Deep Web vs Dark Web
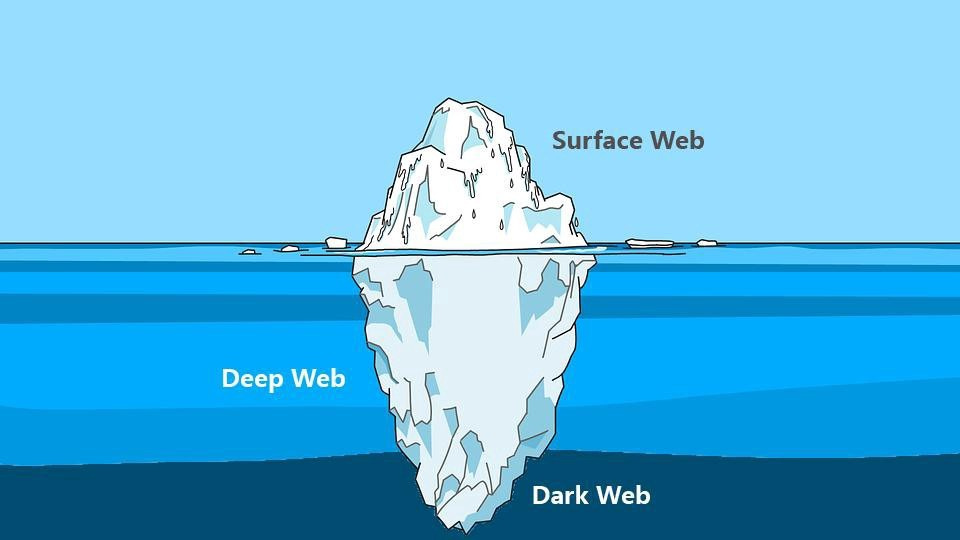
The terms “dark web” and “deep web” are commonly used interchangeably, but they actually denote separate concepts. Simply put, the main distinction lies in the fact that the deep web comprises internet content that isn’t indexed by search engines, whereas the dark web is a clandestine network accessible only through specialized browsers.
While you access the deep web daily for tasks like checking email or making online purchases, accessing the dark web requires the use of the Tor Browser.
ad
This article will delve into both the deep web and the dark web, outlining their differences.
What is the Deep Web?
The Deep Web constitutes a portion of the Internet inaccessible through regular search engines but can be reached using standard browsers. It consists of content not indexed by Google, Bing, or similar search engines, making it distinct from the surface web.
ad
Pages on the Deep Web often require authentication, such as login credentials or paywalls, to access, ensuring their privacy. They encompass personal content like webmail inboxes, account pages, as well as internal company data and sites protected by authentication protocols.
In terms of size, the Deep Web significantly outweighs the Surface Web. In fact, estimates suggest that 90-95% of the Internet exists within the Deep Web, with only 5-10% accessible via traditional search engines.
What is the Dark Web?
The Dark Web, part of the Deep Web, remains inaccessible through regular web browsers. It requires the use of Tor-enabled browsers for access, and finding Dark Web sites often involves specialized search engines, following links, or word of mouth.
Primarily, the Dark Web is utilized for illicit purposes. It hosts markets for trading stolen data, firearms, drugs, and illegal services. Additionally, it serves as a meeting ground for cybercriminal groups to plan attacks, providing insight into emerging cybersecurity threats and data breaches.
However, despite its reputation for illegal activities, the Dark Web has legitimate uses. The technology enabling it, Tor, was originally developed by the U.S. government for lawful purposes. Furthermore, it offers a platform for protecting the anonymity of individuals such as journalists, activists, and whistleblowers who face censorship or danger on mainstream, non-anonymous platforms.
Differences Between the Deep Web and the Dark Web
The Dark Web, technically a component of the Deep Web, exhibits several notable distinctions. Some of the most significant differences include:
- Scope: The Deep Web surpasses both the Dark Web and the Surface Web in size. Every private account page across various websites contributes to the Deep Web’s vastness.
- Purpose: While the Deep Web prioritizes privacy, its sites typically lack anonymity. In contrast, the Dark Web emphasizes anonymity, making it more conducive to illicit activities compared to the Deep Web.
