What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)?
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) stands as an innovative technology employing virtual machines for the management and provision of virtual desktops. Instead of being limited to a specific physical device, a virtual desktop represents a preconfigured image of an operating system, and its applications are accessible from any compatible device. Through VDI, desktop environments can be centralized on a server and delivered to end-users as needed. Microsoft’s Azure Virtual Desktop is among the widely used Desktop as a Service (DaaS) offerings, featuring Windows 10 VDI multi-session to efficiently scale with numerous users on a smaller set of virtual machines. Windows VDI, a cloud-based desktop and app virtualization service, delivers a multi-user Windows 10 experience. In essence, VDI empowers organizations to deploy Windows virtual machines accessible from any location and at any time, making it an optimal solution for remote workers.
ad
How does Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) work?
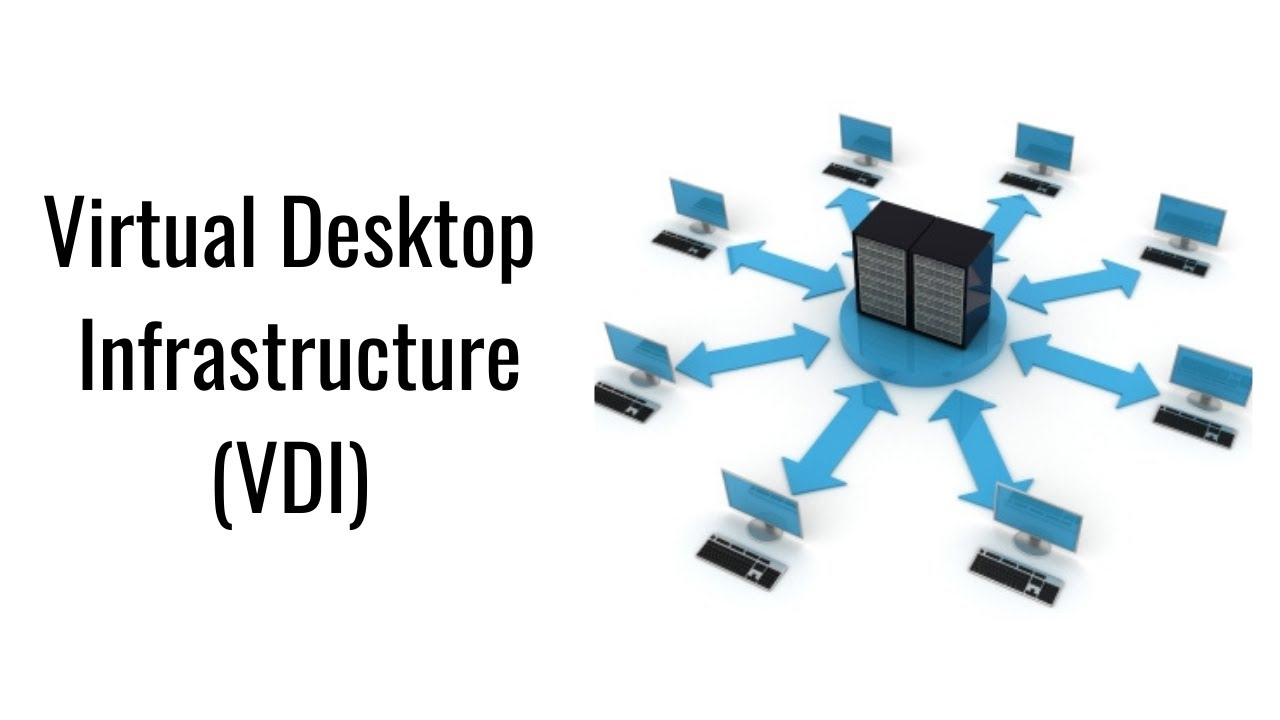
In the context of VDI, a hypervisor divides servers into virtual machines, which then act as hosts for virtual desktops accessible to users remotely from their devices. These virtual desktops are available from any location or device, and all processing takes place on the host server. Users connect to their desktop instances through a connection broker, a software-based gateway that serves as an intermediary between the user and the server.
Persistent VDI vs Non-persistent VDI
VDI comes in two forms: persistent and non-persistent, each offering distinct advantages:
ad
Persistent VDI involves users connecting to the same desktop consistently. In this setup, users can personalize their desktops, as changes are retained even after the connection is reset. Essentially, desktops in a persistent VDI environment mimic personalized physical desktops.
On the other hand, non-persistent VDI entails users connecting to generic desktops where no changes are preserved. This approach is typically more straightforward and cost-effective, as there’s no requirement to maintain customized desktops between sessions. Non-persistent VDI is commonly adopted in organizations with numerous task-oriented workers or employees engaged in a limited set of repetitive tasks, where a personalized desktop is unnecessary.
Why VDI?
VDI provides several benefits, including user mobility, easy accessibility, flexibility, and enhanced security. Historically, its demanding performance criteria made deployment expensive and challenging on older systems, creating a hurdle for many businesses. Nevertheless, the increasing adoption of hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) in the enterprise sector presents a solution that delivers scalability and high performance at a reduced cost.
Benefits of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
While VDI’s intricacy may not make it the optimal choice for every organization, it does offer numerous advantages for those that opt for its implementation. Some of these benefits include:
- Remote Access: VDI users have the flexibility to connect to their virtual desktops from any location or device, facilitating easy access to files and applications. This feature enables employees to work remotely from anywhere globally.
