What Is VLAN?
A VLAN, or virtual local area network, is a virtualized link that integrates various devices and network nodes from distinct LANs into a unified logical network.
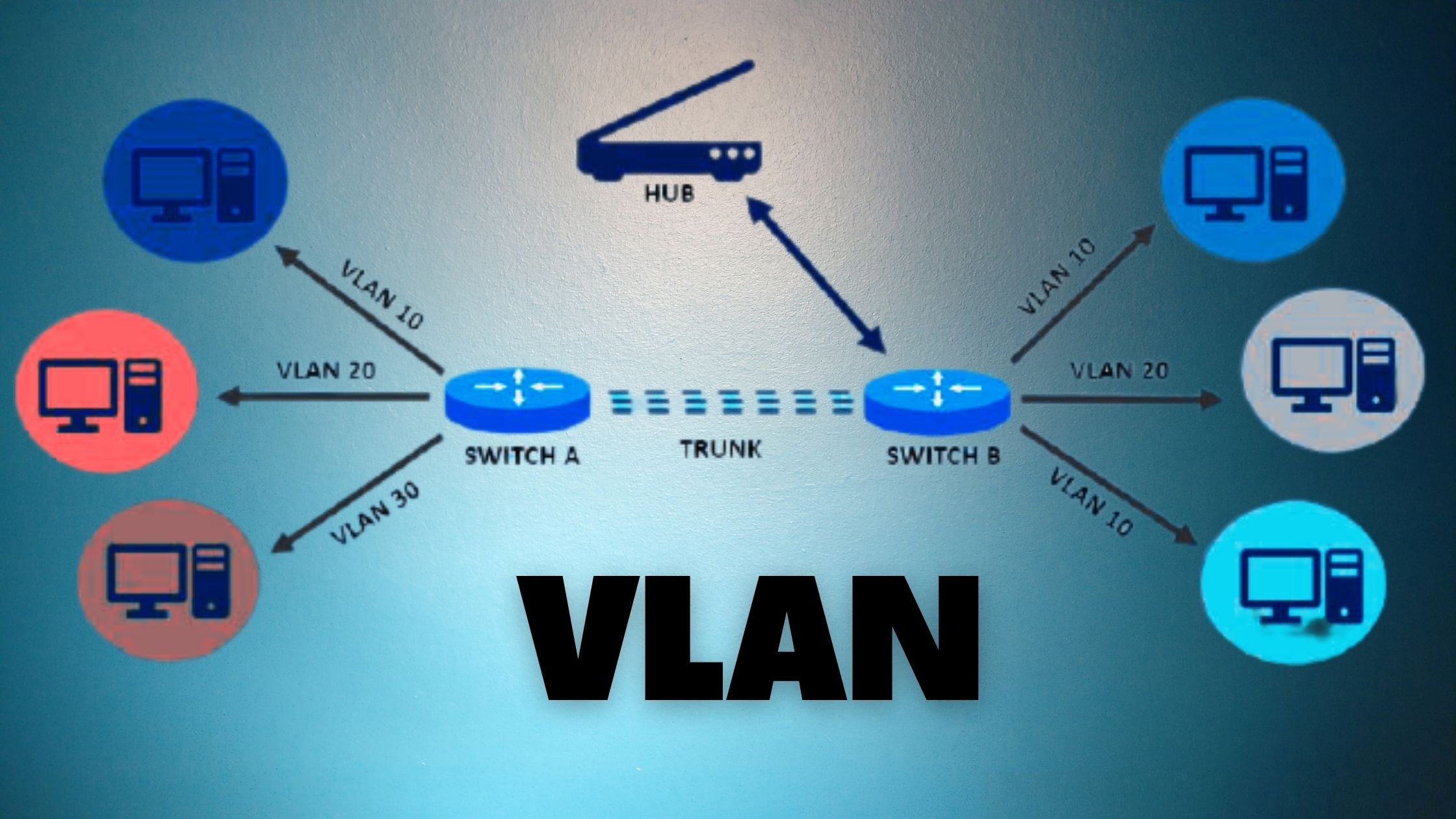
What are the types of VLAN?
