What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)?
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a network security technology designed to identify vulnerability exploits against a target application or computer.
The IDS functions as a passive device, solely observing and analyzing traffic, and subsequently relaying the findings to an administrator. It lacks the capability to autonomously intervene to thwart a detected exploit from seizing control of the system.
ad
Upon infiltrating the network, attackers possess the ability to swiftly exploit vulnerabilities. Consequently, the IDS alone is insufficient for preventive measures. Both intrusion detection and intrusion prevention systems play integral roles in security information and event management.
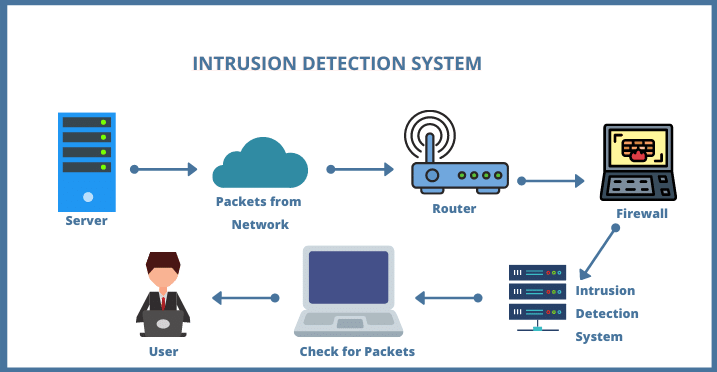
How Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Works
An IDS’s primary function is to identify potential threats, and it is positioned out of band on the network infrastructure. Consequently, it does not reside in the real-time communication path between the sender and receiver of information.
ad
IDS solutions commonly utilize a TAP or SPAN port to analyze a duplicate of the inline traffic stream. This approach ensures that the IDS does not adversely affect inline network performance.
During the development of IDS, the necessary depth of analysis to detect intrusions couldn’t be executed rapidly enough to keep pace with components on the direct communications path of the network infrastructure.
Network intrusion detection systems serve the purpose of identifying suspicious activity to intercept hackers before causing harm to the network. Two types of IDS are network-based and host-based, with host-based IDSes installed on client computers and network-based IDSes positioned on the network itself.
An IDS operates by identifying deviations from normal activity and recognized attack signatures. Anomalous patterns are transmitted up the stack and scrutinized at the protocol and application layers. It can identify events such as DNS poisonings, malformed information packets, and Christmas tree scans.
Implementation of an IDS can take the form of a network security device or a software application. For safeguarding data and systems in cloud environments, cloud-based IDSes are also available.
Types of IDS Detection
There are five types of IDS: network-based, host-based, protocol-based, application protocol-based, and hybrid.
Network-based intrusion detection system (NIDS)
NIDS monitors an entire protected network, strategically placed at key points like the most vulnerable subnets. It examines all traffic to and from devices on the network, making assessments based on packet contents and metadata.
Host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS)
HIDS oversees the computer infrastructure on which it is installed, deployed on a specific endpoint to protect against internal and external threats. It accomplishes this by analyzing traffic, logging malicious activity, and notifying designated authorities.
Protocol-based (PIDS)
A protocol-based intrusion detection system is usually installed on a web server, monitoring and analyzing the protocol between a user/device and the server. Typically positioned at the front end of a server, it monitors the behavior and state of the protocol.
Application protocol-based (APIDS)
An APIDS is a system or agent usually located inside the server. It tracks and interprets correspondence on application-specific protocols, for instance, monitoring the SQL protocol to the middleware while transacting with the web server.
Hybrid intrusion detection system
A hybrid intrusion detection system combines two or more intrusion detection approaches, utilizing system or host agent data along with network information for a comprehensive system view. It is more potent compared to other systems, with Prelude serving as an example.
Signature-based
A signature-based IDS scrutinizes inbound network traffic, searching for specific patterns and sequences that match known attack signatures. While effective for this purpose, it cannot detect unidentified attacks with no known patterns.
Anomaly-based
The anomaly-based IDS is a relatively newer technology designed to detect unknown attacks, going beyond the identification of attack signatures. This type of detection uses machine learning to analyze large amounts of network data and traffic, creating a defined model of normal activity to identify anomalous behavior. However, it is prone to false positives, such as flagging rare but healthy behavior as an anomaly, resulting in false alarms.
IDS vs. Firewalls
IDses and Next-Generation Firewalls serve as network security solutions. The key distinction between an IDS and a firewall lies in their respective purposes.
An IDS device adopts a passive monitoring approach, documenting a suspected threat after it has occurred and triggering an alert. The IDS observes network packets in transit, enabling incident response to assess the threat and take appropriate action. However, it does not provide protection for the endpoint or network.
In contrast, a firewall employs an active monitoring strategy, proactively searching for threats to prevent them from escalating into incidents. Firewalls possess the capability to filter and block traffic, allowing or denying it based on preconfigured rules that consider ports, destination addresses, and the source.
Firewalls reject traffic that fails to comply with established rules. Nonetheless, if an attack originates from within the network, the IDS will not generate an alert.
