What is an Ethernet LAN: Everything You Need To Know
Ethernet is the most commonly used communication protocol invented by Robert Metcalfe and others at Xerox PARC in 1973 that connects computers on a network via a wired connection. It is a popular LAN protocol, also known as Alto Aloha Network. It links computers in a local area network and a wide area network. LAN and WAN can connect a variety of devices such as printers and laptops within buildings, homes, and even small neighborhoods.
What is Ethernet LAN?
Ethernet, also known as the IEEE 802.3 protocol, is a network protocol that governs how data is transmitted over a LAN. Over time, the protocol has evolved and improved to transfer data at speeds of more than a gigabit per second.
It has a simple user interface that allows you to easily connect various devices such as switches, routers, and computers. A local area network (LAN) can be built with a single router and a few Ethernet cables, allowing communication between all connected devices. This is because your laptop has an Ethernet port into which you can plug one end of a cable and connect the other to a router. Ethernet ports are slightly wider and resemble telephone jacks.
Most Ethernet devices are backward compatible with lower-speed Ethernet cables and devices. The connection, however, will be as fast as the lowest common denominator. If you connect a computer with a 10BASE-T NIC to a 100BASE-T network, for example, the computer will only be able to forward and receive data at 10 Mbps. In addition, if you connect the device to a Gigabit Ethernet router, the maximum data transfer rate will be 100 Mbps.
Wireless networks have largely replaced Ethernet in many areas; however, Ethernet remains the most popular wired networking protocol. Wi-Fi eliminates the need for cabling by allowing users to connect their smartphones or laptops to a network without the use of a cable. When compared to Gigabit Ethernet, the 802.11ac Wi-Fi standard provides faster maximum data transfer rates. Nonetheless, wired connections are more secure and less susceptible to interference than wireless networks. This is the primary reason why many businesses and organizations continue to use Ethernet.
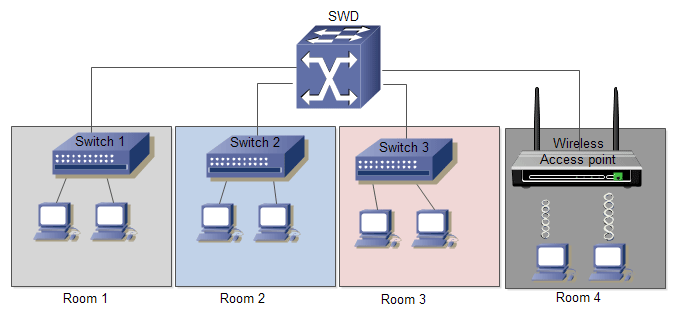
A local area network (LAN) is a network of computers and other electronic devices that covers a small area, such as a room, office, or building. In contrast, a wide area network (WAN) covers a large geographical area.
Many people have unknowingly used Ethernet technology their entire lives. Any wired network in your office, bank, or home is most likely an Ethernet LAN. Most desktop and laptop computers include an Ethernet card and are ready to connect to an Ethernet LAN.
History of Ethernet Networking
Ethernet was developed over several years in the early 1970s from ALOHAnet at the University of Hawaii. Then a test was carried out, culminating in a scientific paper published in 1976 by Metcalfe and David Boggs. Xerox Corporation filed a patent on this technology in late 1977.
Companies Xerox, Intel, and Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) established Ethernet as a standard; first, these companies collaborated to improve Ethernet in 1979, then published the first standard in 1980. Other technologies, such as the CSMA/CD protocol, were also developed with the assistance of this process, which was later known as IEEE 802.3. This process also resulted in the development of a token bus (802.4) and token ring (802.5).
IEEE technology became standard in 1983, and 802.3 was born before 802.11. Many modern PCs began to include Ethernet cards on the motherboard after the invention of single-chip Ethernet controllers reduced the cost of the Ethernet card. As a result, some small businesses started using Ethernet networks in the workplace, but they still used telephone-based four-wire lines.
