What Is Dynamic DNS (DDNS)? -How it Works and Why Use It?
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) refreshes a name server automatically. It dynamically updates DNS records. When a host's IP address changes, it's useful for updating A and AAAA records.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a system that allows an Internet domain name, such as abc.com, to be assigned to an IP address that is dynamic, meaning that it changes and is not always the same. Due to the fact that the dynamic IP address is always changing, DDNS makes it possible for other computers on the internet to establish connections to a specific machine without those computers having to know the actual IP address of the machine.
Large networks that host their own internal services and make use of their own internal DNS and DHCP servers are the types of networks that make use of dynamic DNS.
However, most home and small business networks do not have their own DNS server, so why would they need Dynamic DNS ?
In this guide, we will look the core working principles of dynamic DNS and show you how to configure it on a home router.
What is a Dynamic DNS (DDNS)?
DDNS, often known as Dynamic DNS, is a method for automatically renewing a name server. It can update DNS records automatically and without human intervention. It is incredibly useful for updating A and AAAA records when the IP address of the host has changed.
Consider this scenario. You have a server at your office and are offering employees with some service. Standard/consumer-grade Internet service is provided by a regular ISP (Internet service provider). You are assigned a temporary IP address that may change the next time you connect or automatically after a period of time. To render a service, you have three options:
- A Static IP address that may be costly.
- Change the IP address manually whenever it changes.
- Dynamic DNS or DDNS will automatically update IP addresses.
DDNS is a service that periodically and automatically updates the A (IPv4) or AAAA (IPv6) entries of your DNS when your IP address changes. Your Internet provider handles these IP address changes.
With DDNS, you do not need to bother about IP address changes!
How does DDNS work?
The DDNS functions in the following manner: The DDNS client checks changes to the IP address. The DDNS (or Dynamic DNS) service refreshes your IP address when the address changes (which it will if you have a dynamic IP address).
Let’s return to the previous example, in which you possess a server linked to the Internet and wish to provide its services.
This server will communicate with the Internet via a NAT (network address translation) router, which will be connected to the internal network. The NAT router will assign the server an internal IP address, most likely using DHCP. To make it accessible externally, we must execute port forwarding and get an external IP address and external Port (Portex) (IPex). Now the service you wish to share is visible to IPex and Portex, and Internet users can access it. The issue arises when this IP address changes.
First, you must register with a Dynamic DNS service provider such as us and install client software on your server. In the Dynamic DNS settings, you will give this server a fixed name. Put the IPex, and tell the NAT to automatically update it and forward the information to the DNS server. In the NAT settings, we will include information from our Dynamic DNS supplier (our account and password). Now, everything is complete.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) – setup and how to use it
Small businesses and individuals often utilize Dynamic DNS Services when they want to publish a service on the Internet but that service is housed on an internal network or at home. This is the case when the service is hosted on an internal network.
The standard method by which home networks link to the internet is through the use of a NAT router. This ensures that no devices on the local network may be accessed from the wider internet.
We are going to proceed with the assumption that we want to create a web server that is hosted on an internal server accessible via the internet in the following discussion.
The configuration is depicted in the network diagram that can be found below.

Internal IP addresses are assigned to internal servers by NAT routers and DHCP services.
However, while making a service accessible through the Internet, we often provide it a static internal IP address.
Port forwarding is the method we employ to make the web service accessible via the internet ( see the port forwarding and Internal vs external IP address tutorials for more details).
Now, our external client believes that our web server is located at IPex and port Portex.
If we enter some usual numbers, we will notice that our web server is located at
Ip Address= 81.157.34.43 and the Port Number is 80
All that remains is to inform our external customer to utilize these values.
The external IP address IPex (81.157.34.43) may also be dynamically allocated by the ISP, and we cannot make it static without paying for a static IP address.
Additionally, the external client is responsible for remembering the IP address.
Dynamic DNS Service
If we now include a Dynamic DNS service into the equation, we will observe the following:
Using Dynamic DNS, we’re able to give the web server’s name to external clients.
This is a fixed domain name supplied by the DDNS service provider.
The external IP address is then assigned to the name.
As this external IP address will vary occasionally, we will need to periodically update the DNS record.
Obviously, we could accomplish this manually, but it would be extremely unreliable because you wouldn’t know when the information has changed unless you checked.
