What is Virtual Network Computing (VNC)?
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) represents a groundbreaking technology transforming how we remotely access and manage computers. This innovation enables seamless connections and control over computers globally, contingent upon an internet connection.
The capacity to remotely handle computers has significantly impacted businesses, empowering them to offer technical assistance and resolve problems without requiring physical presence at the site. Furthermore, VNC has broadened horizons for remote collaboration, facilitating teams to collaborate on projects despite geographical disparities. This piece aims to extensively explore the realm of Virtual Network Computing, encompassing its history, technological aspects, and diverse applications.
ad
What is Virtual Network Computing (VNC)?
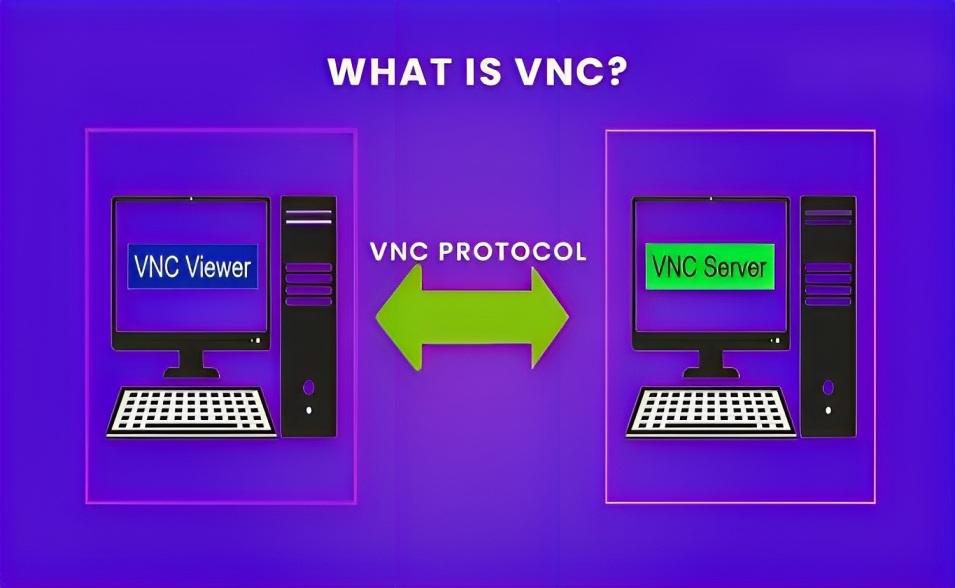
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a technology that allows remote access and control of a computer across a network. It establishes a graphical desktop sharing system that empowers users to remotely access and manage a computer’s desktop environment, making it well-suited for remote technical support, collaborative endeavors, and related tasks.
The VNC technology follows a client-server model, with the VNC server operating on the remote computer, and the VNC viewer functioning on the local computer. The server captures the desktop environment and transmits it over the network to the viewer, which then renders the desktop environment on the local machine. The viewer subsequently relays the user’s inputs to the server for processing.
ad
Originally developed by the British company Olivetti Research Laboratory in the late 1990s, VNC is currently under the maintenance and expansion by RealVNC Ltd. and the open-source community. It has gained popularity as a tool for remote administration, enabling users to oversee computers and servers from a distant location.
What is a Virtual Network Computing port?
A Virtual Network Computing (VNC) port serves as the gateway for VNC servers and clients to establish connections across a network. In computer networking, a port denotes a communication endpoint identified by a number. This number is utilized by networking protocols to direct traffic to the appropriate destination.
By default, VNC servers operate on TCP port 5900, enabling VNC viewers to connect to the server through this port. Nevertheless, the VNC protocol allows for multiple ports, facilitating concurrent sessions for various users to access and control either the same or different desktop environments simultaneously.
Beyond the default port 5900, VNC servers can also operate on other ports within the range of 5800 to 5899. These ports are specifically designed for VNC connections over the HTTP protocol. This functionality proves valuable in environments permitting only HTTP traffic, such as in scenarios involving a web proxy or firewall.
Furthermore, the VNC protocol supports the encryption of VNC traffic via a secure iteration of the protocol known as VNC over Secure Shell (VNC over SSH). This secure protocol utilizes port 22, the standard SSH port, to establish a secure connection between the VNC server and client.
Which protocol does Virtual Network Computing use?
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) operates through its unique, proprietary protocol facilitating communication between the VNC server and viewer. This protocol, streamlined and lightweight, facilitates the transmission of graphical desktop environments and user inputs across a network.
Designed to be platform-agnostic, the VNC protocol enables access and control of computers running on various operating systems like Windows, macOS, Linux, and others. Its extensibility allows developers to integrate additional features and functionalities as required.
Positioned at the application layer within the TCP/IP protocol stack, the VNC protocol utilizes TCP as its fundamental transport protocol. It functions on a client-server model: the VNC server software resides on the computer being remotely accessed, while the VNC viewer software operates on the local computer used to access the remote system.
