Types of SSL Certificates, which one suits your needs?
Choosing the right SSL for your website can be tough if you don't know what it does or the differences between them.
A website encrypted with an SSL certificate assures visitors that it is safe to access. It also garners the approval of search engines, which serves as another evidence that your website is risk-free for users to navigate. As a result, you are required to acquire a current SSL certificate for your website.
SSL is an acronym that stands for Secure Sockets Layer. SSL is a security protocol that authenticates and encrypts data while it is being transferred over network connections between a web server and a web browser. A malevolent third party cannot access the connection that exists between your website and your visitors if you have an SSL certificate installed.
An SSL certificate secures a site’s connection with browsers. Website owners should implement this feature if they collect sensitive user data. Some SSL certificates are better for some websites than others. Ideal certificate fits your firm, budget, and site size.
This tutorial will explain the many types of SSL certificates that are available so that you can make a wise decision. The advantages and disadvantages of each one, as well as the distinctions between the various SSL validation levels, will be discussed.
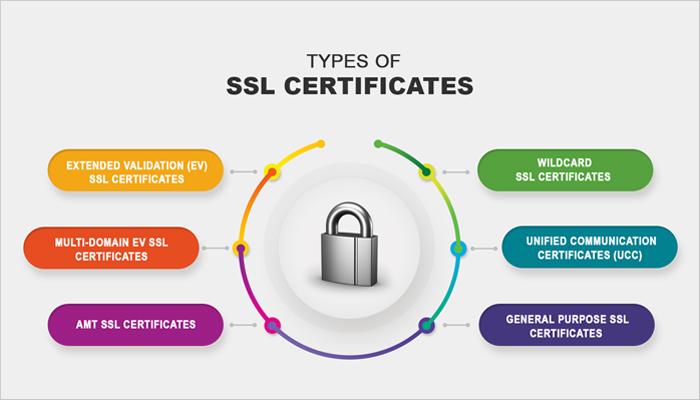
Extended Validation (EV SSL) Certificates
With an EV SSL, the Certificate Authority (CA) confirms the applicant’s domain name eligibility and business. The CA/Browser forum accepted the EV Requirements in 2007 to define exact guidelines for EV SSL Certificates. A CA must fulfill the aforementioned steps before issuing a certificate:
- Verifying the legal, physical and operational existence of the entity
- Verifying that the identity of the entity matches official records
- Verifying that the entity has exclusive right to use the domain specified in the EV SSL Certificate
- And verifying that the entity has properly authorized the issuance of the EV SSL Certificate.
The most recent, and possibly most important, innovation in SSL technology since its introduction adheres to the defined Extended Validation requirements. Microsoft Internet Explorer 7+, Opera 9.5+, Firefox 3+, Google Chrome, Apple Safari 3.2+, and iPhone Safari 3.0+ recognize Extended SSL Certificates and activate browser interface security features. This is the appropriate solution for consumers that want to establish the highest levels of authenticity.
EV SSL Certificates are accessible for all types of enterprises, including government bodies and incorporated and unincorporated entities. The EV Audit Rules, a second set of guidelines, establish the criteria under which a CA must be successfully audited before issuing EV SSL Certificates. The audits are carried out on a yearly basis to assure the integrity of the issuance process.
Certificates with Organization Validation (OV SSL)
The CA not only verifies the applicant’s eligibility to use a particular domain name, but it also checks the organization’s legitimacy. When clients click on the Secure Site Seal, more validated firm information is shown to them, increasing their understanding of who is in charge of the website and their ability to trust it. The certificate’s ON field contains the name of the organization as well.
Certificates that are Domain Validated (DV SSL)
The CA verifies the applicant’s eligibility to use a certain domain name. Aside from the encryption-related information displayed within the Secure Site Seal, no firm identity information is verified or displayed. While you can be certain that your data is encrypted, you cannot be certain who is actually receiving it.
Similar to OV SSL, DV SSL Certificates are fully accepted and recognized by browsers, but they have the advantage of being granted virtually instantaneously and without the need to submit business papers. Because of this, DV SSL is the best option for businesses who require a low-cost SSL immediately and without the hassle of submitting business documents.
