URI vs URL: The Main Differences Between URL & URI
URI vs URL Although commonly used interchangeably, these terms have important distinctions.
In this article, we’ll clarify the differences between URLs and URIs and how each is used on the internet.
ad
What is URI and what does URI stand for?
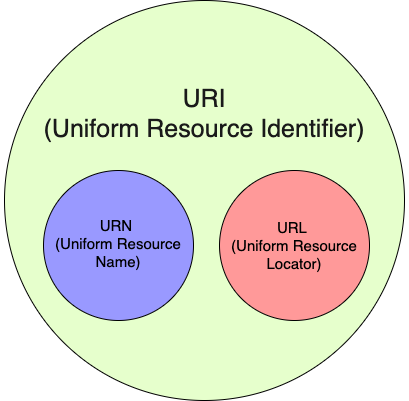
A URI, which stands for Uniform Resource Identifier, is a sequence of characters used to identify a name or a unique resource on the Internet. URIs are categorized into two main types: URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) and URNs (Uniform Resource Names).
A URI includes components such as scheme, authority, path, query, and fragment. Common URI schemes include HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), HTTPS, FTP, LDAP, and Telnet.
ad
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is often described as a string of characters that directs to an address. It is a widely used method for locating resources on the web by specifying their network location or primary access method.
In contrast, a URN is a type of URI that identifies a resource by name rather than by its location. URNs offer a persistent and location-independent way to identify resources. For instance, a URN might be used to reference a specific book in a library catalog, regardless of the book’s physical location.
What is URL & What does URL Stands for?
As noted earlier, a URL, or Uniform Resource Locator, is a string of characters that specifies the location of a resource on the internet. URLs are used to access web pages and other online resources, such as images and videos.
A URL generally comprises several components, including the protocol (like “http” or “https”), the domain name (such as “example.com”), and the path to the specific resource (for instance, “/index.html”). For example, the URL “https://www.example.com/index.html” indicates the location of the “index.html” page on the “example” website using the “https” protocol.
URLs are a specific type of URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) and are designed to locate resources on the internet. They offer a standardized way to identify and access resources, regardless of their location or access method. URLs are fundamental to the internet, enabling web browsers to retrieve and display web pages and other online content.
Main difference between URL and URI
The key difference between a URL and a URI is that a URL specifies the location of a resource on the internet, whereas a URI can identify any type of resource, not limited to those on the internet.
URIs are commonly used in XML, tag library files, and other contexts, such as JSTL and XSLT.
URL Syntax
A URL has a specific structure, which includes the following components:
- Protocol: This specifies how the resource should be accessed and is indicated at the beginning of the URL by a scheme name followed by a colon (e.g., “http:”, “https:”, “ftp:”, etc.).
- Domain Name: This identifies the web server where the resource is hosted and is typically the second part of the URL, following the protocol.
- Path: This specifies the location of the resource on the server and appears after the domain name. The path can include subdirectories and the resource name (e.g., “/images/logo.png”). It may also include a namespace-specific string (NSS) that identifies the internet resource and can contain ASCII codes, digits, punctuation marks, and special characters.
URL Examples:
Here are some URL examples:
- “https://www.example.com/homepage“
- “ftp://files.example.com/documents/report.pdf”
- “https://maps.google.com/search?query=New+York+City“
URI Syntax
A URI, by contrast, can identify any type of resource, not limited to those on the internet. URIs are divided into two main categories: URLs and URNs.
A URL is a type of URI that designates the location of a resource on the internet and includes a protocol at the start. A URN, on the other hand, is a type of URI that identifies a resource by its name rather than its location.
URI Examples:
Here are some examples of URIs:
- “urn:uuid:123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000” (a URN that identifies a resource by a UUID)
- “mailto@company.com” (a URI that specifies an email address)
- “tel:+44-20-7946-0958” (a URI that specifies a phone number)
What is a URN?
As previously mentioned, a URN is a type of URI that identifies a resource by its name rather than its location. URNs offer a persistent and location-independent method for identifying resources.
For instance, a URN can be used to identify a particular book in a library catalog, regardless of the book’s physical location.
URI vs URL vs URN
A URI, which stands for Uniform Resource Identifier consists of a sequence of characters that serves to identify a resource or a name. URIs are versatile. Can be employed to pinpoint types of resources, like web pages, images, videos or specific pieces of information.
On the hand a URL, short for Uniform Resource Locator represents a form of URI that indicates the precise location of a resource on the internet. URLs are primarily utilized to access web pages and other online resources. Typically encompass elements such as a protocol (“http” or “https”) a domain name and a path leading to the specific resource.
Meanwhile a URN (Uniform Resource Name) is another variant of URI used for identifying resources based on their names than their locations. URNs offer a means to consistently identify resources irrespective of their location.
Understanding the distinctions between URIs/URLs and their functionalities holds significance for individuals involved in web development. For instance structuring REST APIs utilizing an hierarchical framework in either URI or URL format can enhance the performance of the APIs significantly.
Additionally queries represent an element containing hierarchical data in the form of key=value pairs, within a query string. This component is typically introduced by appending a question mark.
Simply put a URI is a term, for a sequence of characters that pinpoint a resource whereas a URL is a kind of URI that indicates where a resource can be found on the web. On the hand a URN is another type of URI utilized for identifying resources by their names.
FAQ’s
What is a URI?
A URI, or Uniform Resource Identifier, is a sequence of characters used to identify a unique resource on the Internet. It can represent various resources and includes components like the scheme, authority, path, query, and fragment.
What is a URL?
A URL, or Uniform Resource Locator, is a type of URI that specifies the location of a resource on the internet. It includes a protocol (e.g., “http” or “https”), a domain name (e.g., “example.com”), and a path (e.g., “/index.html”).
What is the main difference between a URL and a URI?
A URL specifies the location of a resource on the internet, while a URI can identify any type of resource, not limited to those online.
What is the syntax of a URL?
A URL includes a protocol, domain name, and path. For example: “https://www.example.com/homepage”.
What is a URN?
A URN, or Uniform Resource Name, is a type of URI that identifies a resource by its name rather than its location, offering a persistent way to identify resources.
How do URI, URL, and URN differ?
A URI identifies any resource; a URL specifies a resource’s location on the internet; and a URN identifies a resource by name, independent of location.
What is a query in a URL?
A query is an optional component that includes additional parameters in key=value pairs, introduced by a question mark.
Conclusion
While URI, URL, and URN are terms often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings and functions. A URI is a broad term for identifying resources, encompassing both URLs and URNs. A URL is a specific type of URI that details the location of a resource on the internet, enabling access to web content. In contrast, a URN identifies resources by name, independent of their location. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective web development and resource management.
ad


Comments are closed.