What is GPS spoofing?
For those interested in internet security, it is crucial to understand GPS spoofing and its significant threat in today’s digitally connected world. This knowledge aims to empower individuals and businesses to proactively secure their information and systems, protecting sensitive data from fraudsters and cybercriminals.
GPS spoofing is a malicious technique that alters Global Positioning System (GPS) data, misleading a GPS receiver about its true location. This can cause major disruptions by misdirecting navigation systems, misleading delivery vehicles, or tricking smartphone apps. This article will explore GPS spoofing in detail, explaining how it works, the risks it poses, and how to defend against it.
ad
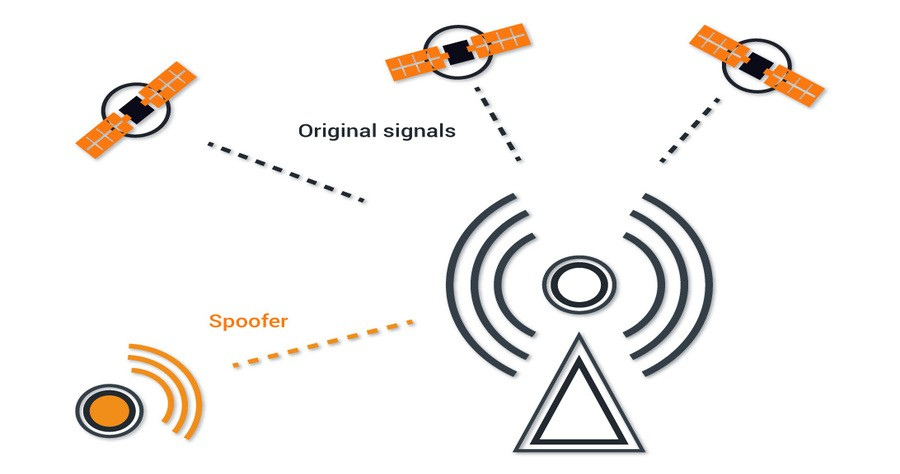
What is GPS Spoofing?
GPS spoofing, also called GPS simulation, involves tricking a GPS receiver by broadcasting false GPS signals. This misleads the receiver into believing it is in a different location, causing it to provide inaccurate location data. Such a cyberattack compromises the reliability of GPS data, which is essential for applications like navigation and time synchronization.
Although the concept of GPS spoofing isn’t new, it has significantly evolved over the years. Once a theoretical threat, it has become a practical concern due to the availability of inexpensive software and hardware capable of transmitting fake GPS signals. This development has exposed industries, governments, and individuals to potential risks and significant security challenges.
ad
How Does GPS Spoofing Work?
GPS spoofing takes advantage of inherent vulnerabilities in the GPS infrastructure, specifically the weak signal strength of GPS satellites. The Global Positioning System operates by transmitting signals from satellites to GPS receivers on Earth, which then calculate their position based on the time these signals take to arrive. However, the weak signal strength of GPS satellites allows these signals to be easily overwhelmed by fake ones, leading to inaccurate location data on the receiving device.
A GPS spoofer typically starts by understanding the victim’s GPS setup, including the types of signals used and how they are processed. Armed with this information, the attacker sends counterfeit GPS signals that mimic the real ones but are stronger. These stronger fake signals cause the receiver to accept them as authentic, resulting in the GPS receiver processing the counterfeit signals and producing erroneous location information.
Real-World Implications of GPS Spoofing
GPS spoofing has extensive implications that extend beyond the digital realm and can have potentially catastrophic real-world effects, especially in navigation. For example, misleading a ship or aircraft about its location could steer it off course, potentially leading to accidents. Additionally, GPS spoofing can significantly impact various industries, including logistics and supply chain, telecommunications, energy, and defense.
Individuals who rely heavily on GPS data in their daily lives are also vulnerable to this threat. Smartphone applications that use location data, such as ride-sharing and food delivery apps, can be manipulated through GPS spoofing. This could result in drivers heading to incorrect locations, deliveries going astray, or customers being charged incorrect amounts. Ultimately, the consequences of GPS spoofing are severe, making it a significant concern for everyone in the digital age.
Notable GPS Spoofing Incidents
Iranian Capture of the U.S. Drone
In 2011, Iran claimed to have captured a U.S. RQ-170 Sentinel drone, marking a notable instance of GPS spoofing. Reports suggested Iranian forces used GPS spoofing to manipulate the drone’s navigation, leading it to land within Iranian territory. This event underscored the tangible impact of GPS spoofing in geopolitical conflicts.
Shanghai Superyacht Race
During a superyacht race in Shanghai in 2013, researchers demonstrated the risks of GPS spoofing in a controlled setting. They successfully executed a GPS spoofing attack, causing participating yachts to deviate from their intended course without crew awareness. This experiment highlighted the susceptibility of GPS systems, even in environments presumed to have high security.
