What is Endpoint Management?
Endpoint management refers to the procedure of managing endpoint devices that are connected to a network. Organizations rely on endpoint management software to administer network access for remote devices and enforce security policies to safeguard the IT environment.
ad
What are the benefits of endpoint management?
Endpoint management offers various advantages, including:
- Simplified device management
- Efficient application deployment
- Dynamic enforcement of access controls
- Compliance with security policies
- Improved management of security patches and device updates
- Scalability for enhancements and automation
- Configuration management for Wi-Fi and VPN settings
What Is Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)?
ad
Unified endpoint management (UEM) is the capability for the information security (infosec) team to centrally secure and manage all endpoints using a unified console or dashboard.
With the UEM dashboard, network administrators can:
- Distribute operating system (OS) and application updates and patches to all relevant devices.
- Implement and uphold security policies across registered devices.
- Remotely access devices and execute specific actions, such as password resets or device wiping in case of loss or theft.
- Establish a protocol for employees to register personal devices they intend to connect to the network.
Benefits of UEM
Utilizing a UEM solution to oversee all endpoints and associated activities offers several key advantages for the organization, including:
- Swift identification of security threats.
- Enhanced speed and effectiveness in responding to and mitigating breaches.
- Rapid and streamlined deployment of the most recent OS/software updates and security patches.
- Reduced total cost of ownership through economies of scale.
How are endpoint management systems set up?
The process of establishing an endpoint management system begins with the selection of an IT or IT-security vendor to furnish endpoint management software. Subsequently, upon deploying the software, IT administrators remotely enroll devices onto the management platform and proceed to automate network policy enforcement, configure Wi-Fi and VPN settings, among other essential tasks.
Endpoint-Management Strategies
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is a solution focused on monitoring and managing mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets to ensure their security. MDM solutions empower organizations to enforce security policies on mobile endpoints, control access to corporate data, and remotely wipe stolen devices if necessary.
Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)
Solutions are designed to manage and authenticate various endpoint devices, including PCs, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. UEM platforms enable comprehensive device, application, and user management through a unified security platform.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Solutions are dedicated to identifying and responding to advanced threats that traditional antivirus and anti-malware software may miss. Endpoint management solutions enhance EDR capabilities to protect endpoint devices against sophisticated threats.
Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPPs)
Utilize a range of techniques including machine learning, behavioral protection, and file reputation to prevent attacks. For example, Systems Manager collaborates with endpoint security solutions like, integrating EPP and EDR capabilities to prevent, detect, and respond to threats effectively.
Network Access Control (NAC)
Solutions regulate access to network applications based on predefined policies and device security posture, for instance, supports dynamic NAC with customizable security policies that manage network access based on device posture, location, installed software, user identity, and more.
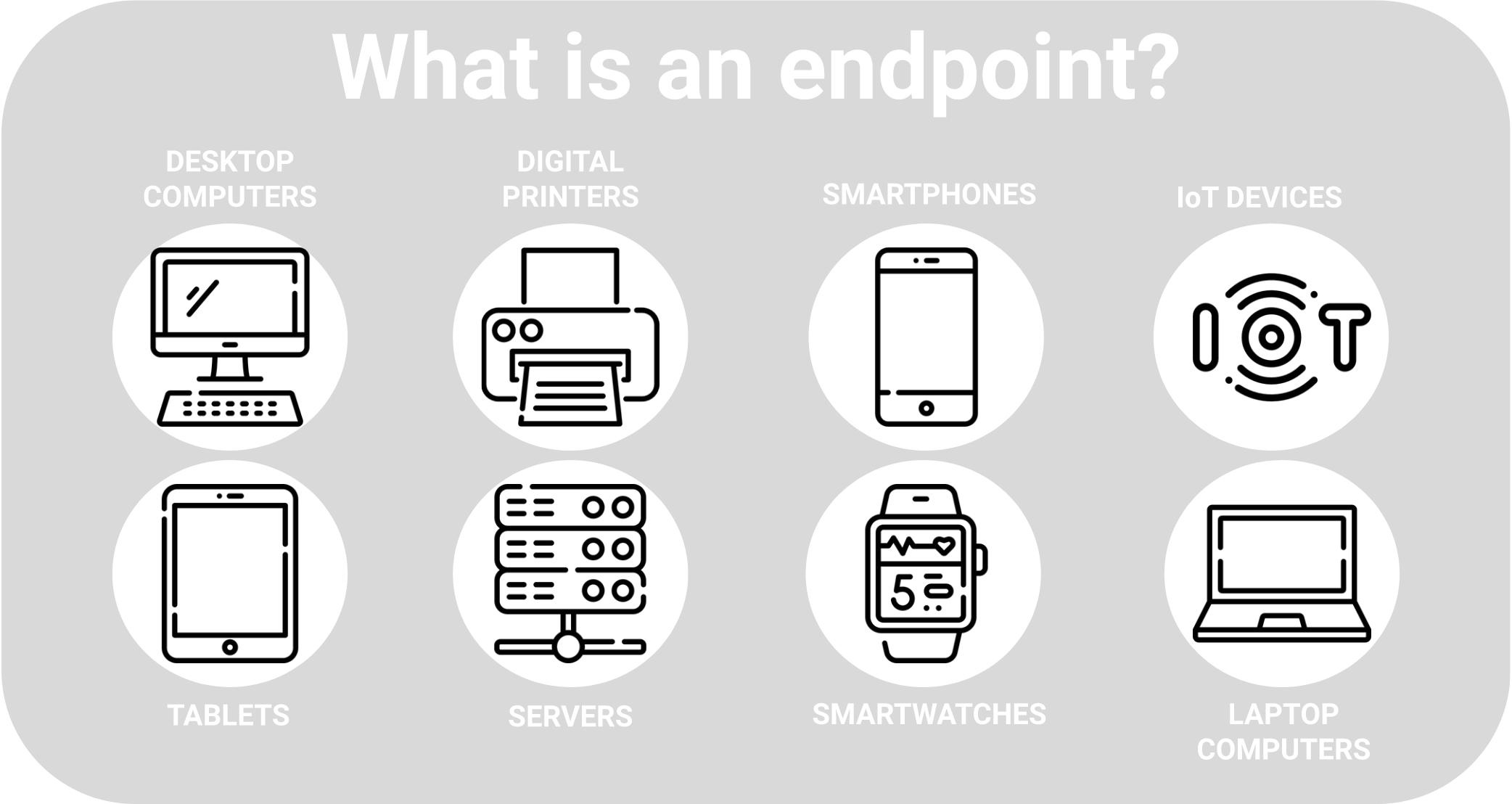
What Is an Endpoint?
