What is Eavesdropping?
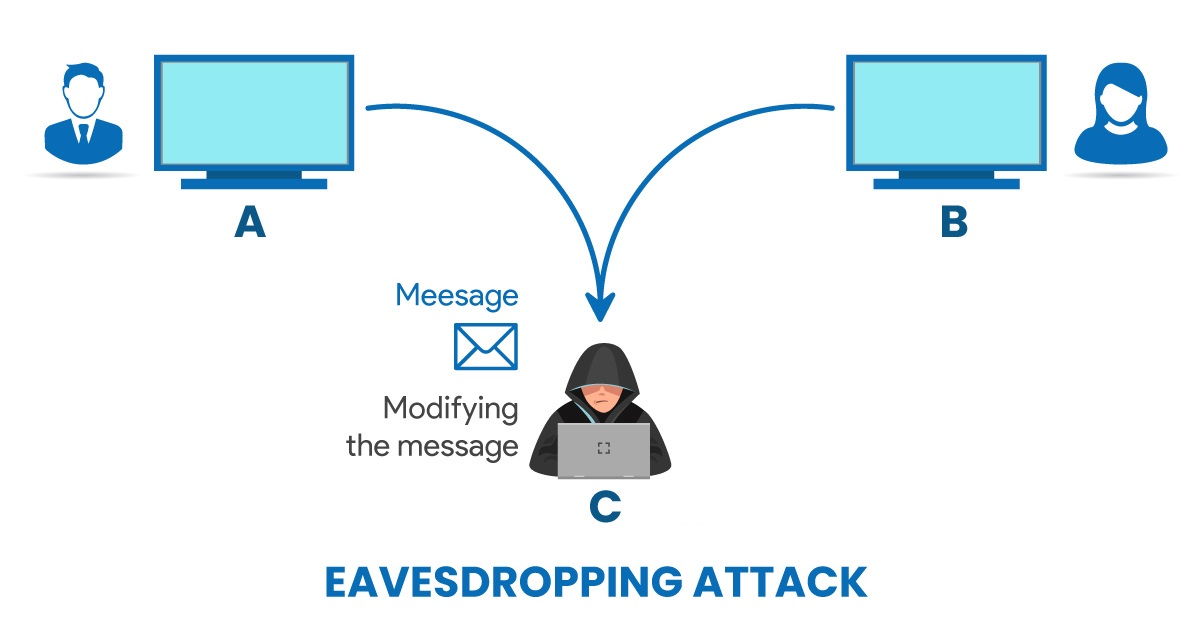
An eavesdropping attack happens when a hacker intercepts, deletes, or alters data being transmitted between two devices. Eavesdropping, also referred to as sniffing or snooping, exploits insecure network communications to access data while it’s in transit between devices.
To elaborate on the concept of being “attacked through eavesdropping,” it typically occurs when a user connects to a network lacking security measures or encryption and sends sensitive business data to a colleague. This data traverses an open network, providing an opportunity for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities and intercept it using various methods. Eavesdropping attacks can be challenging to detect. Unlike other cyber attacks, the presence of a bug or listening device might not impact the performance of devices and networks.
ad
Eavesdropping Methods
Eavesdropping enables attackers to employ various methods to conduct attacks, typically involving the use of eavesdropping devices to monitor conversations and observe network activity.
A common example of an electronic listening device is a concealed bug strategically placed in a residence or workplace. This could involve placing a bug beneath furniture or on surfaces, or embedding a microphone within inconspicuous objects like pens or bags. While this method is straightforward, it could lead to the deployment of more sophisticated, harder-to-detect devices, such as microphones concealed within lighting fixtures, books on shelves, or within wall-mounted picture frames.
ad
Despite the numerous technological advancements facilitating digital eavesdropping, many attacks still hinge on intercepting telephone communications. This is because telephones offer electrical power, integrated microphones and speakers, ample space for concealing bugs, and ease of bug installation. Eavesdropping attackers can monitor conversations within the vicinity of the telephone and intercept calls to telephones worldwide.
Modern computerized phone systems enable electronic interception of telephones without direct physical access to the device. Attackers can transmit signals through telephone lines to capture conversations in the vicinity, even if the handset is inactive. Similarly, computers feature advanced communication tools allowing eavesdropping attackers to intercept various forms of communication, including voice calls, online chats, and keyboard bugs to log typed text.
Furthermore, computers emit electromagnetic radiation that skilled eavesdroppers can exploit to reconstruct the contents of a computer screen. These signals can propagate several hundred feet and can be extended further via cables and telephone lines, which serve as effective antennas.
Pickup Device
Attackers utilize devices like microphones and video cameras to capture sound or images and convert them into electrical signals for eavesdropping. Ideally, these devices operate on power sources within the target room, eliminating the need for the attacker to access the room to recharge or replace batteries.
Certain listening devices can store digital data and transmit it to a designated listening post. Attackers may also employ miniature amplifiers to enhance clarity by filtering out background noise.
Transmission Link
For eavesdropping purposes, a transmission link between the pickup device and the attacker’s receiver can be intercepted. This can involve radiofrequency transmissions or wired connections, utilizing active or unused telephone lines, electrical wiring, or ungrounded conduits. Some transmitters operate continuously, while more advanced methods include remote activation.
Listening Post
A listening post serves to relay intercepted conversations from telephone bugs. When a call is initiated or received, it triggers a recorder that automatically stops recording when the call concludes.
Listening posts are secure locations where signals can be monitored, recorded, or forwarded by attackers for analysis. They can be situated anywhere from an adjacent room to several blocks away from the telephone. These posts often feature voice-activated equipment to eavesdrop on and document activities.
