Powerline Networking- What You Need To Know | download.zone
Powerline Networking defines as a data network that employs a building's electrical infrastructure and wall outlets as transmission ports. It's used to extend a wired Ethernet network.
Currently, the majority of people have a wireless network in their homes. But, Wi-Fi does not always function as intended, and it is not the only networking option available. Ethernet offers the fastest speeds but is unsightly when draped from devices and running along the floor.
Then,
Why not use your current electrical power lines to link your gadgets to your home network instead of running new Ethernet cables?
This is the concept underlying Powerline and Homeplug networks.
Note: HomePlug is the family name for power line networking specifications over existing residential electrical wiring.
HomePlug adapters are commonly used to set home network with non-Wi-Fi devices and to increase the range of existing networks.
Typically, you get homeplug adapters in pairs, and in this instance, you need only plug them in for them to function.
In contrast, fixing broken equipment or expanding an existing powerline network are two distinct tasks.
What is Powerline networking?
Essentially, a Powerline network is a wired network with (largely) concealed wires. Consider that you have a smart Samsung HD TV in the living room and a broadband router in the hallway. The only way to watch catch-up TV on this TV would be to run an Ethernet connection from the router, down the hall, and across the living room floor to the television. You attempt to conceal the cord with a large rug. It doesn’t work.
The Powerline solution is less obtrusive, employing a “no new wires” strategy. You purchase a basic package that includes two Powerline adapters and two Ethernet cables. One of the Ethernet cables is connected to your router and the first adapter. The device is then plugged into the nearest power outlet. The second Ethernet cable is inserted into the rear of the HDTV and the second adaptor. The second adapter is plugged into the nearest power outlet.
And that is all. The adapters auto-detect each other (no drivers, no lengthy configuration process) and auto-connect, allowing data packets to zoom from the router to the TV via the Ethernet cable, the first adapter, the electrical wiring in the walls, and the second adapter. In 2001, when the initial HomePlug Powerline standard was introduced, data speeds were restricted to 14Mbps. However, the most recent Powerline systems now offer networking at the gigabit rate.
Advantages
- No additional wiring required
- Wiring is usually hidden
- Can use Powerline adapter to power the device e.g. with pass through devices
- Fast speeds of 500Mbps are possible with new models
- Long range and not affected by thick walls and other obstacles like Wi-Fi.
Common Uses of Powerlines
They are frequently used:
- To connect devices beyond the wireless router’s range to a home network.
- To connect to the network a device that demands a fast and reliable connection, such as a gaming console.
- To extend wireless range with a powerline Wi-Fi amplifier.
Powerline/Homeplug Standards
Powerline standards have evolved since homeplug 1.0 was introduced. Due to the possibility of interoperability concerns, it is crucial to be knowledgeable of the various standards.
The standards are:
- Homeplug 1.0 Speeds 14Mbs
- Homeplug 1.0 with Turbo Speeds 85Mbs
- Homeplug AV speeds 200Mbs speeds of 500Mbps are now available and marketed normally as AV500.
- Homeplug AV2 (latest) Maximum speed currently 1200Mbps
- HomePlug Green PHY -low power version and low speed.
Why is it so useful?
Wi-Fi is utilized worldwide in homes, organizations, and even sidewalks, thus it is evidently functional. So why do we require an other Internet connection method? Because there are circumstances in which Powerline connections are more advantageous. Here are the major advantages.
Spend less on installation
Suppose you have a device, such as a television, that can connect to the internet via a conventional Ethernet connection but lacks Wi-Fi. Your router is positioned on the opposite side of the room. You may put Ethernet connections through your walls, along your baseboards, or under your carpet, but doing so can be time-consuming, unsightly, and require numerous wires. Purchasing a pair of Powerline adapters is typically a faster and more cost-effective option.
Solve Wi-Fi woes
There are several locations where Wi-Fi cannot dependably reach. It may be impossible to use a wireless connection in homes with excessive interference or size. In such situations, Powerline adapters can supplement Wi-Fi networks or provide individual solutions for equipment requiring a physical connection. This may also assist with improving other issues, such as sporadic streaming or sluggish speeds.
Easy setup
Powerline networking is simple to implement. You can accomplish it on your own in a few minutes. If only one or two devices in your home require Internet access, Powerline may be the most convenient option for you.
How does Powerline networking work?
Sending signals through a home’s electrical wiring is not a concept of the 21st century. Since the 1920s, power companies have sent control signals across the mains; this is how electricity meters know when to switch to off-peak rates. The typical home’s electrical wiring may accommodate a number of frequencies. Due to the fact that electricity employs 50/60Hz signals, more data can be transmitted via the same wiring at significantly higher frequencies without producing interference.
