What is an intrusion prevention system?
An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is a network security tool, available as either hardware or software, that continuously monitors network activity for malicious behavior and takes action to stop it, such as reporting, blocking, or dropping the threat.
It goes beyond an intrusion detection system (IDS), which can only detect and alert administrators to malicious activity but cannot take preventive measures. IPS is often integrated into next-generation firewalls (NGFW) or unified threat management (UTM) solutions. Like other network security technologies, an IPS must be capable of scanning large volumes of traffic without hindering network performance.
ad
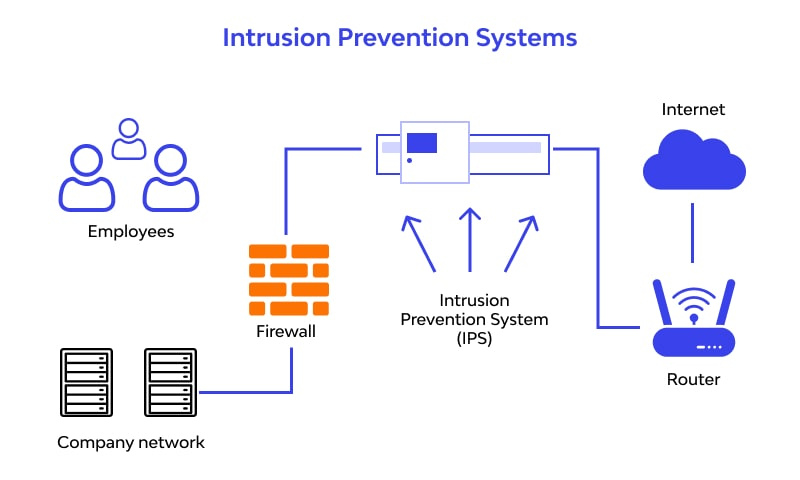
How does an intrusion prevention system work?
An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is installed inline within the network traffic flow, situated between the source and destination, and typically positioned just behind the firewall. It utilizes several techniques to identify potential threats:
- Signature-based: This technique matches network activity against known threat signatures. However, it can only detect and prevent attacks that have been previously identified, making it ineffective against new, unknown threats.
- Anomaly-based: This technique monitors for unusual behavior by comparing network activity to a baseline standard. It is more capable than signature-based methods but can sometimes result in false positives. Some advanced IPS systems use artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance anomaly-based detection.
- Policy-based: This less common technique relies on security policies defined by the organization, blocking any activity that violates these policies. It requires administrators to establish and configure these security rules.
ad
Once an IPS detects malicious activity, it can automatically take several actions, such as alerting administrators, dropping malicious packets, blocking traffic from the source, or resetting the connection. Some IPS systems also use “honeypots,” which are decoy data traps, to lure attackers and prevent them from reaching their actual targets.
Types of intrusion prevention systems
IPS solutions can be implemented as software applications on endpoints, dedicated hardware devices within the network, or provided as cloud services. Since IPSs are designed to block malicious activity in real time, they are always positioned “inline” on the network, meaning that all traffic passes through the IPS before reaching its destination.
IPSs are classified based on their location within the network and the type of activity they monitor. Organizations often deploy multiple types of IPSs for comprehensive protection.
- Network-based Intrusion Prevention Systems (NIPS): A network-based intrusion prevention system (NIPS) monitors both inbound and outbound traffic across the network, inspecting individual packets for suspicious behavior. NIPS devices are strategically placed within the network, often just behind firewalls at the network perimeter, to block malicious traffic before it penetrates further. They may also be located inside the network to monitor traffic to and from critical assets, such as data centers or sensitive devices.
- Host-based Intrusion Prevention Systems (HIPS): A host-based intrusion prevention system (HIPS) is installed on specific endpoints, like laptops or servers, and focuses solely on monitoring traffic to and from that particular device. HIPS are typically used alongside NIPS to provide additional security for critical assets. They can also block malicious activity from a compromised network node, such as preventing ransomware from spreading from an infected device.
- Network Behavior Analysis (NBA): Network behavior analysis (NBA) solutions monitor overall network traffic flows. While NBAs can inspect packets like other IPSs, they primarily focus on higher-level aspects of communication sessions, such as source and destination IP addresses, ports used, and the volume of packets transmitted. NBAs use anomaly-based detection methods, identifying and blocking traffic flows that deviate from normal patterns, such as a DDoS attack or a malware-infected device communicating with an unknown command and control server.
- Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems (WIPS): A wireless intrusion prevention system (WIPS) monitors wireless network protocols for suspicious activities, such as unauthorized users and devices attempting to access the company’s Wi-Fi. If a WIPS detects an unknown entity on the wireless network, it can terminate the connection. Additionally, WIPS can identify misconfigured or unsecured devices on a Wi-Fi network and intercept man-in-the-middle attacks, where a hacker covertly eavesdrops on users’ communications.