📚 Also Read: IDS Vs IPS
IDS Evasion Techniques
There exist various techniques that intruders may employ to elude detection by IDS. These methods pose challenges for IDS systems, as they are designed to bypass current detection mechanisms:
Fragmentation
- Fragmentation involves breaking a packet into smaller, fragmented packets, allowing intruders to remain unnoticed due to the absence of an attack signature.
- The recipient node reconstructs fragmented packets at the IP layer, forwarding them to the application layer. Fragmentation attacks generate malicious packets by replacing data in constituent fragmented packets with new data.
Flooding
- This attack aims to overwhelm the detector, causing a failure in the control mechanism. Once the detector fails, all traffic is permitted.
- A common method for causing flooding is by spoofing the legitimate User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). The resulting traffic flooding serves to camouflage the perpetrator’s anomalous activities, making it challenging for the IDS to identify malicious packets amid the overwhelming volume of traffic.
Obfuscation
- Obfuscation aims to avoid detection by rendering a message difficult to understand, effectively concealing an attack. The term refers to altering program code to maintain functional indistinguishability.
- The goal is to reduce detectability in the reverse engineering or static analysis process by obscuring and compromising readability. For instance, obfuscating malware enables it to evade IDS.
Encryption
- While encryption provides multiple security capabilities such as data confidentiality, integrity, and privacy, malware creators exploit these attributes to conceal attacks and evade detection.
- For example, an attack on an encrypted protocol remains unreadable by an IDS. When the IDS cannot match encrypted traffic to existing database signatures, the encrypted traffic goes undetected, making it highly challenging for detectors to identify attacks.
Why Intrusion Detection Systems are Important
The complexity and sophistication of cyberattacks are continually on the rise, with Zero Day Attacks being commonplace. Consequently, network protection technologies must evolve to address emerging threats, and businesses need to maintain elevated levels of security.
The primary goal is to ensure secure and trusted communication of information. Therefore, an IDS holds significance in the security ecosystem, serving as a defense for systems security in instances where other technologies fall short.
Key functions of an IDS include:
- Identifying security incidents.
- Analyzing the quantity and types of attacks.
- Aiding in the identification of bugs or problems with device configurations.
- Supporting regulatory compliance through enhanced network visibility and documentation of IDS logs.
- Enhancing security responses by inspecting data within network packets, eliminating the need for manual system censuses.
While IDSes are beneficial, their impact is heightened when combined with IPSes (Intrusion Prevention Systems), which add the capability to block threats. This combination has emerged as the predominant deployment option for IDS/IPS technologies.
An even more effective strategy involves integrating multiple threat prevention technologies to create a comprehensive solution. This includes:
- Vulnerability protection
- Anti-malware
- Anti-spyware
Together, these technologies form advanced threat protection. The service scans all traffic for threats, encompassing ports, protocols, and encrypted traffic. Advanced threat prevention solutions go beyond just detecting threats upon entering the network; they actively seek out threats throughout the entire cyberattack lifecycle. This layered defense approach aligns with a Zero Trust model, emphasizing prevention at all points.
FAQ’s
What is the main purpose of an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)?
An IDS is designed to identify vulnerability exploits against a target application or computer within a network.
How does an IDS operate within the network infrastructure?
An IDS functions as a passive device, observing and analyzing traffic, and then relaying its findings to an administrator. It lacks the capability to autonomously intervene.
Why is intrusion prevention essential alongside intrusion detection?
IDS alone is insufficient for preventive measures, as attackers can exploit vulnerabilities rapidly. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively block threats.
What are the different types of IDS?
There are five types of IDS: network-based, host-based, protocol-based, application protocol-based, and hybrid.
Can you explain the role of a Network-based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)?
NIDS monitors the entire network, strategically placed at key points, assessing traffic to and from devices based on packet contents and metadata.
How does a Hybrid Intrusion Detection System function?
A hybrid IDS combines two or more intrusion detection approaches, utilizing system or host agent data along with network information for a comprehensive system view.
What distinguishes Signature-based from Anomaly-based IDS?
Signature-based IDS looks for specific patterns matching known attack signatures, while Anomaly-based IDS uses machine learning to detect unknown attacks based on anomalous behavior.
In what ways does an IDS contribute to security incident response?
An IDS identifies security incidents, analyzes attack types and quantities, aids in identifying bugs or device configuration issues, and supports regulatory compliance through enhanced network visibility.
What evasion techniques do intruders use against IDS?
Intruders may use techniques such as fragmentation, flooding, obfuscation, and encryption to elude detection by IDS.
Why is the integration of multiple threat prevention technologies recommended?
Combining vulnerability protection, anti-malware, and anti-spyware forms advanced threat protection, providing a comprehensive solution that actively scans all traffic for threats and aligns with a Zero Trust model.
Conclusion
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are indispensable in addressing the growing complexity of cyber threats. Serving as a crucial defense component, IDS plays a pivotal role in identifying and analyzing security incidents. The diversity of IDS types underscores the need for a comprehensive security approach. While effective on its own, IDS achieves greater impact when integrated with Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) and advanced threat protection technologies. This combination ensures a robust defense strategy, aligning with the dynamic nature of cyber threats and promoting heightened security for organizations.
ad


Comments are closed.