Here is a screenshot of my TP-Link router’s Dynamic DNS settings page (BT Home Hub).
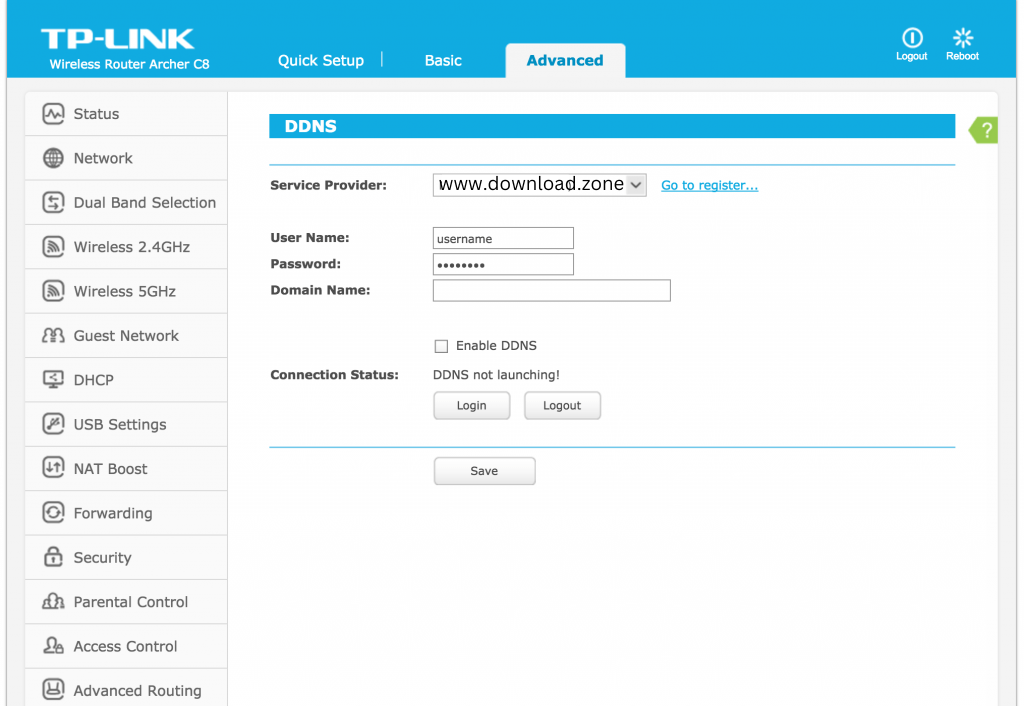
Input the name of your DDNS service provider and your login credentials during configuration.
The application should result in a connection confirmation.
Note: Check your username and password and retry if you receive an error message.
Registration with a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) Service Provider
You are going to require an account with a DDNS provider in order to be able to enable Dynamic DNS.
There is a choice between a few different providers. The majority offer a free service with an optional paid upgrade.
The primary service providers all operate in a manner that is analogous to one another, and the signup procedure is straightforward.
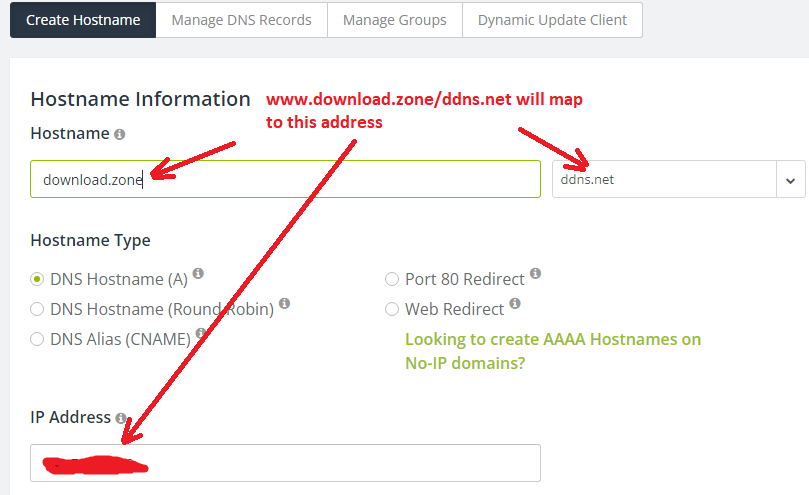
I will be utilizing noip.com for the purposes of this online guide.
