Multi-Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud Solutions: What’s the Difference?
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate. Its benefits, such as mobility, cost savings, and access to advanced hardware, provide companies transitioning to the cloud with a clear competitive edge. With nearly 50% of corporate data now hosted in the cloud, there has never been a better time to make the shift.
But how do you choose the right cloud strategy? Multi-cloud deployment enables organizations to leverage the flexibility, scalability, and innovative technology offered by major cloud providers. On the other hand, hybrid cloud solutions offer greater control over specific components of a company’s IT infrastructure.
ad
What’s the difference? To distinguish between hybrid cloud and multi-cloud, it’s crucial to first understand public and private cloud services.
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
What is a public cloud solution?
ad
Public cloud environments provide computing resources over the internet, often serving multiple organizations on shared servers. These services are typically hosted in large data centers by providers like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
What is a private cloud solution?
Private cloud solutions are dedicated, privately hosted infrastructures used exclusively by one organization. Often on-premises and protected by company firewalls, they cater to specific workloads and offer a high degree of security and customization.
By understanding these cloud services, companies can better assess whether a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy is more suitable.
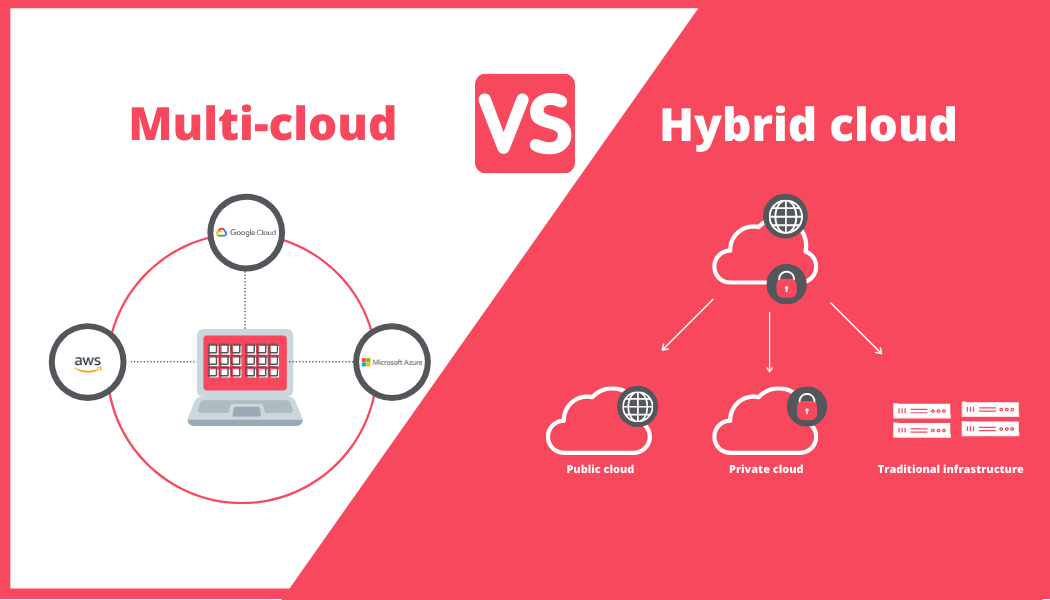
What is Multi-Cloud?
Multi-cloud strategies involve using two or more public cloud services without integrating private clouds. Most companies adopting this approach combine offerings from multiple public cloud providers.
Advantages of multi-cloud include:
- Choosing the best service for each task.
- Generally lower costs compared to private cloud setups.
- Flexible and scalable environments.
- Enhanced backup and redundancy options.
- Freedom to select providers that align with business needs.
Despite its benefits, multi-cloud strategies can present challenges:
- Managing multiple providers can be complex.
- Security risks may arise if integration is poorly executed.
- Costing models can vary significantly across vendors.
Multi-cloud strategies allow businesses to optimize workloads by choosing services that best suit their needs, offering resilience, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
What is Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid cloud architecture combines two or more distinct cloud environments, integrating at least one private cloud with one public cloud resource. This setup allows organizations to utilize multiple types of cloud infrastructure.
