What Is a Video Card?
Are you curious about the inner workings of computers and the essential components that enable stunning graphics and smooth visual experiences? If so, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we will delve into the world of video cards, also known as graphics cards or GPUs (Graphics Processing Units). By understanding the role and importance of video cards in a computer system, you’ll gain insights into their functionalities, benefits, and how they enhance your overall computing experience. So, let’s embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries of video cards and discover why they are indispensable for modern-day gaming, graphic design, and multimedia tasks.
What Is a Video Card?
ad
A video card, also known as a display adapter, graphics card, video adapter, video board, or video controller, is a type of expansion card that connects to the motherboard of a computer. Its principal job is to generate and display images on a display device such as a monitor. The visual content on your screen would be non-existent without a video card. Essentially, it is a critical hardware component within your computer that handles image and video processing, offloading some of the processes often handled by the CPU (central processing unit). Video cards are very popular among gamers because they provide greater processing power and dedicated video RAM, much exceeding the capability of integrated graphics present in most computers.
History Of Video Card
The history of video cards can be traced back to the early 1970s, when the first video chips were developed. These early chips were simple and only capable of displaying text and simple graphics. However, they laid the foundation for the more advanced video cards that we use today.
IBM produced the first two video cards for its PC in the early 1980s: the Monochrome Display Adapter (MDA) and the Color Graphics Adapter (CGA). These cards were simple, but they were an advance over the text-only displays that were typical at the time.
ad
In the mid-1980s, video cards became more advanced. New standards, such as the Enhanced Graphics Adapter (EGA) and the Video Graphics Array (VGA), were established, allowing for better resolutions and more colors. These standards also enabled visuals to be displayed in a variety of formats, including text, graphics, and mixed modes.
Video cards began to see major performance improvements in the late 1980s and early 1990s. The development of new graphics chips, such as the 3dfx Voodoo and the NVIDIA RIVA 128, contributed to this. These chips might accelerate 3D graphics rendering, allowing for substantially better frame rates for playing games and running other 3D applications.
In the 2000s, video cards continued to advance in performance. New standards, such as DirectX and OpenGL, were introduced, allowing for ever more powerful graphical effects. Video cards began to include features like as hardware T&L and pixel shaders, which enhanced performance even further.
Video cards are now an essential part of every gaming PC. They are also utilized in a wide range of other applications, including video editing, 3D modeling, and CAD. Since their inception, video cards have gone a long way, and they continue to advance as new technologies develop.
Here is a timeline of some of the key events in the history of video cards:
- 1974: The first video chip, the Motorola MC6845, is developed.
- 1981: IBM releases the MDA and CGA video cards for its PC.
- 1984: IBM releases the EGA video card.
- 1987: IBM releases the VGA video card.
- 1996: 3dfx releases the Voodoo1 video card.
- 1997: NVIDIA releases the RIVA 128 video card.
- 2000: DirectX 8 is released.
- 2002: OpenGL 1.5 is released.
- 2004: DirectX 9 is released.
- 2006: OpenGL 2.0 is released.
- 2009: DirectX 10 is released.
- 2010: OpenGL 3.0 is released.
- 2014: DirectX 12 is released.
- 2015: OpenGL 4.0 is released.
As you can see, video cards have come a long way since their early days. They have grown in power and sophistication, and they are now a crucial component of every gaming PC.
Overview of a computer video card
Two visual images demonstrating the interior appearance of a video card within a computer are shown below. The first image shows an older generation AGP video card with a wide variety of connections and components. Meanwhile, the second image depicts a modern PCI Express video card, which is commonly used in gaming computers today. These images show the unique design aspects of video cards used in computer systems, representing both previous and present generations.

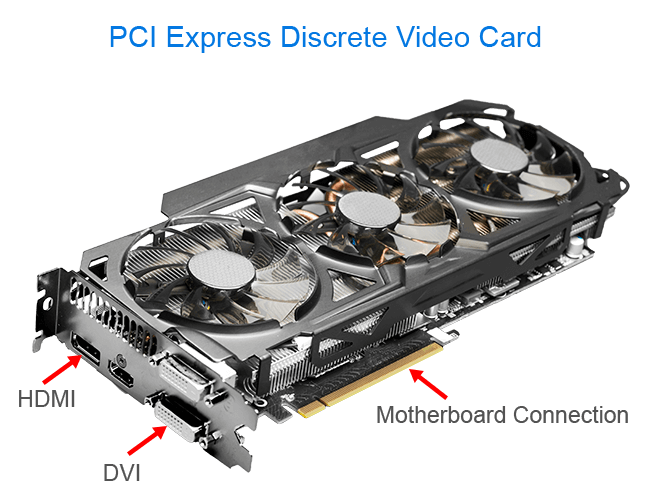
Video Card Ports
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface): DVI is a digital video interface that allows for high-quality video streams. It’s quite frequent on older monitors and video cards. Depending on the type of DVI connector used, DVI ports can carry both analog and digital signals.