- Cost Savings: As processing occurs on the server, the hardware requirements for end devices are significantly reduced. Users can access their virtual desktops from older devices, thin clients, or even tablets, minimizing the necessity for IT to invest in new and costly hardware.
- Security: In a VDI environment, data resides on the server rather than the end client device. This setup serves as a safeguard for data in the event of an endpoint device being stolen or compromised.
- Centralized Management: VDI’s centralized structure allows IT to efficiently patch, update, or configure all virtual desktops in the system. This centralized management enhances the ease of maintenance for IT administrators.
What is VDI used for?
Even though VDI is applicable in diverse environments, there are specific use cases that align uniquely with VDI, including:
- Remote Work: VDI’s capability to deploy and update virtual desktops seamlessly from a centralized location makes it increasingly popular for companies with remote workers.
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD): VDI serves as an optimal solution for environments permitting or mandating employees to use their personal devices. With processing centralized on a server, VDI accommodates a broader range of devices and enhances security by storing data on the server rather than the end client device.
- Task or Shift Work: Nonpersistent VDI proves especially well-suited for organizations like call centers, where a substantial number of employees perform specific tasks using the same software. This facilitates efficient management and deployment of virtual desktops in a dynamic work environment.
Difference between VDI and Desktop Virtualization
Desktop virtualization is a broad concept encompassing any technology that severs the connection between a desktop environment and the hardware utilized to reach it. While VDI represents a form of desktop virtualization, there are alternative implementations such as remote desktop services (RDS). In RDS, users establish connections to a communal desktop operating on a remote server.
Difference between VDI and Virtual Machines (VMs)
The technology propelling VDI is virtual machines (VMs). VMs are software-based “machines” formed by dividing a physical server into numerous virtual servers using a hypervisor, a process commonly referred to as server virtualization. Virtual machines find applications in various scenarios, one of which involves running a virtual desktop within a VDI environment.
How to implement Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)?
In strategizing for the deployment of VDI, larger enterprises should contemplate implementing it within an HCI environment, given that HCI’s scalability and superior performance align seamlessly with VDI’s resource demands. Conversely, for organizations requiring fewer than 100 virtual desktops, incorporating HCI for VDI might not be necessary and could prove excessively costly.
In addition to infrastructure considerations, several best practices should be observed when implementing VDI:
- Prepare Your Network: Given the close correlation between VDI performance and network performance, understanding peak usage times and anticipating demand spikes is crucial to ensure ample network capacity.
- Avoid Underprovisioning: Engage in capacity planning beforehand, employing a performance monitoring tool to comprehend the resource consumption of each virtual desktop and ensuring a comprehensive understanding of overall resource needs.
- Understand Your End-Users’ Needs: Determine whether your users require the ability to customize their desktops or if they are task-oriented workers comfortable with a generic desktop. Assess your users’ performance requirements, provisioning the setup differently for those using graphics-intensive applications compared to those requiring internet access or a couple of simple applications.
- Perform a Pilot Test: Utilize testing tools offered by most virtualization providers to conduct a preliminary VDI deployment test. This step is crucial to verifying that resources have been provisioned accurately.
FAQ’s
How does VDI work?
In VDI, a hypervisor divides servers into virtual machines, acting as hosts for virtual desktops accessible remotely. Users connect to their desktop instances through a connection broker, a software-based gateway serving as an intermediary between the user and the server.
What are the differences between Persistent and Non-persistent VDI?
Persistent VDI allows users to connect consistently to the same desktop, retaining personalization even after resetting. Non-persistent VDI involves users connecting to generic desktops with no changes preserved, proving more cost-effective for task-oriented workers.
What are the benefits of VDI?
VDI offers advantages such as user mobility, easy accessibility, flexibility, enhanced security, cost savings, and centralized management. It facilitates remote access, reduces hardware requirements, enhances security, and allows efficient management of virtual desktops.
How is VDI used in specific scenarios?
VDI is employed for remote work, enabling the deployment of virtual desktops for companies with remote workers. It’s also suitable for BYOD environments and task-oriented scenarios, where non-persistent VDI is efficient for organizations with employees performing specific tasks.
What is the difference between VDI and Desktop Virtualization?
Desktop virtualization severs the connection between a desktop environment and hardware. VDI is a form of desktop virtualization, allowing remote access to virtual desktops. Desktop virtualization includes alternatives like remote desktop services (RDS), connecting users to a shared desktop on a remote server.
How is VDI different from Virtual Machines (VMs)?
VDI relies on virtual machines (VMs) created by dividing a physical server. While VDI focuses on virtual desktops, VMs find applications in various scenarios, including running a virtual desktop within a VDI environment.
How to implement VDI effectively?
For larger enterprises, implementing VDI within a hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) environment is recommended for scalability and high performance. Considerations should include network preparation, capacity planning, understanding end-users’ needs, and conducting a pilot test for accurate resource provisioning.
Conclusion
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) stands out as a transformative solution, using virtual machines for efficient desktop management. With benefits like enhanced security and centralized management, VDI, exemplified by Microsoft’s Azure Virtual Desktop, meets the evolving needs of remote work. The integration of hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) enhances scalability, making VDI a valuable asset for modern workplaces.
ad


Comments are closed.