What is an SD-WAN?
A wide area network (WAN) is a network that links local area networks (LANs) across extensive distances. Large organizations often utilize WANs to connect their various branch offices and locations to the central corporate network. In traditional WANs, the software controlling network traffic is closely integrated with the hardware directing the traffic, typically purchased from a single networking vendor.
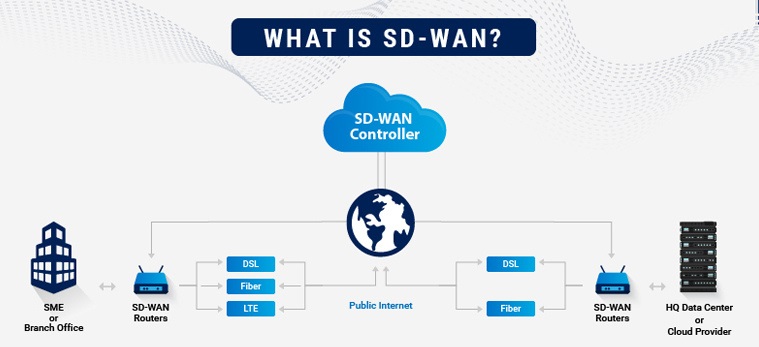
A software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) offers a more flexible architecture, capable of leveraging multiple hardware platforms and connectivity options. The controlling software is compatible with any networking hardware, allowing organizations to establish an SD-WAN using off-the-shelf hardware instead of specialized equipment. This makes SD-WANs more cost-effective, flexible, and scalable than traditional WANs.
ad
Think of the difference between a desktop computer running a proprietary operating system and one running an operating system compatible with various computers, like Linux. In the former, software and hardware are tightly integrated, requiring a bundled purchase. Conversely, Linux operating systems can run on various desktop computers from different vendors. Those opting for a Linux-operated computer have a wide range of choices, from affordable models to high-end gaming computers, or they can build their own computer using off-the-shelf hardware components.
Although the considerations for desktop computers differ from those for traditional WANs versus SD-WANs, a similar principle applies: like Linux operating systems, SD-WAN software is independent of the underlying hardware, providing organizations with more options for choosing their hardware.
How do SD-WANs work?
ad
The feasibility of SD-WANs is achieved through the separation of the control plane from the data plane. In networking, the control plane encompasses all components that dictate the path of data. The data plane, on the other hand, transmits data in accordance with the instructions provided by the control plane.
Traditionally, the control plane and the data plane were closely intertwined through vendor-specific hardware appliances. SD-WANs, however, decouple the control plane, which is software-based, from the data plane, which is hardware-based. This separation allows routing to be executed in software running on generic hardware rather than on specialized hardware routers.
What are some of the advantages of using an SD-WAN?
- Flexibility: SD-WANs have the capability to employ various routing approaches, including legacy methods utilized by traditional WANs. The provisioning of SD-WANs is more straightforward, as organizations can acquire commodity hardware as needed, eliminating the reliance on a single networking vendor.
- Cost savings: By avoiding the necessity to procure both software and hardware from a single vendor, organizations can opt for more affordable hardware with lower maintenance costs. Furthermore, SD-WANs have the flexibility to utilize standard Internet connections instead of the pricier multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) connections.
- Scalability: SD-WANs exhibit easy scalability to accommodate fluctuations in business requirements. The utilization of regular Internet connections simplifies the process of adding or removing sites and expanding bandwidth.
What is software-defined networking (SDN)?
Software-defined networking (SDN) refers to a set of technologies that enable the management of a network and the adjustment of network topology using software. SD-WANs represent an application of SDN principles. It’s important to clarify that while all SD-WANs incorporate SDN, not all networks built with SDN can be classified as SD-WANs.
SD-WAN vs. network-as-a-service (NaaS)
Network-as-a-service (NaaS) is a framework where organizations acquire networking services from a cloud provider instead of configuring their own network.
In the NaaS model, an organization only needs Internet connectivity to set up and utilize its internal network. Depending on the service configuration, NaaS may deliver greater flexibility and cost savings, similar to how other cloud service models like SaaS and IaaS outperform traditional on-premise computing.