The initial speed of the original HomePlug 1.0 standard (IEEE 1901) was fairly sluggish at 14Mbps, while actual speeds were closer to 5Mbps. A ‘Turbo’ upgrade increased version 1.0’s maximum capacity to 85Mbps (real-world speeds of around 20Mbps). In 2005, a redesigned HomePlug AV increased the rate even more, claiming 200Mbps on the box (80-90Mbps in tests) sufficient for music and video streaming, hence the ‘AV’ moniker.
In January 2012, a newer, quicker version of the HomePlug Powerline standard was introduced. HomePlug AV2, which supports HD and 3D video, uses MIMO technology to deliver data across the two fastest wires in a standard three-wire (live, neutral, ground) house electrical system.
Technical aspects of powerline networking
Most Powerline packages consist of two Ethernet-capable adapters. Using an Ethernet cable, one device connects to an electrical outlet and a modem or router’s LAN port. The second unit is plugged into an electrical socket close to the desired network-connecting device.
Without getting too technical with the hardware and software layers, the first adapter attached to your modem or router translates the Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) protocol it gets into the HomePlug AV2 protocol. Similar to how routers convert and disseminate wireless connectivity, this data is then “broadcast” through the electrical cables (IEEE 802.11). Rather than utilizing antennas, adapters transmit via the Line and Neutral power connectors.
Historically, Line and Neutral wires were only utilized for a single input and output (11). The addition of the Ground wire to the HomePlug AV2 protocol enables MIMO transmissions and beamforming to accommodate Ultra HD video transmissions. The adaptor transfers data utilizing any two pairs, such as Line and Neutral or Line and Ground (22).
All other connected adapters receive both power and data transmission. They eliminate the latter, revert everything back to Ethernet protocol, and force the network connection through the Ethernet port. There are Powerline adapters with Wi-Fi connectivity.
HomePlug AV2 is superior
Powerline networking is compatible with all Internet-capable wired devices, and all wireless devices if the adapter supports Wi-Fi. All adapters synchronize and collaborate to generate, for example, a digital map of discovered stations and their connections, which is beneficial for network management.
Currently, the finest Powerline protocol is HomePlug AV2, a more flexible version of the earlier HomePlug standard meant to boost speeds, extend coverage, and give a power-saving sleep mode, among other significant characteristics.
Always search for the most recent protocol when purchasing Powerline adapters (more on this later), as there is a substantial improvement in quality between generations.
Is Powerline better than Wi-Fi?
You may be wondering why you need Wi-Fi if Powerline offers so many advantages. Is Powerline better? That is a valid inquiry.
A Wi-Fi router is likely the more cost-effective alternative than purchasing multiple Powerline adapters. This and the extra flexibility of a wireless signal are important reasons why millions of Internet users prefer Wi-Fi. With the introduction of Wi-Fi 6 (which is discussed in greater detail below), Wi-top Fi’s speeds and advantages for mobile devices have become significantly more significant than Powerline.
Powerline supports up to 984 feet of distance, however adapters do not communicate in a straight line. Data must travel up and down walls and through the attic, adding distance that cannot be observed. Moreover, if the electrical wiring in a home or office is too old or if the Powerline adapters are too far apart, you will certainly observe significantly less than the maximum achievable in the real world.
Powerline adapters also have its limitations:
- They must be directly connected to a power outlet: Powerline adapters do not function effectively when connected to surge protectors, power strips, or uninterruptible power supplies.
- Avoid electrical outlets with AFCI and GFCI breakers: AFCI and GFCI breakers might decrease performance by as much as 50 percent.
- They shouldn’t share the same outlet with devices that produce electrical “noise”: These devices include chargers, fluorescent lights, and electric appliances.
Certain Powerline adapters provide pass-through power connectors so that you do not lose an open power connection for other devices. You may also encounter adapters with integrated Wi-Fi that support smartphones and other wireless devices.
Before purchasing a kit, check your home or office’s electrical system, evaluate the circuit breaker box, and determine where Powerline adapters may connect safely. Before committing, you should also analyze the current state of Powerline and how it compares to the most recent Wi-Fi standards.
Is Powerline safe?
Electrical signals are susceptible to hacking, just as Wi-Fi signals. Therefore, it is essential to choose Powerline adapters with the greatest encryption technology currently available (currently 128-bit AES). Adapters typically include security buttons that encrypt communications when triggered. Ensure that these buttons are always active.
What’s the future of Powerline networking?
HomePlug Green PHY (also known as HomePlug GP), a subset of the AV2 standard, comes next. It is not an evolution of AV2, therefore do not anticipate a network speed gain in the near future. In reality, HomePlug Green is slower, offering speeds of approximately 10Mbps, while consuming up to 75 percent less power than standard HomePlug devices.