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface): HDMI is a digital video and audio interface that is widely utilized. It transmits both video and audio signals in high definition over a single cable. Modern video cards, televisions, and audio-visual equipment all have HDMI ports.
- S-Video: S-Video (Separate Video) is an analog video connection that transmits video signals. It is often used for connecting video cards to older televisions or displays that do not have digital inputs. S-Video ports use a round, multi-pin connector.
- VGA (Video Graphics Adapter): VGA is an analog video connection that has been commonly used for decades. It is distinguished by its blue, trapezoid-shaped connector with 15 pins. VGA ports are typically seen on older video cards and monitors.
- AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): AGP is an earlier type of expansion slot that was created primarily for video cards. When compared to regular PCI slots, it enabled a quicker connection between the video card and the motherboard, allowing for greater graphics performance.
- GPU Heat Sink: The GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is the main chip on a video card that is in responsible for rendering graphics. A heat sink is a cooling device attached to the GPU that dissipates heat created during intensive graphical processing. It helps to keep the GPU cool and assures peak performance.
- Video Memory: VRAM (Video Random Access Memory) is a dedicated memory on the video card used to store and quickly access graphical data. It is critical in games and other graphics-intensive applications for rendering high-quality images and textures.
- Motherboard Connection: The video card is attached to the motherboard via a variety of interfaces, including PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots for current video cards and AGP slots for older ones. Data transfer and communication between the video card and other system components are enabled by the motherboard connection.
How to Install Video Card
Installing a video card in your computer involves a few steps. Here’s a general guide to help you with the process:
Note: The specific steps may vary slightly depending on your computer model and the type of video card you’re installing. Be sure to consult the user manual or documentation provided with your video card for any specific instructions.
1. Preparation:
- Turn off your computer and unplug it from the power source.
- Open the computer case by removing the side panel. This may involve unscrewing screws or sliding a latch, depending on your computer case design.
2. Check Compatibility:
- Ensure that the video card you’re installing is compatible with your computer’s motherboard and power supply. Check the card’s interface (e.g., PCIe), power requirements, and physical dimensions to ensure a proper fit.
3. Remove Existing Video Card (if applicable):
- If your computer already has a video card installed, you may need to remove it. Start by disconnecting any power cables or video output cables attached to the card.
- Unscrew any screws holding the card in place on the rear side of the case.
- Gently remove the card from its slot by pulling it straight out. Be careful not to apply excessive force or damage any components.
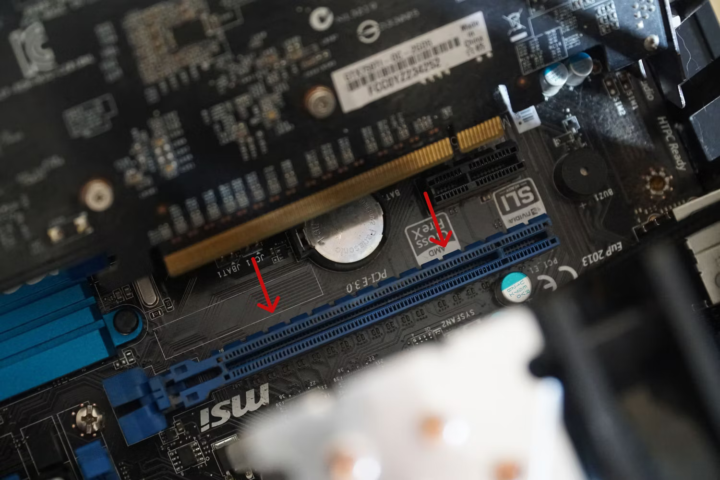
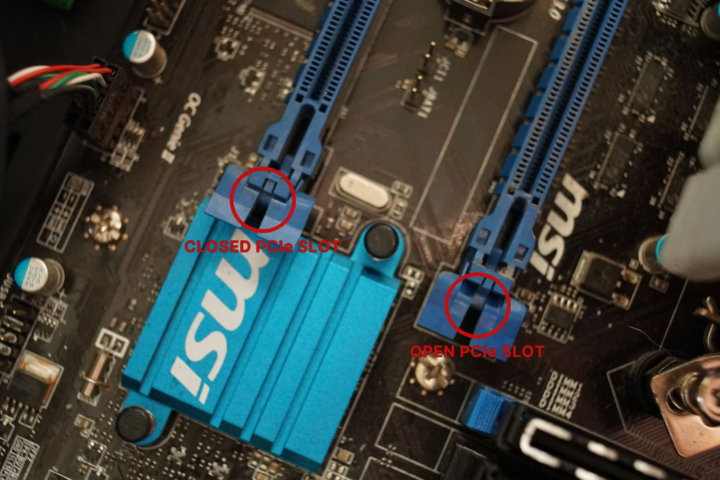
4. Prepare the PCIe Slot:
- Identify an available PCIe slot on your motherboard where you’ll install the new video card. PCIe slots are typically longer and have a locking mechanism at the end.
