What Is A Web Browser?
A web browser, also known as an internet browser, is a software application that enables users to access and navigate the World Wide Web. It serves as a gateway to online information, allowing users to browse websites, stream videos, download files, and interact with web applications.
ad
What Is a Web Browser?
A web browser is a client program that requests and displays information from a web server. Some of the most popular web browsers include:
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Safari
- Microsoft Edge
- Opera
Each browser has unique features, performance levels, and privacy options tailored to different user preferences.
ad
History of Web Browsers
The internet and the web are often used interchangeably, but the internet predates the World Wide Web. The internet is a vast network of interconnected computers, whereas the World Wide Web (WWW) is a system of web pages accessed through browsers.
The first web browser, WorldWideWeb, was created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989. However, it was NCSA Mosaic that revolutionized browsing by introducing multimedia support, making it user-friendly for non-technical audiences. Mosaic evolved into Netscape Navigator, which later influenced the development of Mozilla Firefox.
📚 Also Read:
- You may like to read about the history of the internet
- Know the difference between HTTP and HTTPS
- Brave browser : The best web browser for private browsing
How Does a Web Browser Work?
A web browser follows a structured process to retrieve and display web content:
- User Input – The user enters a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) in the address bar.
- DNS Lookup – The browser queries the Domain Name System (DNS) to retrieve the IP address associated with the website.
- Server Request – The browser sends an HTTP or HTTPS request to the web server.
- Data Retrieval – The server processes the request and returns the necessary files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.).
- Rendering – The browser’s rendering engine interprets the files and displays the web page on the screen.
Key Components of a Web Browser
A web browser consists of multiple components that work together to deliver a seamless browsing experience:
1. User Interface (UI)
The visible part of the browser includes the address bar, back/forward buttons, menu, tabs, and bookmarks.
2. Browser Engine
Acts as an intermediary between the UI and the rendering engine.
3. Rendering Engine
Interprets HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to display web pages. Different browsers use different rendering engines:
- WebKit (Safari, older Chrome versions)
- Blink (Google Chrome, Opera)
- Gecko (Mozilla Firefox)
- Trident/EdgeHTML (Internet Explorer, older Edge versions)
4. Networking Layer
Handles HTTP/HTTPS requests, downloads, and security protocols.
5. JavaScript Engine
Processes JavaScript code, enabling dynamic and interactive web content.
6. Data Storage
Browsers store cookies, cache, bookmarks, and browsing history using IndexedDB, WebSQL, or local storage.
Essential Features of a Web Browser
A web browser offers various features to enhance user experience:
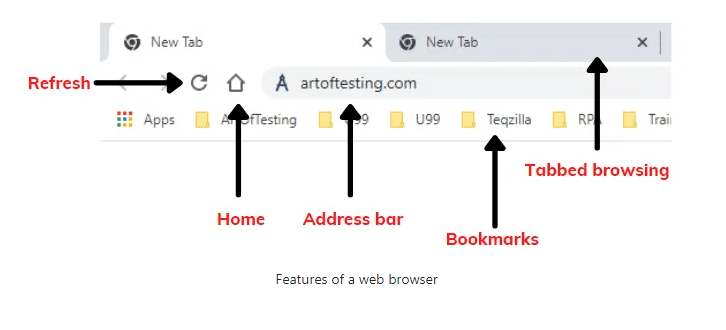
- Home Button – Returns the user to their set home page.
- Address Bar – Allows users to enter website URLs.
- Refresh Button – Reloads the current page.
- Bookmarks – Saves frequently visited websites.
- Tabbed Browsing – Enables multiple web pages in a single window.
- Navigation Buttons – Helps move forward and backward between visited pages.
Popular Web Browsers in 2025
There are numerous web browsers available, each with distinct features:
1. Google Chrome
The most widely used browser due to its speed, reliability, and vast extension support.
2. Mozilla Firefox
Known for its privacy-focused features, customizable interface, and open-source development.
3. Safari
Apple’s default browser optimized for macOS and iOS, offering iCloud Keychain integration.
4. Microsoft Edge
Built on Chromium, Microsoft Edge offers performance improvements and strong security features.
5. Opera
A feature-rich browser with built-in ad blocker, free VPN, and customizable UI.
FAQ’s
What is the best web browser for privacy?
Mozilla Firefox, Brave, and Tor Browser are among the best for privacy due to their strong tracking protection and security features.
Which web browser is the fastest?
Google Chrome is often considered the fastest due to its efficient Blink rendering engine. However, Microsoft Edge and Safari also offer competitive speeds.
How do I clear my browser cache?
To clear your cache:
- Google Chrome: Settings > Privacy and Security > Clear Browsing Data.
- Mozilla Firefox: Options > Privacy & Security > Clear Data.
- Safari: Preferences > Privacy > Manage Website Data.
What are the safest web browsers?
Firefox, Brave, Tor, and Edge offer enhanced security and anti-tracking features.
Which browser uses the least memory?
Browsers like Firefox and Microsoft Edge tend to use less RAM compared to Chrome, making them better for low-memory devices.
Is Google Chrome better than Microsoft Edge?
Microsoft Edge is gaining popularity due to its Chromium-based performance and lower RAM consumption, but Google Chrome still leads in terms of extension support and syncing capabilities.
What is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS?
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Unsecured communication between browser and server.
- HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure): Encrypted communication using SSL/TLS for enhanced security.
Can I use multiple web browsers on my computer?
Yes! You can install and use multiple browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Edge simultaneously without any issues.
Conclusion
The best web browser for you depends on your needs—whether you prioritize speed, security, privacy, or compatibility. Google Chrome dominates in speed and extensions, while Firefox excels in privacy, Edge in efficiency, and Safari in Apple ecosystem integration. Try different browsers and choose the one that best fits your preferences!
ad



Comments are closed.