Until the early 1990s, it was not possible to establish an Ethernet connection using twisted pair and fiberoptic cables. This resulted in the creation of the 100 MB/s standard in 1995.
Purpose of Ethernet
Ethernet is still a popular type of network connection due to its high speed, security, and reliability. It connects devices in a network used by specific organizations for local networks, such as school campuses and hospitals, company offices, and so on.
In comparison to technology such as IBM’s Token Ring, Ethernet initially gained popularity due to its low cost. As network technology advanced, Ethernet maintained its popularity because of its ability to develop and deliver higher levels of performance while maintaining backward compatibility. The original ten megabits per second of Ethernet was increased to 100 Mbps in the mid-1990s. Furthermore, current Ethernet versions can support up to 400 gigabits per second.
Types of Ethernet LAN
Fiber optic media converters connect an Ethernet device using CAT5/CAT6 copper cables to a fiber optic cable. This fiber optic cable extension significantly increases the network’s coverage distance. There are several types of Ethernet networks, which are discussed further below:
Fast Ethernet: This type of Ethernet is typically supported by a twisted pair or CAT5 cable that can transfer or receive data at speeds of up to 100 Mbps. If any device, such as a camera, laptop, or other, is connected to a network, they operate at 100Base and 10/100Base Ethernet on the fiber side of the link. Fast Ethernet communicates by using fiber optic cable and twisted pair cable. Fast Ethernet is classified into three types: 100BASE-TX, 100BASE-FX, and 100BASE-T4.
Gigabit Ethernet: This type of Ethernet network is an upgrade from Fast Ethernet, which communicates via fiber optic cable and twisted pair cable. It has a data transfer rate of 1000 Mbps or 1Gbps. Gigabit Ethernet is more common nowadays. This network also employs CAT5e or other advanced cables capable of transmitting data at a rate of 10 Gbps.
10-Gigabit Ethernet: This network can transmit data at a rate of 10 Gigabits per second and is considered a more advanced and fast network. It employs CAT6a or CAT7 twisted-pair cables, as well as fiber optic cables. With the help of a fiber optic cable, this network can be extended up to nearly 10,000 meters.
Switch Ethernet: Adding switches or hubs to a network helps to improve network throughput because each workstation in this network can have its own dedicated 10 Mbps connection rather than sharing the medium. When a switch is used in a network, a regular network cable is used instead of a crossover cable. It supports 1000Mbps to 10 Gbps for the latest Ethernet and 10Mbps to 100Mbps for fast Ethernet.
The primary goal of developing gigabit Ethernet was to meet the needs of users, such as faster data transfer, faster communication networks, and so on.
Ethernet FAQ
How Ethernet Works?
To fully comprehend the Ethernet protocol, technical knowledge in computer science is required. Here’s an easy explanation:
When one network machine wants to send data to another, it detects the carrier, which is the main wire connecting the devices. If the network is free, which means no one is sending anything, it sends the data packet, and the other devices check the packet to see if they are the recipient. The packet is consumed by the recipient. If a packet is on the highway, the device that wants to send waits a few thousandths of a second before trying again until it can send.
What are advantages of Ethernet Network?
- Creating an Ethernet network is not expensive. It is relatively inexpensive when compared to other computer-connection systems.
- Because it employs firewalls for data security, the Ethernet network provides high data security.
- Furthermore, the Gigabit network allows users to transmit data at speeds ranging from 1-100Gbps.
- The data transfer quality is maintained in this network.
- Administration and maintenance are simplified in this network.
- The most recent versions of gigabit ethernet and wireless ethernet can transmit data at rates ranging from 1-100Gbps.
What are disadvantages of Ethernet?
- Because it requires deterministic service, it is not recommended for real-time applications.
- The wired Ethernet network has distance limitations and is best used for short distances.
