A fiber optic cable is a network cable that contains strands of glass fibers inside an insulated casing. They are intended for long-distance, high-performance data networking and telecommunications. Fiber optic cables have a higher bandwidth and can transmit data over longer distances than wired cables. Fiber optic cables underpin much of the world’s internet, cable television, and telephone systems.
How Fiber Optic Cables Work
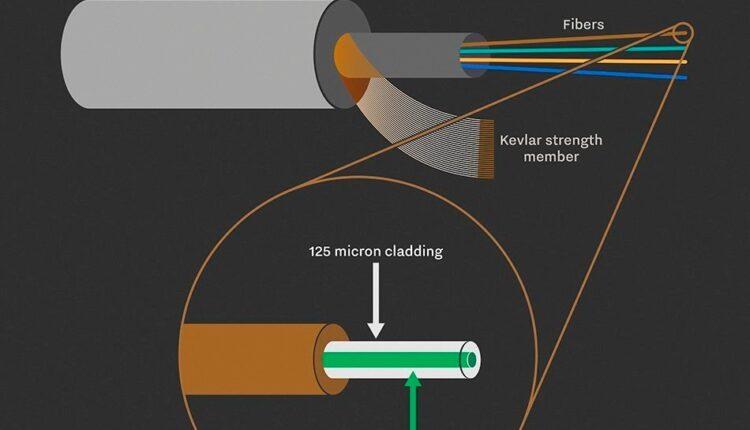
A fiber optic cable is made up of one or more glass strands that are only slightly thicker than a human hair. The center of each strand is known as the core, and it serves as the path for light to travel. The core is surrounded by cladding, which is a layer of glass that reflects light inward to avoid signal loss and allows light to pass through bends in the cable.
Single mode and multi-mode optical fiber cables are the two most common types. To generate light, single-mode fiber uses extremely thin glass strands and a laser, whereas multi-mode optical fiber cables use LEDs.
Wave Division Multiplexing techniques are frequently used in single-mode optical fiber networks to increase the amount of data traffic that a strand can carry. WDM enables the combination (multiplexing) and subsequent separation (de-multiplexing) of light at multiple wavelengths, effectively transmitting multiple communication streams via a single light pulse.
The Benefits of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables have a number of advantages over long-distance copper cabling.
- Fiber optics provide greater capacity. A fiber cable can easily carry more network bandwidth than a copper cable of comparable thickness. Fiber cables with speeds of 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, and 100 Gbps are common.
- Because light can travel much longer distances without losing strength over a fiber cable, the need for signal boosters is reduced.
- An optical fiber cable is less susceptible to interference. Shielding is required for copper network cables to protect them from electromagnetic interference. While this shielding is beneficial, it is insufficient to prevent interference when many cables are strung together in close proximity. The physical properties of fiber optic cables prevent the majority of these issues.
- Fiber optic cables are stronger, thinner and lighter than copper wire cables.
- They do not need to be maintained or replaced as frequently.
Other Deployments, Fiber Networks, and Fiber to the Home
Whereas most fiber optics are installed to support long-distance connections between cities and countries, some residential internet providers have invested in extending their fiber installations to suburban neighborhoods to allow households direct access. Last-mile installations are what providers and industry professionals refer to.
Verizon FIOS and Google Fiber are two well-known fiber-to-the-home services on the market. Households can benefit from gigabit internet speeds through these services. Customers are usually offered lower capacity packages as well. These acronyms are frequently used to shorten different home-consumer packages:
- Fiber to the Premises (FTTP): Fiber that has been laid all the way to the building.
- Fiber to the Building/Business/Block (FTTB): The same thing as FTTP.
- Fiber to the Curb of Node (FTTC/N): Fiber is laid to the node, but copper wires complete the connection inside the building.
- Direct fiber: Fiber that leaves the central office and is connected to a single customer. This provides the most bandwidth, but it is also the most expensive.
- Shared fiber: Similar to direct fiber in that it splits into other optical fibers as it approaches the premises of nearby customers.
What Exactly Is Dark Fiber?
The term dark fiber (often spelled dark fiber or called unlit fiber) most commonly refers to installed fiber optic cabling that is not currently in use. The term sometimes also refers to privately operated fiber installations.
Why should we use optical fiber cable?
- They have virtually limitless information.
- They have a large carrying capacity (high bandwidth, THz or Tbits/s).
- They have extremely low transmission losses (0.2dB/km for microwave, cf1dB/km for twisted copper pair).
- They do not dispel heat.
- They are not affected by cross-talk or electromagnetic interference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is fiber optic superior to cable?
Better depends on your point of view. Fiber optic internet is less likely to go down during a power outage than other types of high-speed internet because it does not use electricity. Fiber optic internet is more reliable, faster, and more expensive than traditional internet cables.
When compared to cable internet, how fast is fiber optic internet?
Cable technology currently supports 1,000 Mbps of bandwidth, whereas fiber optic internet can support speeds of up to 2,000 Mbps. At 1,000 Mbps, you can download a 2-hour HD movie in about 32 seconds. A 2-hour HD movie takes about 17 seconds to download at 2,000 Mbps.
What are the fundamental elements of fiber optic cable?
The core, cladding, and coating are the three essential components of fiber optic cable.
How can fiber optic technology help an AV system stay ahead of the curve?
The transition to digital video standards and higher resolutions has revealed many of copper cabling’s limitations. High-resolution digital video signals travel at multi-gigabit data rates, taxing copper cabling. Fiber optic cables installed in today’s systems provide a path for future video signals. Fiber optic cable is an ideal cabling solution for future AV systems that require multi-gigabit data rates and long distances.
ad




Comments are closed.