Wildcard SSL certificates
Wildcard SSL certificates allow you to secure a primary domain as well as an unlimited number of subdomains with a single certificate. If you need to secure several subdomains, purchasing a Wildcard SSL certificate is substantially less expensive than purchasing individual SSL certificates for each of them. The common name of a wildcard SSL certificate includes an asterisk *, which denotes any valid sub-domains that share the same base domain. A single Wildcard certificate for *website, for example, can be used to secure:
- payments.yourdomain.com
- login.yourdomain.com
- mail.yourdomain.com
- download.yourdomain.com
- anything.yourdomain.com
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates (MDC)
A Multi-Domain certificate can protect many domains and/or sub-domain names. Except for local/internal TLDs, this covers the combination of entirely unique domains and sub-domains with different TLDs (Top-Level Domains).
As an example:
- www.example.com
- example.org
- mail.this-domain.net
- example.anything.com.au
- checkout.example.com
- secure.example.org
Multi-Domain certificates do not support sub-domains by default. If you need to secure both www.example.com and example.com with a single Multi-Domain certificate, you must specify both hostnames when requesting the certificate.
📚 Also Read: What Is Certificate Pinning?
Certificate for Unified Communications (UCC)
Multi-Domain SSL certificates are also known as Unified Communications Certificates (UCC). Initially, UCCs were intended to safeguard Microsoft Exchange and Live Communications servers. Nowadays, any website owner can utilize these certificates to secure many domain names with a single certificate. UCC Certificates are organizationally certified and appear in a browser as a padlock. UCCs can be used as EV SSL certificates to provide the highest level of assurance to website visitors via the green address bar.
It is critical to understand the various types of SSL certificates in order to secure the correct sort of certificate for your website.
Types of SSL certificate validation level
A bank won’t lend without a credit check. Before issuing an SSL certificate to an entity, a CA must verify that the organization owns and administers the domain. SSL certificate validation.
Different levels of validation range from minimal to rigorous. Any of these SSL certificates delivers the same TLS encryption; the only difference is how fully the CA has authenticated the organization’s identity.
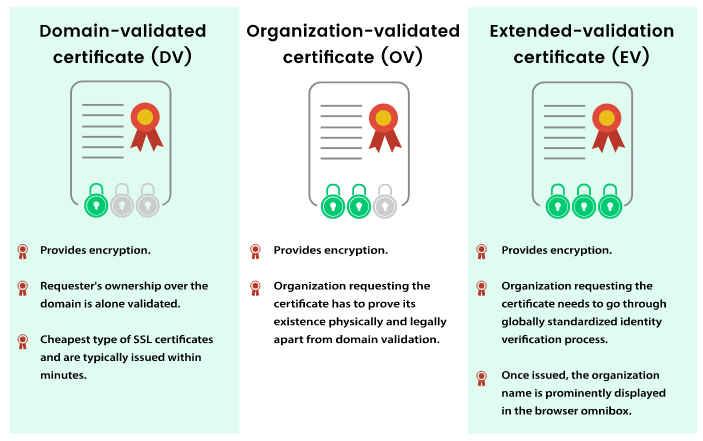
Domain Validation SSL
Domain Validation is the weakest stage. An organization must prove domain control to get an SSL certificate. They can change the domain’s DNS record or email the CA. Automated often.
The cheapest validation level. It’s suitable for blogs, portfolio sites, or small businesses wishing to quickly implement HTTPS, especially if they don’t sell items online (e.g. a restaurant or coffee shop).
Organization Validation SSL Certificate
The CA will contact the organization requesting the SSL certificate and may perform further investigation. Organization Validated SSL certificates feature the organization’s name and address, making them more trustworthy.
Extended Validation SSL Certificates

Extended Validation checks the organization’s background. The CA verifies that the business exists, is lawfully registered, is present at the listed address, etc. Extended Validation SSL certificates take the longest and cost the most, but they’re more trustworthy. These certificates are required for a website’s URL bar to glow green, indicating a trustworthy TLS-encrypted site.
Extended Validation certificates are for large businesses, banks, and eCommerce stores. This is especially important if a site or app handles passwords, credit card numbers, or names and addresses.
Why is it necessary for me to have an SSL Certificate?
Having an SSL certificate does more than just safeguard sensitive information from being intercepted. This section will go over some additional justifications for why you require this digital certificate.
SSL certificate for Strengthening security
There are numerous different approaches you may take to securing your website. The installation of an SSL certificate offers an additional and critically important layer of protection against assaults carried out by hostile actors.
Even if the website does not support financial transactions, you are still responsible for protecting the login credentials, addresses, and any other personally identifiable information that users provide.
Websites that don’t have SSL certificates use HTTP, which is a text-based protocol. Because of this, it’s much simpler to intercept and read the traffic coming from these websites. The data exchanged over HTTPS is encrypted using cryptographic keys, which provides a higher level of security and makes it more difficult for potential attackers to read the data as it is being transmitted.