In a VNC session’s initiation, the VNC server captures the remote computer’s desktop environment, transmitting it to the viewer over the network. The viewer software then displays the desktop environment on the local screen, enabling the user to interact with the remote system as if physically present.
Moreover, the VNC protocol allows the transmission of user inputs (such as keyboard and mouse events) from the viewer back to the server. These inputs are processed by the remote computer, enabling users to control the remote system from their local machine.
Advantages of Virtual Network Computing
Virtual Network Computing offers various benefits for remote computer access and control, encompassing:
- Accessibility and control of a computer from any global location with an internet connection.
- Compatibility across different operating systems supporting VNC, like Windows, Linux, macOS, and others.
- Efficiency in low bandwidth situations, making it suitable for use over sluggish or unstable network connections.
- Simultaneous desktop environment sharing among multiple users, enabling collaborative efforts and remote technical support.
- Secure communication via encryption, safeguarding the confidentiality of sensitive information transmitted over the network.
How does Virtual Network Computing work?
VNC follows a client-server model, with the VNC server software running on the computer being accessed remotely, and the VNC viewer software running on the computer used to access the remote system.
In the initiation of a VNC session, the VNC server captures the remote computer’s desktop environment and transmits it through the network to the viewer. The viewer software then renders the remote desktop environment on the local computer screen, enabling the user to interact with the remote system as if they were physically present in front of it.
Furthermore, the VNC protocol facilitates the transmission of user inputs, encompassing keyboard and mouse events, from the viewer back to the server. These inputs are subsequently processed by the remote computer, permitting the user to control the remote system from their local machine.
Best Virtual Network Computing software alternatives
Although Virtual Network Computing is a robust tool for remote computer access and control, there exist numerous alternative solutions offering comparable functionalities. Here are some of the most widely used alternatives to VNC:
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
The Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), developed by Microsoft, enables users to remotely access and control a Windows desktop environment. It’s an integral part of Windows and is available across most Windows operating system versions. RDP offers a more seamless remote desktop experience compared to VNC, providing better performance and advanced features like support for multiple monitors and remote audio playback.
TeamViewer
TeamViewer is a popular solution for remote access and support, providing a wide range of features. It works on Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices, allowing users to remotely access and control computers and devices over the internet. Notable features of TeamViewer include file transfer, remote printing, and session recording.
LogMeIn
LogMeIn serves as a solution for remote access and support, offering a variety of features and functionality. Accessible on Windows, macOS, and mobile devices, it enables the remote access and control of computers and devices via the internet. LogMeIn includes advanced functionalities like remote printing, remote wake-on-LAN, and session recording.
AnyDesk
AnyDesk is a swift and lightweight remote desktop solution that ensures top-notch video and audio transmission over the internet. It’s compatible with Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices, allowing remote access and control of computers and devices. AnyDesk presents advanced capabilities like file transfer, remote printing, and session recording.
Splashtop
Splashtop stands as a remote access and support solution, delivering rapid and secure remote access to computers and devices. Accessible across Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices, it presents advanced features such as file transfer, remote printing, and session recording. Additionally, Splashtop offers support for accessing computers with multiple monitors, along with remote wake-on-LAN and session recording. Its high performance and security features make Splashtop a favored option for businesses and professionals needing swift and dependable remote access to their computers and devices.
Several VNC alternatives offer similar functionality, each presenting distinct features and advantages. The selection of a remote access solution hinges on your individual needs and specific requirements.
FAQ’s
What exactly is Virtual Network Computing (VNC)?
VNC, short for Virtual Network Computing, is a technology that allows remote access and control of a computer over a network. It establishes a system where users can access and manage a computer’s desktop remotely, enabling tasks like technical support and collaborative work.
How does VNC operate?
VNC follows a client-server model. The VNC server, situated on the remote computer, captures the desktop environment and sends it to the VNC viewer located on the local machine. The viewer displays this desktop environment, allowing users to interact with the remote system. Moreover, user inputs from the viewer are sent back to the server for remote control.
What advantages does VNC offer for remote computer access and control?
VNC offers various advantages, including access from anywhere with an internet connection, compatibility with different operating systems, functionality in low bandwidth situations, collaborative desktop sharing for multiple users, and secure communication through encryption.
What are some popular alternatives to VNC for remote access?
There are several widely used alternatives to VNC, including Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), TeamViewer, AnyDesk, LogMeIn, and Splashtop. Each alternative provides unique features and functionalities catering to diverse user needs.
How does VNC ensure secure communication?
VNC supports encryption for secure data transmission over the network. Additionally, it offers a secure protocol known as VNC over Secure Shell (VNC over SSH) that utilizes port 22 to establish a secure connection between the VNC server and client.
Conclusion
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) revolutionizes remote computer access, empowering businesses with remote technical support and fostering collaboration among geographically dispersed teams. Evolving since the late 1990s, VNC remains a cornerstone in remote administration due to its secure, adaptable, and platform-agnostic nature. Its numerous alternatives underscore the diverse user needs it caters to, solidifying VNC’s position as a pioneering technology for remote system control.
ad


Comments are closed.