- Access: Despite its absence from search engine indexes, the Deep Web remains accessible through conventional web browsers like Firefox or Chrome. In contrast, the Dark Web necessitates specialized browsers employing Tor for anonymity protection.
| Details | THE DEEP WEB | THE DARK WEB |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Much broader scope than the dark web, covering a range of content that is not accessible by web search engines. | A subnet of the deep web, the dark web is much narrower in scope. |
| Operations | Doesn’t require a special browser or unique protocols. Most of its content is password-protected. | Can’t be accessed without a special browser called Tor, which is designed to maintain user anonymity. |
| Size | 400 to 500 times larger than the surface web. | Only 0.01% of the deep web and 5% of the total internet. |
| Applications | Intranets used by institutions or companies. Free services like Gmail, and subscription-based services like Netflix and Amazon. | Used mostly for criminal activity, whistleblowing and expressions of dissent. |
| Security | Attacks are focused on your login credentials, in the form of various types of scams like phishing emails and fake login prompts. | The risk comes in when you download illegal materials which contain viruses or malware, like trojans, worms, or keyloggers. |
Risks of Accessing the Deep Web and Dark Web
Both the Deep Web and Dark Web pose inherent risks. On the Deep Web, these risks stem from the need for authentication to access private sites and the abundance of sensitive personal data within them. Cybercriminals often target these sites to steal credentials through phishing, social engineering, malware, and similar tactics.
In contrast, the Dark Web’s risks primarily arise from its content. Frequently utilized for criminal endeavors, it presents dangers such as malware infections, scams, and exposure to illegal or disturbing material.
Staying Safe on the Deep and Dark Web
While both the Deep and Dark Web carry risks, they can be navigated safely with some precautions. Here are some methods to enhance your online privacy and security:
- Password Security: Opt for strong, unique, and randomly generated passwords for all your online accounts to minimize the risk of a compromised credential granting access to multiple platforms.
- Endpoint Security: Employ a reliable endpoint security solution to protect your device from potential malware infections.
- Install Updates: Stay vigilant about installing operating system and browser updates promptly to prevent potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious websites.
- Use a VPN: Utilize a virtual private network (VPN) to obscure your IP address, thus ensuring anonymity while browsing the Dark Web.
- Choose a Reputable Dark Web Browser: When accessing the Dark Web, opt for a specialized browser from a trusted source to reduce the risk of encountering malware or other threats.
FAQ’s
What distinguishes the Deep Web from the Dark Web?
The Deep Web encompasses internet content not indexed by search engines, while the Dark Web is a subset of the Deep Web accessible only through specialized browsers like Tor.
How do I access the Deep Web and the Dark Web?
The Deep Web can be accessed using standard web browsers, whereas accessing the Dark Web requires a Tor-enabled browser due to its encrypted nature.
What types of content are found on the Deep Web and the Dark Web?
The Deep Web includes private or restricted content such as personal email accounts and company intranets. In contrast, the Dark Web hosts illicit activities, including marketplaces for drugs, stolen data, and cybercriminal forums.
What risks are associated with browsing the Deep Web and the Dark Web?
The Deep Web poses risks related to protecting sensitive data and credentials, with cybercriminals often targeting authentication processes. On the other hand, the Dark Web exposes users to illegal content, malware, and potential scams.
How can I enhance my security while browsing the Deep and Dark Web?
To navigate safely, ensure strong password protection, employ reputable security software, regularly update operating systems and browsers, use a virtual private network (VPN) for anonymity, and rely on trusted sources when accessing the Dark Web.
Conclusion
while often conflated, the Deep Web and Dark Web are distinct entities each with its own risks. The Deep Web comprises hidden internet content inaccessible to standard search engines, emphasizing privacy and authentication. In contrast, the Dark Web is a covert network accessible only through specialized browsers, primarily used for illicit activities. Despite inherent risks, both can be navigated safely with precautions such as strong passwords, endpoint protection, regular updates, and VPN usage. Understanding these differences and implementing appropriate security measures enables users to explore these internet realms while safeguarding their privacy and security.
ad


Comments are closed.