The purpose? Future “smart grid” applications and an entirely new wave of HVAC devices and other linked appliances are being prepared for the new format. According to the HomePlug Alliance, “[HomePlug Green] can be utilized in smart energy applications like demand response, load control, energy efficiency, and home/building automation.”
Plug-in electric vehicles will also utilize HomePlug Green. Audi, BMW, Ford, General Motors, and Volkswagen have all decided to use HomePlug Green as the standard protocol to regulate how future vehicles connect with their charging stations.
HomePlug’s IEEE 1901 format is also part of a unified IEEE 1905 standard that encompasses 802.11 wireless networking, IEEE 802.3 Ethernet connectivity, and Multimedia over Coax. This will further ensure compatibility between wireless and wired home networking solutions.
The smart house is on its way. It is simply taking longer than anticipated.
Powerline Adapters
Pay special attention to the numbers on the labels of Powerline adapter kits while you shop. For example, the TP-Link AV2000 kit advertises up to 2,000Mbps (or 2Gbps), but you will never reach that speed. Additionally, ensure that the kit’s Ethernet ports support speeds of up to 1Gbps, as anything less, such as 100Mbps, will limit your connection regardless of the transfer speed of your electrical connections.
How Powerline Adapters Work
A fundamental grasp of how the powerline network operates is essential for troubleshooting, developing, repairing, and improving it.
Powerline adapters utilize identical physical media (the mains cable).
This indicates that there is a potential security concern in a neighborhood where every home employs powerline adapters.
To circumvent this, powerline adapters create logical networks using a security key or password known as an NMK (Network Management Key).
This key is utilized to encrypt network data with 128-bit AES (AV2 standard) or 56-bit DES (AV1 standard).
Creating Powerline Networks
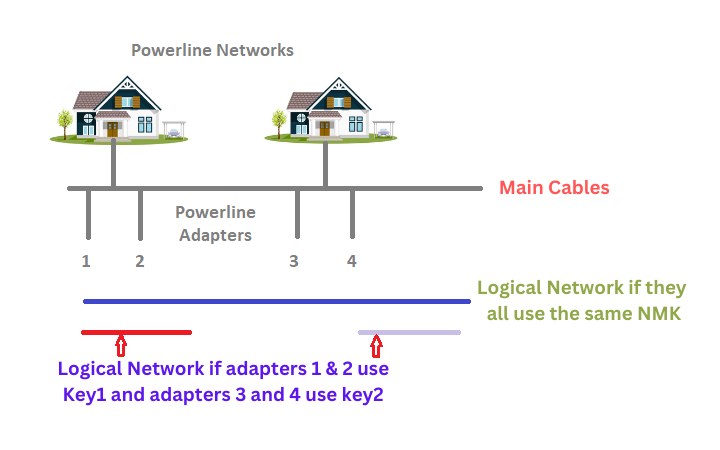
To create a powerline network, at least two homeplug adapters are required.
Typically, adapters are purchased in pairs, and the manufacturer will supply each pair with a shared NMK.
This implies that when they are plugged into a wall outlet, they will create a link and form a logical network.
If they do not automatically create a connection, you must intervene and initiate pairing manually.
Putting one of the adapters in receptive mode allows it to listen for another adapter attempting to establish a connection.
The process is repeated with the second adapter. Both adapters must locate one another and agree on a common key.
Top Powerline adapters
Budget: TP-Link TL-PA7010P Powerline adapter
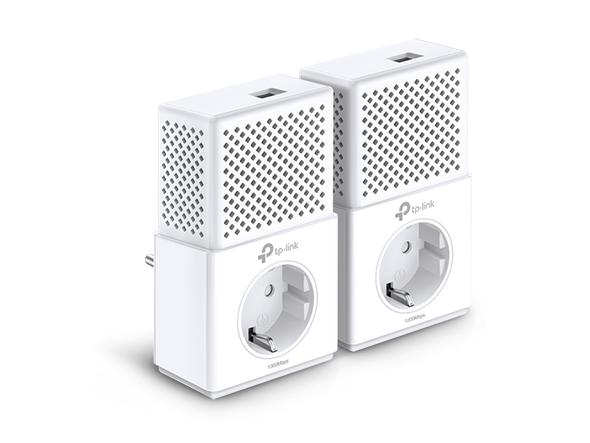

This whole-home kit is based on HomePlug A2 and includes two adapters with pass-through power sockets and a Gigabit Ethernet connector. Similar to the other kits on our list, each adapter has connection health indicators and a simple pairing button for your convenience.
