed?
Use the Google WiFi app (or another speed testing software or website) on the device you wish to test the connection speed on in order to determine your WiFi speed. The app will display the varying speeds for each device that is connected to your WiFi network.
Conclusion
The number of people using Wi-Fi networks is expected to continue to rise. It is practical, easy to use, and inexpensive all at the same time. One is able to access the internet using this method even when they are not at their typical place of employment. If you have Wi-Fi with you, navigation will not interfere with your ability to get work done.
ad


Comments are closed.