- When you create a wired ethernet network that requires cables, hubs, switches, and routers, the cost of installation rises.
- In an interactive application, data must be transferred quickly, and the data is very small.
- After accepting a packet on an Ethernet network, the receiver does not send any acknowledgement.
- If you have no prior experience with networks, setting up a wireless Ethernet network can be difficult.
- Wireless networks are not more secure than wired Ethernet networks.
- The 100Base-T4 version does not support full-duplex data communication.
- Furthermore, finding a problem in an Ethernet network (if one exists) is difficult because it is difficult to determine which node or cable is causing the problem.
What an Ethernet LAN Requires?
You will need the following items to set up a wired Ethernet LAN:
- Connecting computers and devices: Ethernet can connect any computer or other electronic device to its network as long as it has an Ethernet adapter or network card.
- Devices with network interface cards: A network interface card is either built into the computer’s motherboard or installed separately in the device.
- Ethernet cards are also available in USB form, such as external dongles. A network card is what an Ethernet card is. It has ports for connecting cables.
- On the network card, there may be two ports: one for an RJ-45 jack that connects unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables and one for a coaxial jack. (However, coaxial connections are extremely rare.)
- To connect devices, use a router, hub, switch, or gateway: A hub is a device that serves as a connecting point for network devices. It is made up of several RJ-45 ports into which cables are plugged.
- Cables: In Ethernet LANs, UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables are commonly used. This cable is similar to the type used for landline telephones, but it is thicker and has eight twisted pairs of different coloured wires inside. The other end is crimped with an RJ-45 connector, which is a larger version of the RJ-11 jack found on landline phones.
- Network management software: Modern operating systems, such as the latest versions of Windows, Linux, and macOS, are more than capable of managing Ethernet LANs. There is third-party software available that provides more features and greater control.
📚 Also Read: What Is a Fast Flux Network?
How to connect to an Ethernet cable?
Whether you’re connecting an Ethernet cable to your computer or setting up a home network, the procedure is the same. It appears to be a large telephone cord jack, as shown in the image below. Once you’ve found it, insert the cable connector into the port until you hear a click. If the connection is properly established on the other end, you will see a green light indicating that a signal has been found.

What Are The Standard Data Rates For Ethernet?
Ethernet’s standard data rates are 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and 1 Gbps.
How Two Systems In An Ethernet Network Communicate?
A system broadcasts data over an Ethernet network by using an Ethernet frame. The Ethernet frame specifies the destination system by its Ethernet address. All systems in the network wait for an Ethernet frame containing their Ethernet address. When a system receives an Ethernet frame containing its address, it processes the frame and forwards it to higher layers (such as IP) for further processing.
What is a coallision?
In an Ethernet network, only one device can transmit at any given time. If two devices transmit at the same time, the signals from both devices will collide, resulting in a “collision.” When there is a “collision,” the signals become distorted and the frame is lost. In an Ethernet network, collisions are common.
What is an Ethernet address?
Each device in an Ethernet network is identified uniquely by a 48-bit (6-byte) address known as an Ethernet address. Ethernet addresses are also referred to as Media Access Control (MAC) addresses. Ethernet addresses are composed of six hexadecimal digit pairs separated by a colon. The manufacturer burys the Ethernet address in the network adapter. A device’s Ethernet address cannot be changed. Example: 00:60:08:11:AB, 00:c0:5e:83:0e.
What Is A Broadcast Address?
A broadcast address is an Ethernet address with all bits set to 1. It is written as FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF: All nodes in the network receive and process a frame with this address.
What Is An Ethernet Frame ?
An Ethernet frame is used to encapsulate data from the TCP/IP Model’s higher layers. Assume PC1 sends a ping to PC2. The ping, which is an ICMP packet, is encapsulated in the Ethernet frame along with the IP Header. The frame is used to transport the ping packet and eventually deliver it to PC2.
Ethernet @ YT
ad


Comments are closed.