Weak Passwords
Insecure passwords facilitate unauthorized access to user accounts, providing attackers with entry points into corporate systems and networks. This vulnerability allows hackers to compromise confidential communication channels, intercept colleagues’ activities and conversations, and pilfer sensitive business data.
Open Networks
Users who connect to unsecured networks lacking password protection and encryption provide an ideal opportunity for attackers to eavesdrop. Hackers can monitor user activities and intercept communications within the network.
What Does Eavesdropping Mean For Your Business?
Eavesdropping attacks pose risks such as the compromise of critical business data, intrusion into users’ privacy, and potential escalation to broader attacks and identity theft.
An illustrative instance demonstrating the impact of eavesdropping attacks involves the growing adoption of digital assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Home. While these assistants enhance user convenience, they also present vulnerabilities that attackers exploit to eavesdrop and access private information.
The consequences of eavesdropping may include:
Financial repercussions: Cyber attackers can exploit their access to sensitive data, such as corporate information, trade secrets, or user credentials, for financial motives. This could involve selling data to third parties or competitors, or employing ransomware tactics to extort organizations or individuals by restricting data access. Additionally, any data breach risks tarnishing the organization’s reputation, potentially leading to customer loss and subsequent financial setbacks.
Identity theft: Eavesdropping perpetrators can eavesdrop on supposedly secure application conversations, leading users to inadvertently disclose sensitive information. This information can then be leveraged by attackers to steal credentials and perpetrate broader identity theft schemes.
Privacy infringement: The unauthorized access to confidential information through eavesdropping can result in businesses and individuals experiencing privacy violations. Attackers executing eavesdropping attacks can intercept crucial business communications, conversations, and exchanges, impacting users’ privacy.
How To Prevent Eavesdropping Attacks
The digital landscape’s evolution facilitates hackers’ interception of corporate data and user conversations, yet it also empowers organizations to thwart malicious intentions. Effective methods to prevent eavesdropping attacks include:
- Military-grade Encryption: Employing robust encryption for data transmission and private conversations is paramount. Encryption renders intercepted data indecipherable to attackers. For instance, utilizing 256-bit encryption, such as military-grade encryption, creates an almost insurmountable barrier for decryption.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educating employees about cybersecurity risks is fundamental to fortifying organizational defenses against cyber threats, including eavesdropping attacks. Training programs should inform users about attack methodologies, promote best practices to mitigate risks, and foster vigilance against attack indicators. Employees should refrain from downloading insecure software or connecting to vulnerable networks.
- Network Segmentation: Restricting network access through segmentation limits eavesdropping opportunities. By segmenting networks according to role-based access, organizations enhance security by preventing unauthorized access and reducing network congestion and unwanted activities.
- Avoidance of Suspicious Links: Encouraging users to steer clear of untrusted links is critical. Eavesdropping attackers often disseminate malware through dubious links. Users should exclusively download software from reputable sources and official app stores.
- Software Updates and Patching: Promptly applying software updates and patches is imperative to mitigate vulnerabilities exploited by attackers. Enabling automatic updates ensures timely protection against emerging threats.
- Physical Security Measures: Implementing physical security measures in office spaces safeguards data and users from unauthorized intrusions. This includes guarding against physical bugs placed on desks or phones by unauthorized individuals.
- Radiation Shielding: Preventing eavesdropping via computer radiation requires deploying shielding and security measures. For instance, using TEMPEST-protected computers blocks unintended radiation, enhancing data and user security.
FAQ’s
What exactly is an eavesdropping attack?
An eavesdropping attack occurs when a hacker intercepts, deletes, or alters data being transmitted between two devices. It exploits insecure network communications to access data while it’s in transit between devices.
How do eavesdropping attacks typically occur?
Eavesdropping attacks often happen when a user connects to a network lacking security measures or encryption and sends sensitive business data. This data traverses an open network, providing attackers with the opportunity to intercept it using various methods.
What are some common methods used in eavesdropping attacks?
Attackers employ various methods, including electronic listening devices like concealed bugs, intercepting telephone communications, exploiting computerized phone systems, and utilizing electromagnetic radiation emitted by computers.
How do weak passwords contribute to eavesdropping attacks?
Weak passwords provide unauthorized access to user accounts, allowing attackers to breach corporate systems and networks. This enables them to intercept conversations, compromise confidential communication channels, and steal sensitive business data.
What risks does eavesdropping pose to businesses?
Eavesdropping attacks can lead to the compromise of critical business data, invasion of users’ privacy, financial repercussions, identity theft, and privacy infringements, potentially damaging a company’s reputation and leading to financial losses.
What preventive measures can organizations take against eavesdropping attacks?
Effective preventive measures include employing military-grade encryption, raising awareness among employees through training programs, implementing network segmentation, avoiding suspicious links, regularly updating and patching software, implementing physical security measures, and deploying radiation shielding for computers.
How does encryption help prevent eavesdropping attacks?
Encryption renders intercepted data indecipherable to attackers by encoding it in a secure format. Utilizing robust encryption protocols, such as military-grade encryption with 256-bit encryption, creates a significant barrier for attackers attempting to decrypt intercepted data.
Conclusion
Eavesdropping attacks pose significant threats in today’s digital landscape, jeopardizing both businesses and individuals. However, organizations can effectively counter these risks by implementing robust preventive measures. By employing encryption, raising awareness, segmenting networks, avoiding suspicious links, updating software, enhancing physical security, and deploying radiation shielding, businesses can bolster their defenses against eavesdropping attacks. Through proactive measures and vigilance, organizations can safeguard their data and protect user privacy in an ever-evolving cyber threat landscape.
ad


Comments are closed.