What Is Fog Computing?
Fog computing is a trend that anyone, in or considering a career in technology should grasp. It offers uses ranging from industrial and manufacturing environments, to hospitals and healthcare facilities. However what is fog computing. How does it differ from cloud computing? Lets delve into it.
ad
What is Fog Computing?
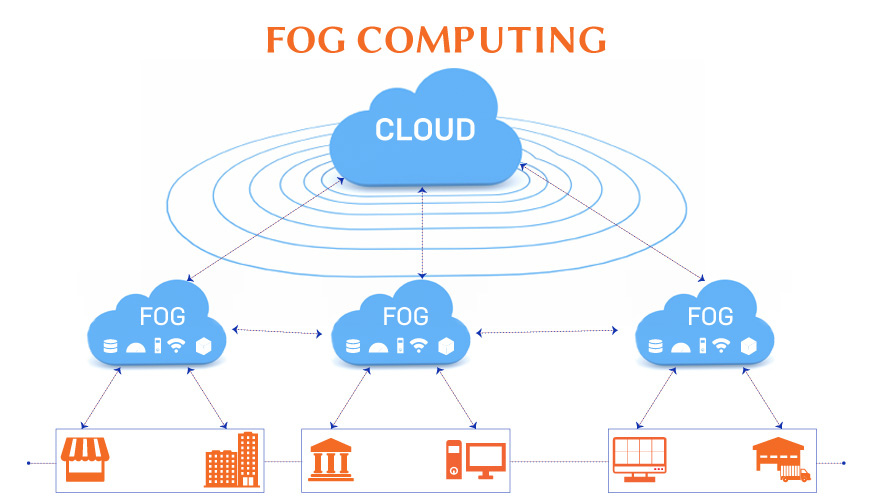
Fog computing is a type of distributed computing that moves computation and data storage closer to the network edge, where many IoT devices are situated. This approach decreases reliance on the cloud for resource-heavy tasks, enhancing performance and reducing latency.
Mist computing advances fog computing by placing computation and data storage even nearer to the edge, frequently using low-power devices known as mist computing servers, which can be deployed in large quantities.
How Does Fog Computing Work?
ad
Fog computing implementation involves developing or adapting IoT applications for fog nodes at the network edge using fog computing software, packages, or other tools. Edge nodes, located closest to the network edge, collect data from devices such as routers or modems and route it to the best location for analysis.
To integrate fog and cloud computing networks, administrators determine which data is most time-sensitive. Data requiring immediate attention is analyzed as close to its source as possible within verified control loops.
Data that can be processed later is sent to an aggregation node. The characteristics of fog computing ensure that the choice of fog node for data analysis depends on the analysis goals, data type, and immediate user needs.
Why Is Fog Computing Used?
Fog computing is used for several reasons:
- To improve latency and performance: Fog nodes, located closer to IoT devices at the network edge, help reduce processing time and enhance performance for applications that need low latency.
- To enhance decision-making: By enabling real-time data collection and analysis from IoT devices, fog computing supports better real-time decision-making.
- To cut costs: Fog computing lowers costs by minimizing the data that must be transmitted to a central location for processing, as it brings computation and storage closer to the edge.
What Are the Types of Fog Computing?
Fog computing refers to technology that extends cloud computing and services to the edge of an enterprise’s network. It enables data, applications, and other resources to be moved closer to, or even directly onto, end users.
The four main types of fog computing are:
- Device-level fog computing: Operates on devices such as sensors, switches, routers, and other low-powered hardware, collecting data from these devices and sending it to the cloud for analysis.
- Edge-level fog computing: Runs on servers or appliances at the edge of a network, processing data before it is sent to the cloud.
- Gateway-level fog computing: Functions on devices that act as intermediaries between the edge and the cloud, managing traffic and ensuring that only relevant data is transmitted to the cloud.
- Cloud-level fog computing: Operates on servers or appliances within the cloud, processing data before it reaches end users.
Where Is Fog Computing Needed?
Fog computing has numerous potential applications, including:
- Connected cars: Real-time data collection and processing from sensors to support features like autonomous driving and infotainment.
- Smart cities: Managing traffic flows, public transportation, energy use, and more.
- Industrial IoT: Improving efficiency and safety in factories, power plants, mines, and other industrial settings.
- Connected health: Facilitating remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and other healthcare services.
- AR/VR: Providing low-latency, high-quality augmented and virtual reality experiences.
Fog computing supports various applications that require edge processing. By moving compute and storage resources closer to the data source, it enhances performance and reduces costs. For instance, connected cars produce large amounts of data that must be analyzed in real-time for features like autonomous driving.
Who Uses Fog Computing?
Fog computing is commonly used in situations that demand real-time responses, such as in industrial control systems, video surveillance, and autonomous vehicles. It also helps offload intensive computations from centralized servers and provides backup and redundancy in case of network failures.
Why Is Fog Computing Beneficial for IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected devices, sensors, and software components that exchange data and information. The strength of the IoT lies in its capacity to gather and analyze large amounts of data from diverse sources, which can enhance efficiency, optimize operations, and support better decision-making.
In IoT, fog computing represents a decentralized computing model that shifts computation and data storage closer to the network edge. This means moving processing power and data storage from centralized server farms to local networks where IoT devices are situated.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Fog Computing?
Advantages of using a fog computing architecture include:
- Reduced latency: Processing data at or near the network edge helps to decrease latency.
- Improved security and privacy: Keeping data and applications closer to the user enhances security and privacy.
- Increased scalability: Fog computing allows for greater scalability by adding resources at the network edge.
Disadvantages of fog computing architecture include:
- Limited resources: The reliance on edge devices can result in limited resources, potentially affecting performance.
- Complex architecture: The distributed nature of fog computing can make implementation and management complex.
- Limited coverage: As a relatively new technology, fog computing may have limited support in terms of devices and locations.
Fog vs. Edge Computing
Edge computing, a form of distributed computing handles data and applications at the periphery of the network near where the data originates. In comparison the conventional centralized approach of cloud computing involves storing data and applications, in a location and accessing them over the network.
The key distinction between fog and edge computing lies, in how fog computing expands cloud services and connectivity to devices located at the networks edge. On the hand edge computing focuses on bringing computation and data storage nearer to devices positioned at the networks edge.
FAQ’s
What is Fog Computing?
Fog computing brings computation and data storage closer to the network edge, improving performance and reducing latency compared to centralized cloud computing.
How Does Fog Computing Work?
It involves deploying IoT applications on edge nodes that collect and process data locally, sending only relevant data to central servers.
Why Is Fog Computing Used?
It improves latency and performance, enhances real-time decision-making, and reduces costs by minimizing data transmission to central servers.
Where Is Fog Computing Needed?
It’s used in connected cars, smart cities, industrial IoT, connected health, and AR/VR applications.
Who Uses Fog Computing?
It’s used in real-time applications like industrial control systems, video surveillance, and autonomous vehicles.
Why Is Fog Computing Beneficial for IoT?
It improves efficiency and decision-making by processing data closer to IoT devices.
How Does Fog Computing Differ from Edge Computing?
Fog computing extends cloud services to the edge, while edge computing focuses on local data processing and storage.
Conclusion
Fog computing enhances network performance by bringing data processing and storage closer to the edge, where IoT devices are located. It reduces latency, improves security, and supports real-time decision-making, making it ideal for applications requiring quick responses and efficient data handling. While it offers numerous benefits, such as reduced latency and improved scalability, it also presents challenges like limited resources and complexity. Understanding fog computing is crucial for leveraging its advantages in various technology-driven environments.
ad


Comments are closed.