The only serious design defect we observed was that the ethernet port was located on top of the television rather than underneath. Although some may appreciate this positioning decision, we found it to be illogical. Nonetheless, this is a minor flaw that does not affect the product’s overall quality.
Other notable features of this set include plug-and-play functionality and an automatic power-saving mode. Unfortunately, this system lacks Wi-Fi connectivity; if you desire it, you will need to purchase an updated TL-WPA7510 kit for $16.
Powerline ensures that you will never again have to struggle with unstable Wi-Fi or a tangle of ethernet cords in your home. These kits provide everything you need at the best price, and all you need is the existing electrical wiring in your house or place of business. This approach may have a few drawbacks, but its advantages far outweigh them.
Midrange adapter: Netgear PL1200-100PAS
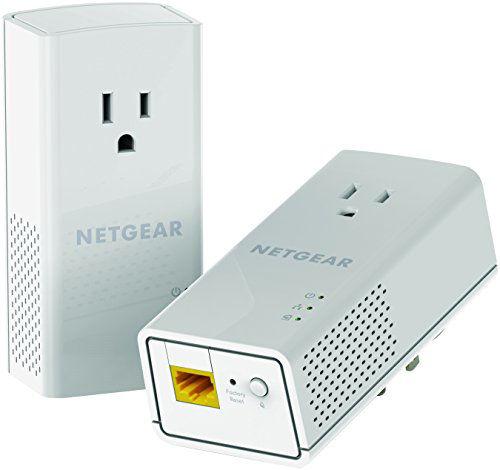 The PL1200-100PAS package from Netgear advertises speeds of up to 1,200Mbps, while actual rates may not exceed 380Mbps. Note that this speed is dependent on the local network and will not increase your internet connection if you only subscribe to 200Mbps.
The PL1200-100PAS package from Netgear advertises speeds of up to 1,200Mbps, while actual rates may not exceed 380Mbps. Note that this speed is dependent on the local network and will not increase your internet connection if you only subscribe to 200Mbps.
Unfortunately, this two-pack does not include built-in power sockets, thus you will lose an electrical outlet. These two adapters only provide a single Gigabit Ethernet port, restricting your physical connections; this is especially true for the type that is tethered to your modem or router.
Other significant features include a physical button to enforce encryption, connection health indicators, MIMO and beamforming connections, and a plug-and-play configuration that requires no additional software.
For high-performance: TP-Link TL-PA9020P adapter
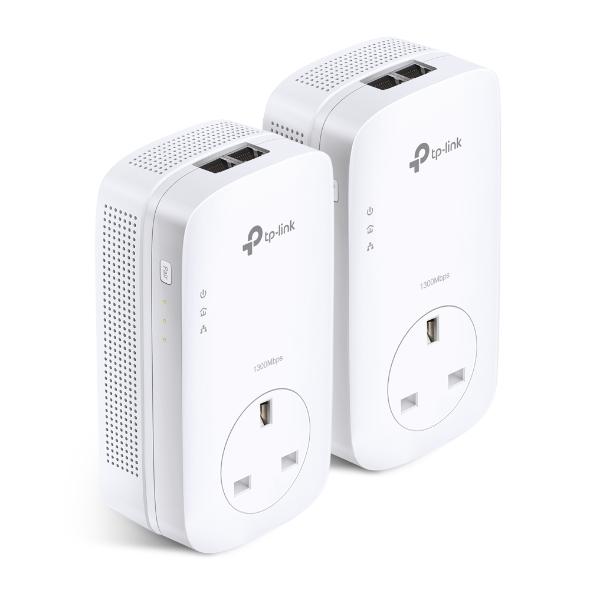 Using the HomePlug AV2 protocol, this package includes two identical adapters that support up to 2,000Mbps. In real-world settings, speeds of up to 400Mbps are possible.
Using the HomePlug AV2 protocol, this package includes two identical adapters that support up to 2,000Mbps. In real-world settings, speeds of up to 400Mbps are possible.
Each adapter has a built-in power socket so you don’t have to sacrifice an outlet, two Gigabit Ethernet ports, and a one-touch pairing button that synchronizes with the other adapter (s). Side-integrated LEDs denote strong (green) and weak (red) connections.
The HomePlug AV2 protocol enables a 22 connection, which corresponds to two broadcast streams and two receive streams. Other features include noise filtering, beamforming, and a mode that conserves energy.
Conclusion
Powerline/Homeplug networks are an excellent option to extend your home network without running wires, as well as for connecting devices that require a quick and dependable connection.
Typically, the speeds and dependability are considerably superior to Wi-Fi.
ad


Comments are closed.