Virtual local area networks (VLANs) have become essential for organizations with intricate networking systems. Organizations seek solutions that enable network scalability, segmentation to enhance security measures, and reduction of network latency. While a local area network (LAN) is utilized to connect a set of devices like computers and printers to a server through cables, VLANs facilitate communication between multiple LANs and associated devices through wireless internet. The following outlines the five distinct types of virtual networks:
Management Virtual Local Area Network
ad
This smaller network is designed to aid in managing traffic originating from devices, application logging, and monitoring. The primary benefit lies in enhanced network security. It can mitigate the impact of broadcast radiation, enhancing safety by restricting access and directing regular traffic to other virtual networks.
Voice Virtual Local Area Network
Configured to carry voice traffic, this network helps conserve bandwidth and enhance Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) quality. It manages traffic from VoIP equipment or devices like IP phones, VoIP endpoints, and voice systems, prioritizing transmission over other network traffic.
Native Virtual Local Area Network
Employed in traditional systems or devices lacking VLAN support, this network functions as a common identifier on opposing ends of trunk links to convey untagged traffic generated by systems or devices configured with the native VLAN via switch ports.
Default Virtual Local Area Network
Serving as the default virtual network for all access ports until they are assigned to other networks like voice or management virtual networks, it allows diverse devices to connect with each other. Furthermore, this network cannot be renamed or deleted.
Data Virtual Local Area Network
Dividing the entire network into two primary groups, namely users and devices, this network exclusively carries user-generated data and cannot handle management or voice traffic. Administrators can group users even if they are not connected to the same network switch.
How to manage and configure VLANs
The objective of a virtual LAN is to establish a beneficial layer of intercommunication among LANs and their associated devices. Switch ports play a crucial role in this network configuration, facilitating the grouping of multiple devices from different LANs. This arrangement enhances the manageability and convenience of communication and data sharing among the connected devices.
How to configure a virtual LAN
Setting up virtual LANs involves comparable processes to configuring physical networks. The initial step is identifying the network nodes that require management. Subsequently, VLAN configuration files are established to document the identified nodes. After completing the configuration, you can either archive or edit the files for troubleshooting diagnostics. Utilizing VLAN configuration tools is one of the easiest methods to exchange information and automate configuration file updates for VLAN setups.
Why is VLAN management important?
Handling VLANs manually can pose challenges, particularly in the context of a large network with multiple LANs. Manual execution and configuration alterations raise the potential for inaccuracies and errors, introducing risks of downtime and latency issues. Additionally, such manual processes can result in avoidable conflicts with security compliance reporting, leading to inefficiencies. The optimal approach involves maintaining an accurate and current configuration setup to uphold security and compliance regulations, thereby identifying potential issues within your virtual network.
VLAN management software proves invaluable by providing real-time network updates and immediate alerts regarding changes in network nodes. These tools are also beneficial in disaster recovery management.
What are the advantages of VLAN?
VLAN presents numerous benefits, including streamlined administration, improved performance, enhanced flexibility, and more.
Cost savings
Devices linked to a specific VLAN can communicate through switches, eliminating the necessity for routers to transmit data between the virtual LAN and external computer networks. Routers may introduce bottlenecks and security concerns due to the extensive exchange of external data. Conversely, switches, while having fewer capabilities than routers, efficiently handle data within the network, reducing the need for investing in routers and minimizing overall network latency.
Increased flexibility
Virtual LANs surpass physical networks in terms of flexibility. They can be easily configured, updated, and assigned based on criteria such as port, subnet, and protocol. Being independent of physical connections like wires and cables, these networks facilitate seamless collaboration and data exchange within your team.
Streamlined administration and enhanced security
Virtual LANs do not demand intensive administrative monitoring. These networks enable you to manage access controls and permissions by limiting, changing, deleting, updating, or modifying them. Segmenting systems and devices into multiple LANs allows you to provide access to specific user groups while ensuring security. Furthermore, there’s no need to reconfigure virtual LANs when devices, systems, or user groups associated with a particular network are relocated, saving time, cost, and resources for your organization.
What are the differences between LAN and VLAN?
LAN
A local area network (LAN) comprises devices or systems connected via cables for exchanging business-critical data between systems. LANs are confined to specific geographic areas such as buildings or floors. This cost-effective network system employs cables and networking devices to maintain connections, is centrally managed, and facilitates the sharing of data and resources like files, applications, and printers among team members.