- To prepare the slot, unlock the retention clip or screw on the PCIe slot by pressing it or unscrewing it, depending on the design. This will open the slot and allow you to insert the video card.
5. Insert the Video Card:
- Hold the video card by its edges and align the connector at the bottom of the card with the PCIe slot on the motherboard.
- Gently but firmly insert the video card into the slot, ensuring it is fully seated. Apply even pressure, but do not force it.
- Once the video card is inserted correctly, you should hear a clicking sound as it locks into place.
6. Secure the Video Card:
- Use screws or retention clips to secure the video card to the computer case. These screws or clips will help hold the card in place and prevent any movement.
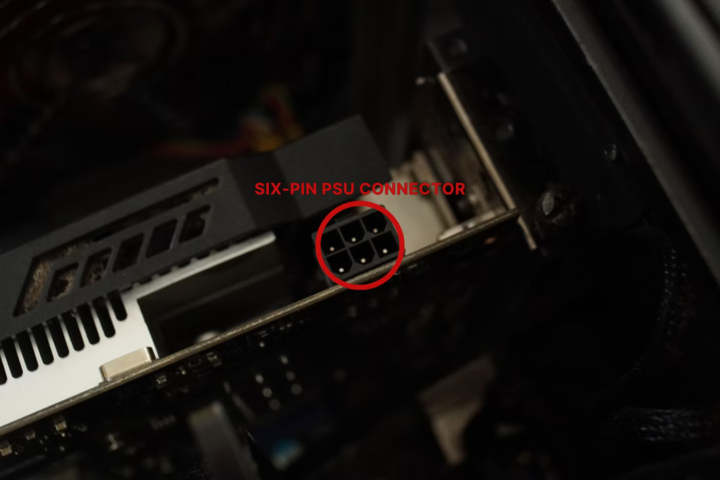
7. Connect Power:
- If your video card requires additional power beyond what the PCIe slot provides, connect the appropriate power cables from your power supply to the connectors on the video card. These connectors are typically located on the side or top of the card.
8. Connect Display:
- Attach your display cable (HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, etc.) from the video card’s output ports to the corresponding input port on your monitor or display device.
9. Close the Case:
- Double-check that all connections are secure and properly seated.
- Put the computer case’s side panel back on and secure it with screws or latches.
10. Power On and Install Drivers:
- Plug in your computer and turn it on.
- Once the operating system loads, install the necessary drivers for your video card. These drivers can typically be downloaded from the manufacturer’s website. Follow the installation instructions provided with the drivers to complete the process.
FAQ’s
Do I need to uninstall the drivers of my old video card before installing a new one?
It is normally suggested that you uninstall the drivers for your old video card before installing a new one. This helps to avoid any conflicts or complications with the new card. You can uninstall the drivers using the Device Manager (in Windows) or the relevant software provided by the card’s manufacturer.
How do I know if my power supply is sufficient for the new video card?
Check the power requirements provided by the new video card’s manufacturer. Compare these needs to the specifications of your power supply unit (PSU), especially the wattage and power connectors available. If your power supply meets or exceeds the recommended specifications, it should be adequate. Otherwise, your power supply may need to be upgraded.
Can I install multiple video cards in my computer?
Yes, you can install several video cards in a computer if your motherboard supports multi-GPU configurations and your power supply can manage the extra power demands. This enables technologies such as NVIDIA SLI or AMD CrossFire, in which two or more video cards collaborate to improve graphics performance. However, for multi-GPU installations, it’s critical to confirm compatibility and follow particular installation instructions.
How do I choose the right video card for my needs?
Consider your planned usage (gaming, graphic design, video editing), budget, power supply capacity, and compatibility with your motherboard and display when selecting the correct video card. You may make an informed decision by researching and comparing specifications, performance benchmarks, and customer reviews.
What is the purpose of a video card/graphics card?
A video card, often known as a graphics card, is in responsible for generating and rendering images, videos, and graphics on a computer display. It relieves the CPU of graphical processing responsibilities, allowing for smoother and more efficient rendering of graphics-intensive programs.
What factors should I consider when choosing a video card?
When selecting a video card, you should consider factors such as the desired usage (gaming, video editing, etc.), compatibility with your computer’s motherboard and power supply, performance benchmarks, available video ports, and budget.
Conclusion
A video card is an essential component that allows images, movies, and graphics to be rendered on a computer display. It makes use of the GPU’s processing ability to conduct complex calculations and improve graphical speed. Choosing the appropriate video card is critical for best visual experiences, whether you’re a gamer, a multimedia fan, or a professional content creation. Keep up with video card technological improvements to ensure top-tier visuals and performance for your computer demands.
ad






Comments are closed.