What Is SAML?
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) serves as an open standard facilitating the transmission of authentication credentials from identity providers (IdP) to service providers (SP). In this article, we will discuss what SAML is, what it is used for and how it works.
ad
What Is Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)?
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an open standard designed to enable identity providers (IdP) to transmit authorization credentials to service providers (SP). Essentially, this means that users can utilize one set of credentials to access multiple websites, simplifying the management process compared to handling separate logins for various platforms such as email, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and Active Directory.
SAML transactions rely on Extensible Markup Language (XML) for standardized communication between the identity provider and service providers, effectively linking user identity authentication with service authorization.
Approved by the OASIS Consortium in 2005, SAML 2.0 brought significant changes from version 1.1, resulting in incompatibility between the two versions. Adopting SAML allows IT environments to integrate software as a service (SaaS) solutions while maintaining a secure federated identity management system.
ad
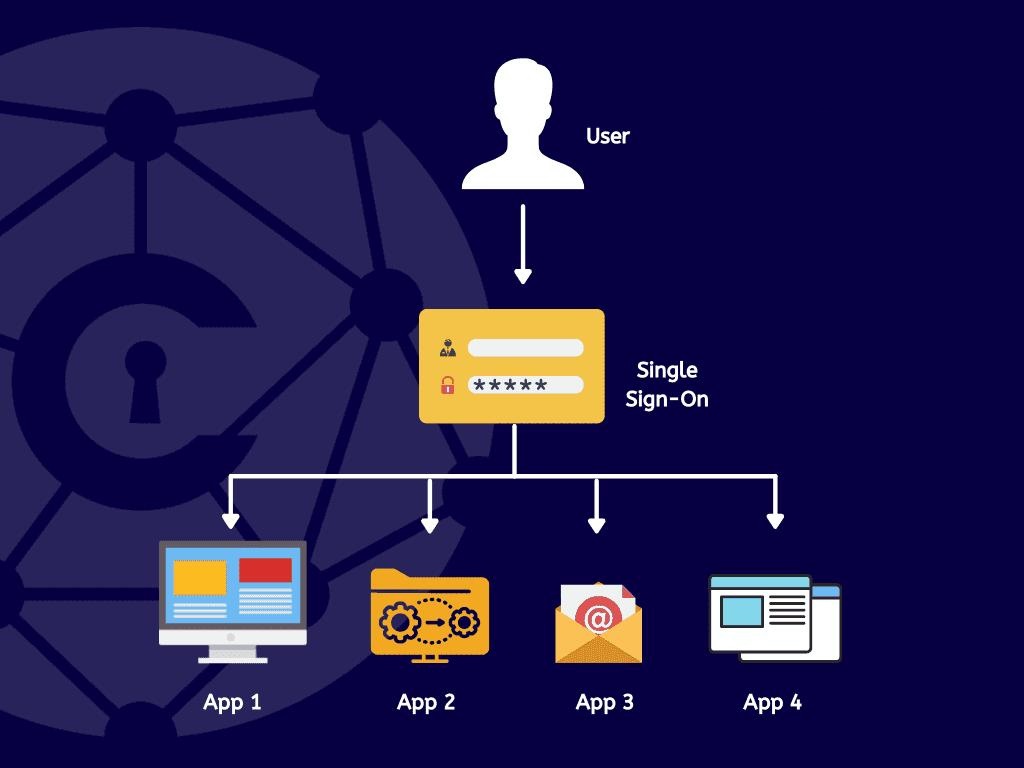
By enabling Single-Sign-On (SSO), SAML allows users to log in once, with the same credentials being reused to access other service providers.
What is SAML Used For?
SAML streamlines federated authentication and authorization procedures for users, identity providers, and service providers. It offers a solution where your identity provider and service providers can function independently, leading to centralized user management and facilitating access to SaaS solutions.
Through SAML, a secure mechanism is implemented for transferring user authentications and authorizations between the identity provider and service providers. When a user logs into a SAML-enabled application, the service provider requests authorization from the relevant identity provider. The identity provider verifies the user’s credentials and then furnishes authorization to the service provider, enabling the user to utilize the application.