An endpoint refers to any device that links to the corporate network, whether from within or outside its firewall. Examples of endpoint devices comprise:
- Laptops
- Tablets
- Mobile devices
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- Point-of-sale (POS) systems
- Switches
- Digital printers
- Other devices that communicate with the central network
What is endpoint security?
Endpoint security, also known as endpoint protection, is the cybersecurity strategy aimed at safeguarding endpoints against various external and internal digital threats, applicable to both traditional on-premises networks and cloud environments.
How Are Endpoint Security and Endpoint Management Related?
Endpoint security and endpoint management are integral components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, with each being closely intertwined and reliant on the other for effectiveness.
Whenever an endpoint is active on the network, it generates and exchanges data. Despite the seemingly benign nature of this activity, it can serve as an attack vector for cybercriminals.
Endpoint security encompasses a range of tools, technologies, processes, procedures, and policies aimed at protecting endpoints. These measures typically leverage advanced analytics to monitor network activity across all endpoints for indicators of compromise (IOCs). Additionally, endpoint security involves responding to attacks and removing threats.
In contrast, endpoint management oversees the authentication and authorization of devices accessing the network, ensuring that only approved devices connect at appropriate access levels. Furthermore, endpoint management ensures consistent application and enforcement of endpoint security policies and tools across all devices.
Endpoint Management Policies
Endpoint management encompasses not only device management and support but also several policies governing device authentication and network access. These policies may include:
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
Many organizations have adopted a “BYOD” model, allowing employees to use their personal devices, such as mobile devices, for official business purposes.
This presents a dual challenge for organizations: securing these devices to mitigate risks while respecting employees’ ownership rights, which precludes subjecting them to extensive security measures or restrictions.
The endpoint management team is responsible for developing a clear and effective BYOD policy outlining how the organization will access the device and specifying which apps and data are subject to monitoring and analysis. The team must also address how this policy will be enforced.
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
PAM utilizes the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) to manage and control privileged users and administrative accounts. This aims to minimize identity-based malware attacks and prevent unauthorized access to the network or associated assets.
Zero Trust
Zero Trust is a security framework that mandates authentication, authorization, and continuous validation of all users, regardless of their location within or outside the organization’s network. Access to applications and data is granted or retained only after meeting these strict criteria.
Importance of Endpoint Management Today
Endpoint security begins with effective endpoint management.
As organizations face mounting risks from various attacks and increasingly sophisticated cybercriminal networks, ensuring the proper security of every endpoint is essential. This involves authenticating devices before allowing them to connect to the network, defining access levels, and monitoring activity for signs of risk.
To address these challenges, organizations should partner with trusted cybersecurity experts to maintain visibility and control over all endpoints. This collaboration ensures readiness to confront critical threats, including those originating within cloud environments.
Additionally, deploying an endpoint management solution automates many prevention measures. For example, Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) software and centralized consoles enable cybersecurity teams to manage patching and system upgrades efficiently, reducing the risk of exploitation through OS or software vulnerabilities, also known as zero-day attacks.
However, it’s crucial to recognize that endpoint management is just one component of a broader cybersecurity strategy. To ensure comprehensive protection, organizations must integrate principles from Cybersecurity, Network Security, Application Security, Container Security, and IoT Security alongside their endpoint security strategy and management tools.
Conclusion
Endpoint management is a crucial aspect of modern cybersecurity, ensuring the protection of organizational assets against evolving cyber threats. By effectively managing endpoint devices and implementing robust security measures, organizations can mitigate risks and fortify their defenses. However, it’s important to remember that endpoint management is just one part of a broader cybersecurity strategy. To achieve comprehensive protection, organizations must integrate various security principles across their infrastructure. By embracing a holistic approach to cybersecurity, organizations can enhance resilience and safeguard their digital assets effectively.
ad


Comments are closed.