A common hybrid cloud strategy integrates on-premises or hosted private resources with public cloud services, managed through orchestration to balance workloads.
Advantages of hybrid cloud architecture include:
- Flexibility to allocate tasks between private and public clouds.
- Access to public cloud resources for additional computing power.
- Managing peak demands with techniques like cloud bursting.
- A blend of security and adaptability.
However, hybrid cloud environments can be challenging to implement and manage. Potential drawbacks include:
- Complexity in configuration and deployment.
- Security concerns revolve around protecting data and traffic.
- High costs of deploying and maintaining private cloud infrastructure.
For companies dealing with highly regulated data or legacy private cloud systems, hybrid cloud solutions offer the ownership and security of private clouds while benefiting from the scalability and flexibility of public clouds.
Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud: Key Differences
To effectively compare hybrid and multi-cloud services, it’s essential to examine their architecture first, followed by their impacts.
Architecture
The primary distinction between hybrid and multi-cloud lies in their architecture. A hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud services, whereas a multi-cloud setup involves two or more public cloud services.
In a hybrid cloud, users own and manage a private cloud resource that integrates with public cloud workloads. This private resource is typically hosted in-house, in on-premises data centers, or on dedicated servers at third-party facilities. Multi-cloud systems, however, exclusively use public cloud services.
Pricing
Hybrid cloud models often entail higher costs, particularly when private cloud resources are hosted on-premises. Companies must invest in purchasing, managing, and maintaining the infrastructure.
In contrast, multi-cloud solutions are more cost-effective since they rely solely on public cloud services. These services eliminate upfront capital expenses and leverage the buying power of large public cloud vendors, granting access to advanced technologies at lower costs.
Availability
Multi-cloud environments excel in ensuring high availability. Public cloud vendors offer strong service level agreements (SLAs) and guarantees for uptime. If one resource fails, another can seamlessly take over.
Hybrid cloud resources, however, require owner management. If the private cloud experiences downtime, maintenance is needed, which can result in significant disruptions if no backup resource is available.
Data Storage
Hybrid cloud computing offers a distinct advantage for data storage by allowing companies to manage critical, sensitive, or regulated data on their private cloud. Public resources handle less sensitive tasks, creating a balance between security and functionality.
However, private cloud storage is finite and may face challenges related to uptime and disaster recovery. Conversely, multi-cloud solutions provide nearly limitless storage capacity, along with robust backup and disaster recovery options.
Security
Hybrid cloud environments grant companies control over physical access to their private cloud infrastructure, which is advantageous in regulated industries. Multi-cloud solutions, while not offering physical control, implement strong security measures, often protected by layers of advanced safeguards.
Online security in multi-cloud solutions is top-notch, featuring automation, access controls, encryption, and simplified management. In a hybrid setup, the responsibility for configuring and managing online security for private cloud resources falls to the company.
Flexibility
Flexibility is a standout feature of multi-cloud solutions. Companies can select the ideal resources from various providers, tailoring their cloud environment to specific needs. Additionally, multi-cloud architectures allow easy scaling and eliminate vendor lock-in, enabling businesses to adapt quickly and choose the best provider for each task.
In comparison, hybrid cloud users face limitations tied to their private cloud resources, which might have specific configurations or requirements that restrict scalability and migration options.
By understanding these key differences, businesses can determine which cloud strategy aligns best with their operational goals and needs.
Can a Hybrid Cloud Be a Multi-Cloud?
A hybrid cloud can incorporate multi-cloud within its deployment. The distinction lies in the types of clouds used: both hybrid and multi-cloud strategies leverage public clouds, but only hybrid solutions include private clouds. As such, a hybrid cloud environment can technically qualify as a multi-cloud setup if it utilizes two or more public cloud resources. However, a multi-cloud cannot be a hybrid cloud since it lacks a private cloud component.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Option for Your Business
Selecting the best cloud deployment strategy depends on several factors:
Workload Requirements
Identify the type of workload you plan to migrate. Are you looking for Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), or a custom solution? Your workload needs will influence the most suitable cloud strategy.