Therefore, the HTTPS protocol defends your website from digital dangers such as man-in-the-middle assaults (MITM). The client’s browser or the traffic between the website’s server and the client’s computer can become the target of these attacks if the traffic is intercepted.
Either the information that is being passed around can be stolen or the traffic can be redirected to a phishing website where the attackers can ask for login credentials or other sensitive data.
If you have an SSL certificate, then even if an adversary manages to intercept your connection, they will not be able to decrypt the information that is being sent.
Improve credibility of your site with the SSL certificate
Developing a relationship of trust with your clientele is vital. Your clients, particularly those that transact with you via the internet, require undeniable evidence that it is secure for them to supply their information. According to the findings of recent research, seventeen percent of online buyers do not complete their purchases because they do not trust the website enough to provide their credit card information.
Visitors to a website can be assured that they can safely exchange information with the website through the use of an SSL certificate. This will encourage visitors to utilize your service and keep you ahead of competitors who do not have an SSL certificate.
In addition, it assists visitors in verifying the ownership of the website prior to signing in or supplying any other sensitive information.
Strengthening of your website SEO
Your search engine optimization efforts will also benefit from the installation of an SSL certificate. When assessing page rankings, website security has become an increasingly essential consideration, especially for Google and other search engines.
Visitors to websites that do not use secure socket layer (SSL) encryption will see a warning label that reads “Not Secure” on Google Chrome and other web browsers. This is done in an effort to protect users when they browse the internet.
When compared to competitors who do not have an SSL certificate, you will have an advantage if you own one because it will improve the position of your website on the pages of search engine results (SERPs).
When is it necessary to have an SSL certificate for my website?
Everyone who owns a website ought to make installing an SSL certificate their number one priority. It is crucial to provide a worry-free surfing experience for all of a website’s visitors, regardless of whether or not the website gathers data.
Let’s take a look at some of the most prevalent kinds of websites that want SSL certificates:
SSL for eCommerce Websites
Because client payments are processed through online stores, guaranteeing a secure data transfer is absolutely necessary. SSL prevents unauthorized parties from simply intercepting information acquired from your website and your customers, such as usernames, passwords, or payment information, thereby protecting the confidentiality of such information.
Chrome and Safari, two of the most popular internet browsers, both provide warnings to website visitors advising them not to submit any personal information on HTTP websites. Customers may consequently abandon your online store out of concern that their credit card information might be stolen as a result of this, as a result of which you will lose sales.
In addition, because one of the criteria of PCI is to encrypt the transmission of cardholder data across open networks, all websites that collect money online are required to have an SSL certificate. When accepting payments online, you also have the option of utilizing a third-party payment processor that is SSL-certified, such as PayPal.
Personal blogs and websites
For example, a website for a portfolio is just as susceptible to hacking as a website for an online store. When a potential customer fills out a contact form, SSL encrypts the information they enter so that hackers cannot access it and use it for their own purposes.
Websites of various governments
Any organization that provides a public service has an obligation to safeguard the personal information of its customers. For the sake of preventing information from being modified or snooped on by cybercriminals, data entry forms need to be protected.
Static websites that don’t change often
The content of a static website still has to be protected because hackers can target anyone who views HTTP sites, even though the website does not collect data or accept money.
What should I do if my website doesn’t have a secure sockets layer certificate?
Security flaws have become increasingly sophisticated alongside the development of technology. According to the findings of research, the average cost of a data breach reached $4.24 million in the year 2021. Having an SSL certificate can assist in the prevention and reduction of risks associated with cyberattacks.
Cyberattacks can result in monetary losses, but they can also put the personal information of millions of people at risk and damage a company’s brand. One such instance is the data breach that occurred at Equifax.
In the United States, one of the largest credit reporting agencies is called Equifax. They made the announcement in September 2017 that their systems had been compromised, putting the personal information of 148 million people in the United States at risk. In later revelations, it was found that the SSL certificates in question had already passed their expiration dates.
In order to compensate clients whose data was compromised, the business reached a global settlement agreement for the amount of $425 million. However, it is impossible to evaluate the full impact of data breaches on the faith that customers have in businesses and the reputations of those businesses.
In addition, a website that attracts users from within the European Union is required to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) (General Data Protection Regulation). In its most basic form, it is a law that was enacted to safeguard the personal information and online privacy of citizens of the EU. Those who do not comply run the risk of receiving fines of up to 20 million Euros each.
Does SSL have any disadvantages?