You will need to generate a host name for the IP address, select a domain name from the list that is provided by the service provider, and then input a hostname.
The registration form for noip.com can be seen down below.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) Not Supported on Router
If your router does not support DDNS updates, you can install a DDNS client on a local workstation to do the same function.
The sole disadvantage of this strategy is that the machine must always be running.
Testing Your configuration
Test that you can access the IP address by pinging the domain name, which consists of the hostname plus the domain name.

Or, You may watch the video tutorial:
Common Applications of Dynamic DNS
Even though it is utilized by gamers and tech nerds, it is likely to gain popularity in remote security/surveillance and control fields.
How would you access your cameras from the Internet without Dynamic DNS?
Frequent Asked Questions and Answers
Question: What is the distinction between DNS and dynamic DNS (DDNS)?
A- Dynamic DNS is a DNS functionality. Early DNS systems were static and required manual entry of IP addresses and name mapping. Dynamic DNS automatically modifies Name- IP mappings when they change.
Question: Why is it necessary to use Dynamic DNS?
A- Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is incredibly beneficial for accessing internal network services from the Internet. Standard web hosting is required to host a website for a business.
Question: How long does it take for Dynamic DNS to update?
A- It can take several hours to one day for DNS updates to propagate throughout the entire internet. This change is made not only to the authoritative name servers for your domain, but also to millions of DNS servers worldwide.
Question: Is dynamic DNS carry security threats?
A- Along with its benefits, DDNS is also related with security issues. Utilizing DDNS services, attackers can alter the IP addresses of command-and-control servers. Malware campaigns and even exploit kits are able to employ DDNS services to distribute their payloads.
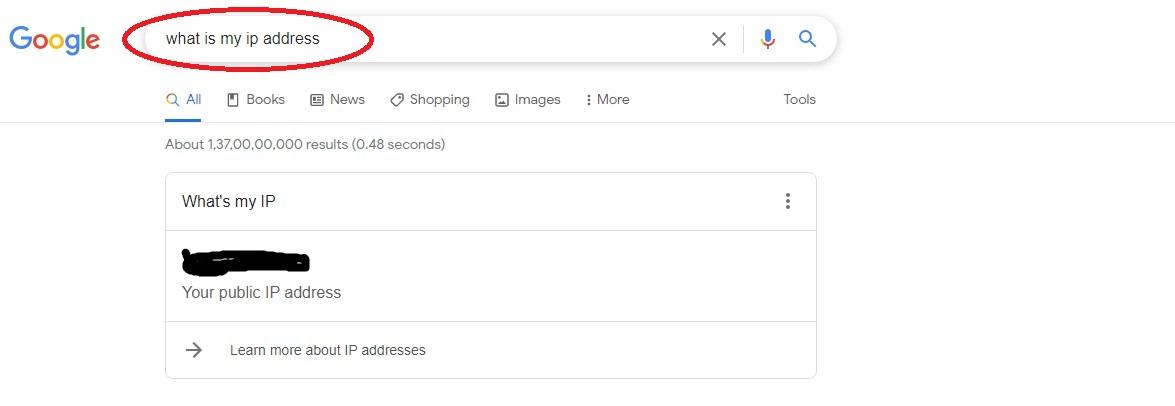
Question: How can I know my external IP address?
A- Visit Google and enter my IP address. Pls see the screen shot
Question: How frequently do IP addresses change?
A- We investigate why dynamic IP addresses vary and identify ISPs that renumber periodically, typically every 24 hours or multiples of 24 hours. We also discover that power disruptions affect address changes. Both industry and academia frequently assume that an IP address can uniquely identify an endpoint host.
Question: Does the use of dynamic DNS require port forwarding?
Remote administration does not require port forwarding because you will be accessing the router itself and not a device within your home network. In other words, this was already configured by the router. Using the DDNS domain name, you may then access your router’s interface from anywhere in the globe.
Question: Is Dynamic DDNS equivalent to port forwarding?
A- No- port forwarding allows an Internet address to access a service (external address). This external address is given a name by DDNS, which is updated if the address changes.
Question: Is Dynamic DNS use the same port as DNS.
A- yes udp/tcp port 53
ad


Comments are closed.