How SD-WAN Helps Today’s IoT
SD-WAN is reshaping network architectures and plays a vital role in the expanding Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. SD-WAN contributes to the benefits of IoT in the following ways:
- Enhanced Performance: SD-WAN employs a centralized control function to intelligently direct traffic across the WAN.
- Improved Security: SD-WAN enhances security by segmenting the network.
- Scalability: As businesses deploy more IoT devices, SD-WAN easily accommodates increased traffic and additional devices.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Businesses can utilize a combination of network services (such as MPLS, 4G/5G, or broadband) based on their needs with SD-WAN.
- Simplified Management: SD-WAN simplifies the task of network management.
- Quality of Service (QoS): SD-WAN allows for the implementation of policies to prioritize specific types of traffic over others.
- Enhanced Visibility: SD-WAN provides improved visibility into network performance and traffic patterns.
SD-WAN offers a flexible, scalable, and secure solution for handling the heightened network traffic and complexity associated with IoT. By enhancing performance and visibility while reducing costs, SD-WAN proves to be an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to harness the potential of IoT.
SD-WAN and Zero Trust
The utilization of multiple connectivity methods in an SD-WAN introduces the possibility of traffic following paths that traditional security measures, assuming placement at the network edge to defend the perimeter, may not have anticipated. SD-WAN implementations can also expand the attack surface by employing a broader range of hardware and various types of connections.
Due to these factors, conventional security measures may prove inadequate in safeguarding SD-WANs against potential attacks. In contrast, Zero Trust security is specifically designed to validate legitimate traffic and block malicious traffic irrespective of its source. Zero Trust security mandates rigorous identity verification for any entity attempting to access resources on a private network, whether located inside or outside the network perimeter. While conventional IT network security tends to trust anything within the network, a Zero Trust architecture inherently trusts no one.
Integration of SD-WAN and Zero Trust is often preferable for organizations seeking a balance between flexible connectivity and stringent security. Ideally, an SD-WAN provider should inherently incorporate Zero Trust security measures, eliminating the need to combine two distinct solutions.
FAQ’s
What makes SD-WANs different from traditional WANs, and how do they work?
SD-WANs stand out by offering a more flexible architecture that separates the control plane from the data plane. This separation allows for routing in software on generic hardware, providing greater flexibility and scalability compared to traditional WANs.
How does SDN play a role in SD-WANs?
Software-defined networking (SDN) is the foundation of SD-WANs. SDN enables the separation of the control plane and the data plane, allowing for more efficient management and adjustment of network topology through software.
What distinguishes SD-WAN from Network-as-a-Service (NaaS)?
NaaS involves acquiring networking services from a cloud provider, while SD-WAN is a specific network architecture. NaaS relies on internet connectivity, providing flexibility and cost savings similar to other cloud service models, but it differs in its approach to network configuration.
How does SD-WAN contribute to the Internet of Things (IoT)?
SD-WAN plays a vital role in the IoT ecosystem by offering enhanced performance, improved security through network segmentation, scalability to accommodate increasing IoT devices, and cost-effectiveness by allowing the use of various network services.
Why is the integration of SD-WAN and Zero Trust security essential?
SD-WAN introduces the potential for traffic paths not anticipated by traditional security measures. Integrating Zero Trust security, which verifies traffic legitimacy and blocks malicious traffic, is crucial. This integration provides a balance between flexible connectivity and stringent security, ensuring a robust defense against potential attacks. Ideally, SD-WAN providers should include native Zero Trust security measures for a seamless and secure solution.
Conclusion
SD-WAN represents a transformative leap from traditional WANs, offering unmatched flexibility and cost-effectiveness. The parallel to user choices in desktop computing underscores its adaptability. In navigating the IoT landscape, SD-WAN proves crucial for enhancing performance and security. The integration with Zero Trust security ensures a robust defense against evolving cyber threats. Embracing SD-WAN signals not just a departure from traditional constraints but a new era of efficiency and innovation in enterprise connectivity.
ad


Comments are closed.