In SAML authentication, the user’s identity and credentials (password, two-factor authentication, etc.) are verified, while SAML authorization dictates the access privileges granted to the authenticated user by the service provider.
What is a SAML Provider?
A SAML provider is a system designed to facilitate a user’s access to a required service. There are two main categories of SAML providers: service provider and identity provider.
A service provider requires authentication from the identity provider to authorize the user.
An identity provider conducts the authentication process to verify the user’s claimed identity and forwards this data to the service provider along with the user’s access privileges for the service.
Common identity providers include Microsoft Active Directory or Azure. On the other hand, services like Salesforce and other CRM solutions typically function as service providers, relying on an identity provider for user authentication.
What is a SAML Assertion?
A SAML Assertion refers to the XML document transmitted from the identity provider to the service provider, containing user authorization details. There exist three distinct types of SAML Assertions: authentication, attribute, and authorization decision.
Authentication assertions confirm the user’s identity and include details such as the login time and authentication method employed.
Attribute assertions convey SAML attributes to the service provider, with these attributes being specific data pieces offering insights into the user.
Authorization decision assertions indicate whether the user is permitted to utilize the service or if the identity provider has rejected their request due to password failure or insufficient service rights.
How Does SAML Work?
SAML functions by facilitating the transfer of information concerning users, logins, and attributes between the identity provider and service providers. Through Single Sign-On, users log in once to the identity provider, which can then relay SAML attributes to service providers when users attempt to access their services. The service provider requests authorization and authentication from the identity provider. Because both systems utilize the same language, SAML, users only need to log in once.
For SAML authentication to function properly, each identity provider and service provider must agree on the configuration. Both ends require precise configuration settings to ensure seamless SAML authentication.
SAML Example
- At the beginning of the week, Sarah (user) logs into the company’s Single Sign-On (SSO) platform.
- Afterward, Sarah tries to access the document management system.
- The document management system, functioning as the service provider, verifies Sarah’s credentials with the identity provider.
- The identity provider then sends authentication and authorization messages to the document management system, permitting Sarah to log in.
- Sarah can now access the document management system and proceed with her tasks.
SAML vs. OAuth
OAuth is a relatively newer standard co-developed by Google and Twitter to facilitate simplified internet logins. Similar to SAML, OAuth employs a comparable methodology to share login information. While SAML offers greater control to enterprises for enhancing the security of their Single Sign-On (SSO) logins, OAuth performs better on mobile platforms and utilizes JSON.
Facebook and Google serve as two OAuth providers commonly utilized for logging into various internet sites.
What are the benefits of SAML?
SAML streamlines user login processes, enhances security measures, and lowers costs and complexities for service providers. It enables individuals to securely utilize their existing credentials across multiple applications.
FAQ’s
How does SAML enhance security?
SAML ensures secure transmission of authentication credentials and protects user data from unauthorized access.
Can SAML work with different applications?
Yes, SAML is versatile and can be implemented across various applications and platforms.
What are the main differences between SAML and OAuth?
SAML is primarily for single sign-on in enterprises, while OAuth is used for third-party access to resources.
How does SAML reduce costs and complexity?
By streamlining user authentication processes, SAML helps organizations save on operational costs and reduces the complexity of managing multiple accounts.
What challenges may arise during SAML implementation?
Challenges may include compatibility issues, configuration complexities, and managing user access rights effectively.
Can SAML integrate with existing identity management systems?
Yes, SAML seamlessly integrates with existing systems like Microsoft Active Directory or Azure.
What are the benefits of using SAML for federated identity management?
SAML enables trust relationships between entities, streamlines access control, and ensures consistent security policies across environments.
Conclusion
SAML plays a crucial role in modern identity management by facilitating secure authentication and streamlining access processes across various platforms. Its versatility, compatibility, and ability to integrate seamlessly with existing systems make it an essential tool for organizations aiming to enhance security and user experience while reducing operational complexities and costs. As technology advances, SAML remains a cornerstone in ensuring efficient and secure access to digital resources.
ad


Comments are closed.