You should now be aware of the many advantages that come with utilizing SSL certificates. However, many people have formed false beliefs about HTTPS websites, which has caused them to question the level of safety and effectiveness they provide.
In this section, we will dispel some of the most widespread misunderstandings regarding SSL certificates and HTTPS websites by addressing some of the most common myths.
Changing from HTTP to HTTPS affects website speed
When it comes to the performance of a website, speed is one of the most important considerations. People frequently hold the false belief that HTTP websites load faster than HTTPS websites due to the fact that HTTPS websites must encrypt data before sending or receiving it.
However, the use of SSL encryption will not significantly slow down the performance of your website. In point of fact, the most recent version of HTTP/2, which is utilized in SSL, can speed up load times. It is possible to compare the load times of pages when utilizing HTTP/1 and HTTP/2 with the help of free website speed testing tools like Dareboost.
SSL Certificates Secure Websites
SSL doesn’t make your site hackproof. It improves data security.
Thus, account and password security must be maintained. Also, keep your site updated and malware-free.
Using an SSL certificate and these methods will boost your website’s security.
SSL protects only payment-processing websites
If information slips into the wrong hands, your online security can be compromised instantaneously.
Cybercriminals don’t just want credit cards and bank details. Hackers can use email addresses from web forms to guess login credentials and access other websites.
All websites that collect personal information, such as membership sites, need an SSL certificate.
SSL is only for login pages
Passing the login page without HTTPS enhances page session hijacking. Public WiFi networks in coffee shops and airports put users at higher danger.
Thus, SSL protects every page session.
SSL certs are expensive
Several hosting firms offer free SSL certificates. Many companies supply affordable SSL certificates, depending on your website’s demands.
Regardless of type, buy it from a reputable issuing agency.
How do I get an SSL certificate?
Determine your website’s security demands and budget before purchasing an SSL certificate.
How and where you host your website affects SSL installation. Hosting companies install SSL certificates for customers.
Hostinger’s plans provide free SSL certificates. Users can install them on hPanel in a few minutes.
If you bought your certificate separately or use a different supplier, configure WordPress to use HTTPS by establishing a dashboard redirect or downloading Really Simple SSL.
How to install an SSL certificate?
We’ll explain how to install an SSL certificate now that you know what it is and how it works. The answer is a Certificate Authority.
Independent, market-trusted CAs generate and distribute SSL formats.
CAs sign certificates with their own encryption keys, so customers may verify their validity. There are free alternatives to this treatment. The certificate must be installed on the website’s original server. This can be difficult, but a good web host will handle it.
Your pages will load over HTTPS once SSL is enabled on the origin server. All website traffic is now encrypted.
What happens when an SSL certificate expires?
SSL expires. SSL certificates are limited to 27 months by the Certificate Authority/Browser Forum. Early SSL certificate renewal adds three months.
To preserve correctness, SSL certificates must be revalidated. Online sales of businesses and websites transform the scene. When sold, SSL certificates’ data changes. The expiration date verifies server and organization authentication information.
SSL certificates were issued for five years, then three, and currently two plus three months. Google, Apple, and Mozilla will need one-year SSL certificates in 2020 despite CABF objections. March 2020. Validity may decrease.
SSL expiration makes sites inaccessible. A browser verifies an SSL certificate in milliseconds (as part of the SSL handshake). Expired SSL certificates provide visitors this message: “Unsecured site. hazard “more
Users can continue, but virus dangers discourage it. Consumers will exit the homepage, raising bounce rates.
Larger companies have trouble tracking SSL certificate expirations. SMEs may only have one or two certificates to manage, but companies with several websites and networks will have many more. Mistake, not ignorance. Certificate management software helps larger companies track SSL certificate expiration. Many things are online. Companies can maintain digital certificates with these. If you utilize one of these platforms, check for renewals often.
Expired certificates prevent safe online transactions. CA reminds you to renew your SSL certificate.
Regardless of the CA or SSL service you choose, you’ll get 90-day expiration notices. Try sending these reminders to an email list instead of a specific person who may have left the firm or moved. Make sure the correct firm stakeholders are on this list.
Conclusion
No of the website’s size, users want security. An SSL certificate protects critical data sent between the web server and browser, boosting the website’s credibility. SSL protects against nefarious intent and boosts SEO. Secure websites rank higher in SERPs. SSL certificates are merely the first line of defense against data theft. Your website and visitors need more security.
This article explains why you need an SSL certificate. Please comment if you have questions.
ad


Comments are closed.