What Does CAPTCHA Mean? | How CAPTCHAs Work
CAPTCHA, which stands for “completely automated public Turing test to tell computers and humans apart,” was created by computer scientists in the 1990s. These tests are meant to be easy for humans but difficult for computers, and they remain widely used today to prevent bots from spamming websites.
Whether it’s selecting squares with kittens, moving a puzzle piece to the correct position, or typing distorted letters, we’ve all experienced these challenges. Despite their occasional inconvenience, CAPTCHAs are essential for protecting websites from exploitation by hackers and other malicious individuals.
ad
What is a CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA, standing for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart, serves as a challenge-response test utilized on websites throughout the internet. Its purpose is to distinguish between human users and bots.
How do CAPTCHAs work?
CAPTCHAs function by providing tests that only humans can solve. These tests are administered to users at critical checkpoints like login and checkout, where website owners prioritize allowing only genuine human interactions. Through elements such as distorted letters and blurry images, CAPTCHAs impede bots from progressing, ensuring that only real humans can proceed with the desired action. Failing to pass the CAPTCHA successfully signals to the website owner that the user is likely a bot, prompting measures to prevent further advancement.
ad
Types of CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHAs come in four standard types: text-based, image-based, audio, and math.
Text CAPTCHAs
Text-based CAPTCHAs, the conventional type, display a series of distorted letters and numbers on an off-white or colored background. Users are required to input the correct sequence of characters into a designated text field to proceed. Variations of text-based CAPTCHAs may incorporate special characters, remove spaces between characters, or employ characters of different shapes, sizes, and colors. These alterations increase the difficulty for bots to solve the challenge as they lack the capability to discern and interpret character variations in the same manner as humans.

Image CAPTCHAs
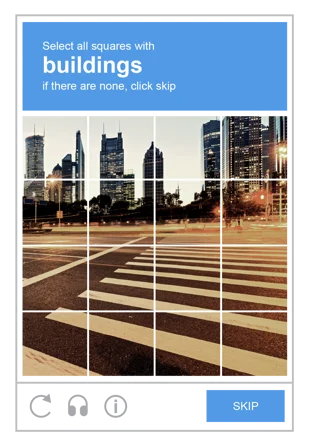
Image CAPTCHAs feature a series of images depicting various scenarios, such as landscapes, animals, or everyday objects. Users are prompted to select only the images containing specific elements, like trees, cars, or traffic lights. In a more advanced iteration, an image may appear in different versions, requiring users to identify consistent attributes across them. For instance, a picture of a beach scene might be presented with varying tides or lighting conditions, prompting users to select the one depicting a sunny day. Bots find image recognition more challenging than text recognition, especially when confronted with unclear or distorted visuals. Additionally, image-based CAPTCHAs evaluate user responses based on human-like judgment rather than strict technical accuracy.
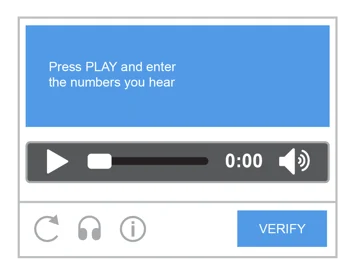
Audio CAPTCHAs
Certain CAPTCHAs offer an alternative option where the numbers or text are presented audibly instead of visually. This adaptation ensures accessibility for individuals who are blind, colorblind, or visually impaired. Users can select the audio test, listen to the provided content, and then input the text they hear.
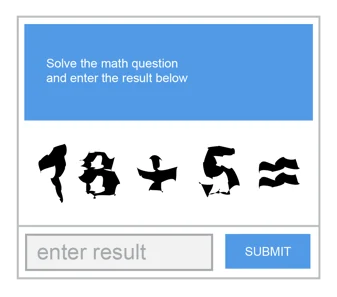
Math CAPTCHAs
Math CAPTCHAs offer users an equation to solve, such as displaying “18 + 5 = ?” and prompting users to input the correct answer, such as “23.” Each visit to the page or failure to submit the correct answer triggers the generation of a new random equation, preventing bots from memorizing a single correct response.