Demand Fluctuations
If you anticipate varying demands, a multi-cloud system offers scalability to adjust resources up or down easily. A hybrid cloud might require more effort to scale. For peak traffic or demand, consider a multi-cloud strategy or a hybrid setup with cloud bursting enabled.
Performance and Speed
For near-real-time information exchange, hybrid clouds can be advantageous. However, multi-cloud deployments often deliver low latency sufficient for most workloads.
Data Storage Requirements
If you handle sensitive or highly regulated data, a hybrid cloud is ideal for storing critical information in a private cloud while utilizing public clouds for non-sensitive data. Public clouds also provide secure storage options for less regulated use cases.
Budget Considerations
Hybrid cloud setups may involve significant upfront costs, especially for private cloud infrastructure, and might require additional staff for maintenance. Multi-cloud solutions avoid these initial expenses, operating on a pay-as-you-go basis for public cloud services.
User Location
If your workforce is remote or spread across multiple offices, a multi-cloud approach using data centers in various locations can enhance accessibility and performance.
By evaluating these factors, you can determine whether a hybrid, multi-cloud, or combined approach aligns best with your business needs.
FAQ’s
What is cloud computing, and why is it important for businesses?
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources like storage, processing power, and applications over the internet. It helps businesses improve mobility, reduce costs, and leverage advanced technology, giving them a competitive edge in today’s market.
What is the main difference between hybrid cloud and multi-cloud strategies?
The primary difference is in architecture. Hybrid cloud integrates private and public cloud environments, offering control and security for sensitive data. Multi-cloud exclusively uses multiple public cloud providers, focusing on flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
Which industries benefit most from hybrid cloud setups?
Hybrid clouds are ideal for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as healthcare, finance, and government, as they allow sensitive data to be securely stored on private clouds while leveraging public clouds for less critical tasks.
Why might a business choose a multi-cloud strategy over a hybrid cloud?
Businesses may prefer multi-cloud for its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ability to avoid vendor lock-in. It’s also suitable for organizations with fluctuating demands or those looking to diversify across several public cloud providers.
Can a hybrid cloud also be a multi-cloud?
Yes, a hybrid cloud can include a multi-cloud setup if it uses multiple public cloud services alongside private cloud resources. However, a multi-cloud cannot be considered hybrid unless it includes a private cloud.
How do public clouds ensure data security?
Public cloud providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, multi-factor authentication, and advanced monitoring. They often comply with industry standards to protect sensitive data.
What are the cost differences between hybrid cloud and multi-cloud setups?
Hybrid cloud setups generally involve higher upfront costs due to private cloud infrastructure requirements. Multi-cloud is typically more cost-efficient, operating on a pay-as-you-go model for public cloud services.
How do hybrid and multi-cloud solutions handle high availability?
Multi-cloud solutions excel in availability, allowing seamless failover between public cloud providers. Hybrid clouds depend on private cloud resources, which may require manual management for uptime and recovery.
What should companies consider when choosing between hybrid and multi-cloud?
Key considerations include workload types, demand fluctuations, performance needs, data storage requirements, budget, and user locations. Each factor can influence which strategy aligns best with business objectives.
Is it possible to migrate from a hybrid cloud to a multi-cloud strategy?
Yes, businesses can transition from hybrid to multi-cloud, often driven by the need for more scalability, reduced costs, or simplified management. However, such migrations require careful planning to ensure seamless operations.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering unparalleled flexibility, cost savings, and access to cutting-edge technology. Choosing between hybrid and multi-cloud strategies depends on a company’s unique needs, including workload types, security requirements, scalability demands, and budget constraints. Hybrid cloud solutions are ideal for organizations prioritizing control and security, while multi-cloud strategies excel in flexibility, redundancy, and cost-effectiveness. By thoroughly evaluating operational goals and technical requirements, businesses can adopt the cloud strategy that best positions them for growth, innovation, and resilience in an increasingly digital world.
ad


Comments are closed.