The Threat to Internet Security
Given the increasingly digital nature of our lives, internet security is of utmost importance. GPS spoofing poses a serious threat to this security landscape. By manipulating location data, malicious individuals or entities can cause significant disruptions and security breaches. For instance, by spoofing the GPS coordinates of a person’s smartphone, cybercriminals could gain unauthorized access to personal information or commit identity theft.
Moreover, GPS spoofing presents a considerable threat to industries that heavily rely on GPS data for their operations. This includes sectors such as logistics, transportation, and emergency services. In these industries, a successful GPS spoofing attack can lead to substantial financial losses, operational disruptions, and even life-threatening situations.
Protection Against GPS Spoofing
Considering the potential risks and damages associated with GPS spoofing, it is crucial to protect yourself against this form of cyberattack. This requires a holistic approach that combines technical measures, operational procedures, and awareness programs. Additionally, using reliable internet security tools can provide an extra layer of protection against such threats. These measures can help safeguard your systems’ integrity and ensure the privacy of your data.
Proactive Measures to Prevent GPS Spoofing
Preventing GPS spoofing begins with recognizing the common signs of an attack. These signs may include a sudden GPS location change that doesn’t match your actual physical location or your GPS indicating an improbable speed of movement. Staying alert can aid in promptly identifying and responding to such attacks.
Businesses should contemplate integrating GPS signal authentication, which validates the integrity of GPS signals before receiver processing. This step helps confirm that the received signals originate from satellites and not from a malicious origin. Additional technical countermeasures may involve employing advanced signal processing methods capable of detecting and discarding false signals.
Policy and Legal Perspective on GPS Spoofing
Developing a policy framework to address GPS spoofing is essential. This framework should define the roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders in preventing and responding to GPS spoofing attacks. It should also offer guidelines on how to react when an attack is suspected or detected.
From a legal perspective, it’s crucial to understand that GPS spoofing is illegal in many jurisdictions. Individuals and organizations involved in GPS spoofing may face severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment. Therefore, comprehending and adhering to the legal frameworks governing GPS usage is vital in mitigating GPS spoofing attacks.
Other Considerations in GPS Spoofing
In certain cases, GPS spoofing may have legitimate applications. For instance, researchers might employ GPS spoofing to assess a system’s resilience against such attacks. Nonetheless, it’s essential to recognize that even legitimate uses of GPS spoofing must adhere to ethical guidelines and legal standards.
Furthermore, with technological progress, new GPS spoofing methods and countermeasures are expected to surface. Staying updated on these advancements can significantly assist in preventing and addressing GPS spoofing attacks.
FAQ’s
What is GPS spoofing?
GPS spoofing, also known as GPS simulation, involves tricking a GPS receiver by broadcasting false GPS signals. This manipulation leads the receiver to believe it is in a different location, providing inaccurate location data.
How does GPS spoofing work?
GPS spoofing exploits weaknesses in the GPS infrastructure, particularly the weak signal strength of GPS satellites. By broadcasting stronger counterfeit signals that mimic authentic ones, attackers can deceive GPS receivers into processing false location information.
What are the real-world implications of GPS spoofing?
GPS spoofing can have severe consequences, especially in navigation. It can misdirect ships, aircraft, and vehicles, leading to accidents or operational disruptions. Additionally, it poses significant risks to industries relying on GPS data, such as logistics, transportation, and emergency services.
How does GPS spoofing threaten internet security?
GPS spoofing compromises location data integrity, enabling cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to personal information or commit identity theft. It also poses substantial risks to industries dependent on GPS data, potentially resulting in financial losses and operational disruptions.
What proactive measures can be taken to prevent GPS spoofing?
Recognizing common signs of GPS spoofing, such as sudden location changes or improbable speed indications, is crucial. Implementing GPS signal authentication and advanced signal processing methods can help detect and discard false signals.
What policy and legal considerations are involved in addressing GPS spoofing?
Developing a policy framework defining roles and responsibilities in preventing and responding to GPS spoofing attacks is essential. It’s vital to understand that GPS spoofing is illegal in many jurisdictions, with severe penalties for individuals and organizations involved.
Are there any legitimate uses of GPS spoofing?
In some cases, GPS spoofing may have legitimate applications, such as testing system resilience against attacks. However, even legitimate uses must adhere to ethical guidelines and legal standards.
How can individuals and businesses stay updated on GPS spoofing developments?
Keeping abreast of technological advancements and emerging GPS spoofing methods and countermeasures is crucial for effective prevention and response efforts. Regularly accessing reputable sources of information and staying informed about industry trends can aid in mitigating GPS spoofing risks.
Conclusion
Understanding the threat of GPS spoofing is crucial in today’s digital world. It poses significant risks to internet security and real-world operations. Proactive measures, including recognizing signs of spoofing and implementing authentication measures, are essential. Adhering to legal frameworks and ethical standards is crucial. By adopting a comprehensive approach, we can mitigate the risks posed by GPS spoofing and safeguard our information, systems, and industries.
ad


Comments are closed.