Benefits of an intrusion prevention system?
An intrusion prevention system (IPS) provides several key benefits:
- Enhanced Security: An IPS complements other security solutions by detecting threats that might be missed by them, especially with anomaly-based detection. It also offers advanced application security due to its deep application awareness.
- Improved Efficiency for Other Security Measures: By filtering out malicious traffic before it reaches other security devices, an IPS reduces their workload, enabling them to operate more efficiently.
- Time Savings: Largely automated, an IPS minimizes the time and effort required from IT teams.
- Compliance: An IPS helps meet compliance standards set by regulations like PCI DSS and HIPAA and provides valuable auditing data.
- Customization: IPSs can be configured with tailored security policies to address the specific security needs of the enterprise using them.
Disadvantages of IPS
Here are some drawbacks of using an IPS:
- False Positives: One significant disadvantage is the potential for false positives, where the IPS mistakenly identifies and blocks normal traffic as a threat. This can lead to network disruptions and delays, which can be inconvenient for users.
- Impact on Network Performance: An IPS can affect network performance due to the resources needed to analyze and block traffic. This may result in latency issues, depending on the network’s size and traffic volume.
Why is an intrusion prevention system important?
An IPS is essential for any enterprise security system for several reasons. In a multi-cloud network with numerous access points and high traffic volumes, manual monitoring and response are impractical. This is especially true in cloud security, where the interconnected nature of the environment increases the attack surface and vulnerability to threats. Furthermore, the range and complexity of threats faced by enterprise security systems are continually expanding. The automated features of an IPS are crucial for enabling rapid threat response without overburdening IT teams. As a component of an enterprise’s security infrastructure, an IPS plays a vital role in preventing some of the most serious and sophisticated attacks.
Why is an intrusion prevention system important?
An IPS is a crucial component of any enterprise security system for several reasons. In a multi-cloud network, which features numerous access points and handles high traffic volumes, manual monitoring and response are impractical. This is especially true in cloud environments, where increased connectivity leads to a larger attack surface and greater vulnerability to threats. Moreover, the threats facing enterprise security systems are becoming more numerous and sophisticated. The automated functions of an IPS are essential in this context, enabling rapid threat response without overloading IT teams. As part of an enterprise’s security framework, an IPS plays a vital role in mitigating some of the most serious and advanced attacks.
IPS and other security solutions
| Integration | Description |
|---|---|
| IPS and SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) | IPS alerts are often sent to an organization’s SIEM, where they are combined with alerts and data from other security tools in a centralized dashboard. This integration allows security teams to enhance IPS alerts with additional threat intelligence, filter out false positives, and ensure threats have been successfully blocked. SIEMs also help SOCs manage data from different types of IPSs, as many organizations use multiple solutions. |
| IPS and IDS (Intrusion Detection System) | IPSs evolved from IDSs and share many of their features. While some organizations may use separate IPS and IDS solutions, most security teams deploy an integrated system that offers robust detection, logging, reporting, and automatic threat prevention. Many IPSs allow security teams to disable prevention functions, enabling them to act solely as IDSs if desired. |
| IPS and Firewalls | IPSs serve as an additional layer of defense behind firewalls. Firewalls block malicious traffic at the network perimeter, while IPSs address threats that bypass the firewall and enter the network. Some firewalls, particularly next-generation firewalls, include built-in IPS capabilities. |
FAQ’s
What is an intrusion prevention system (IPS)?
An IPS is a network security tool that monitors for and stops malicious activity in real time, either by blocking, reporting, or dropping threats. It differs from an IDS, which only detects and alerts without prevention.
How does an IPS work?
An IPS is placed inline in the network traffic flow, using:
- Signature-based Detection: Matches known threat patterns.
- Anomaly-based Detection: Identifies unusual behavior compared to a baseline.
- Policy-based Detection: Blocks activity based on predefined security rules.
What are the disadvantages of an IPS?
- False Positives: May incorrectly block legitimate traffic.
- Performance Impact: Can cause latency due to the resources needed for analysis.
Why is an IPS important?
An IPS is vital for managing high traffic volumes and numerous access points in a multi-cloud network, providing rapid threat response and preventing sophisticated attacks.
Conclusion
An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is crucial for effective network security, offering real-time threat detection and prevention. It enhances security, boosts the efficiency of other measures, and aids in compliance, despite challenges like false positives and potential performance issues. Integrating an IPS with other security tools further fortifies your defense against sophisticated attacks.
ad


Comments are closed.