No CAPTCHA reCAPTCHA (or reCAPTCHA V2)
Google introduced this test in 2014, which involves clicking on a box labeled “I am not a robot.” The CAPTCHA assesses whether the user is human or a bot based on where within the box they click. Bots typically click directly in the middle. In the rare event that a human also clicks in the center, a secondary verification method is triggered, requiring the user to input a combination of numbers or letters.
📚 Also Read: What is hCaptcha?
What are CAPTCHAs used for?
CAPTCHAs are an essential tool for websites aiming to deter bot usage. They fulfill various purposes, including:
- Maintaining poll integrity: CAPTCHAs ensure that each vote originates from a human, reducing the risk of poll manipulation. While they don’t restrict the total number of votes, they introduce a time-consuming step, discouraging multiple submissions.
- Preventing registration abuse: Websites deploy CAPTCHAs to prevent bots from overwhelming registration systems with fake accounts. This safeguards resources and minimizes the potential for fraudulent activities.
- Thwarting ticket exploitation: Ticketing platforms employ CAPTCHAs to hinder scalpers from purchasing excessive tickets for resale. They also deter false registrations for free events, preserving fairness in ticket distribution.
- Combating spam comments: CAPTCHAs discourage bots from inundating message boards, contact forms, or review platforms with spam content. By adding an extra verification step, they deter spamming behavior and contribute to a cleaner online environment.
Disadvantages of CAPTCHAs
While CAPTCHAs can bolster website security and deter certain bots, they also come with notable drawbacks:
- Vulnerability to sophisticated bots: Cybercriminals employ advanced techniques like CAPTCHA-solving bots and CAPTCHA farms, undermining the effectiveness of CAPTCHAs.
- Decreased conversion rates: The complexity of CAPTCHAs may prompt users to abandon the site, leading to reduced traffic, conversion rates, and revenue.
- Negative user experience: CAPTCHAs can frustrate users, resulting in a poor consumer experience and potential abandonment. Users encountering issues may resort to contacting customer support, straining internal resources.
- Browser compatibility limitations: Not all CAPTCHA technologies are compatible with every browser, limiting accessibility for some users.
- False positives: CAPTCHAs can yield false positives, with an 8% failure rate for human users and even higher rates if the text is case-sensitive. This can inadvertently lock out legitimate users, hampering site engagement.
- Inaccessibility: Individuals with visual impairments, reading difficulties, or hearing disabilities may struggle to solve CAPTCHAs. Inaccessibility could lead to discrimination lawsuits if disabled individuals are unfairly blocked from accessing content.
FAQ’s
What is CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA stands for “Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.” It is a challenge-response test used on websites to differentiate between human users and bots.
How do CAPTCHAs work?
CAPTCHAs present tests that are easy for humans to solve but difficult for computers. These tests are typically administered at critical checkpoints like login and checkout, requiring users to identify distorted letters, solve puzzles, or select specific images.
What are the types of CAPTCHAs available?
CAPTCHAs come in various forms, including text-based, image-based, audio, and math CAPTCHAs. Each type presents unique challenges to verify human interaction.
What is the purpose of CAPTCHAs?
CAPTCHAs are used to prevent automated bots from spamming websites, maintaining the integrity of polls, limiting registration abuse, combating ticket exploitation, and preventing spam comments.
What are the disadvantages of using CAPTCHAs?
Despite their effectiveness, CAPTCHAs have drawbacks such as vulnerability to sophisticated bots, decreased conversion rates due to user frustration, negative user experiences, browser compatibility limitations, false positives, and accessibility issues for individuals with disabilities.
What is the “I am not a robot” CAPTCHA by Google?
Introduced in 2014, this CAPTCHA involves clicking on a box labeled “I am not a robot.” It assesses user behavior to determine if they are human or bot. In case of doubt, a secondary verification method requiring the input of a combination of numbers or letters is triggered.
Conclusion
CAPTCHAs are crucial for combating bot activity online. While they effectively enhance website security and prevent spam, they also introduce challenges such as user frustration and accessibility issues. Despite these drawbacks, CAPTCHAs remain essential for ensuring fair online interactions. As technology evolves, developers must balance effectiveness with user experience to maintain the integrity of CAPTCHA systems in the digital realm.
ad


Comments are closed.