Local area networks necessitate specific components for operations, including endpoints, interconnections, protocols, and network devices.
- Endpoints within the network, which can be computers or electronic devices, are essential for sending and receiving data.
- Interconnections, such as NIC, cables, and wireless media, facilitate data transfer by converting data into a specific format for transmission over the LAN.
- Protocols like ARP, IP, and DHCP are crucial for controlling data transmission within the LAN.
- Network devices such as hubs, switches, and routers are employed to integrate endpoints with LAN segments.
Virtual LAN
A logical separation of a local area network (LAN) into multiple segments within a single bandwidth. This network is customizable, eliminating the need for multiple switches to connect subnetworks and thereby generating more bandwidth. The implementation of this network system utilizes switch ports. Two methods exist for establishing a virtual LAN: static and dynamic.
- Static: Manual connection of virtual LANs to the port is required in this network creation method. It is the most secure way to establish a virtual connection, as configurations cannot be altered without the administrator’s permission.
- Dynamic: Dynamic creation employs software or intelligent tools to automatically assign a virtual LAN to the port.
What challenges and considerations arise with VLANs?
Implementing and managing VLANs provides numerous advantages and is a potent strategy to enhance network functionality. However, it is not without its potential challenges, complexities, and drawbacks. As the network expands, the management and maintenance of several VLANs can become intricate and time-consuming. Consistent and interoperable VLAN configurations across switches and routers are essential, and vigilance is required to monitor and troubleshoot VLAN performance and connectivity issues. Security risks, including VLAN hopping or denial-of-service attacks, may arise from misconfigured ports or trunk lines, necessitating additional security controls. Compatibility issues may surface if different vendors, versions of switches, or non-standard devices and routers are employed, emphasizing the importance of ensuring uniform VLAN tagging methods and capabilities.
The successful implementation and management of VLANs demand meticulous planning, comprehensive documentation, ongoing training, and a proactive approach to address challenges. Below are common challenges and strategies to mitigate them for a successful VLAN deployment and operation:
- Misconfiguration: Implement strict change control procedures, thoroughly document configurations, and regularly audit them to align with the network design.
- Scalability Concerns: Employ hierarchical network designs and utilize VLAN naming conventions and documentation to efficiently manage an increasing number of VLANs.
- Inter-VLAN Routing: Implement proper access control lists (ACLs) on routers or layer 3 switches to control traffic between VLANs, ensuring communication while maintaining security.
- VLAN Overlap: Implement a standardized VLAN numbering scheme and document VLAN assignments carefully to prevent conflicts and overlap.
- Troubleshooting Complexity: Utilize network monitoring tools, diagnostic commands, and provide training to effectively troubleshoot VLAN-related issues.
- Device Compatibility: Ensure network devices support required VLAN features and standards before deployment, planning for upgrades or replacements if necessary.
- Resource and Change Management: Plan resource allocation based on expected growth, use IPAM tools for tracking, and implement strict change management processes.
- Training and Documentation: Invest in training and certification programs, encourage knowledge sharing, and maintain up-to-date documentation.
Additionally, design VLANs with security in mind, following best practices to avoid common issues like Native VLAN mismatch and Inter-VLAN bridging. Addressing these challenges will contribute to a secure and efficiently managed VLAN environment.
FAQ’s
What are the types of VLANs?
VLANs come in various types, including Management VLAN, Voice VLAN, Native VLAN, Default VLAN, and Data VLAN. Each serves specific purposes in network configuration.
How to manage and configure VLANs?
Managing VLANs involves establishing a beneficial layer of intercommunication among LANs and their devices. Switch ports play a crucial role in grouping devices, enhancing communication and data sharing.
How do I configure a virtual LAN?
Configuring a virtual LAN involves processes similar to setting up physical networks. Identify network nodes, establish VLAN configuration files, and utilize VLAN configuration tools for efficient information exchange and automated updates.
Why is VLAN management important?
VLANs need accurate and up-to-date configuration setups to uphold security and compliance regulations. Manual management can lead to errors, downtime, and security conflicts. VLAN management software provides real-time updates and alerts for effective network maintenance.
What are the advantages of VLANs?
VLANs offer streamlined administration, improved performance, and enhanced flexibility. They enable cost savings by eliminating the need for routers in communication between devices within the same VLAN.
What are the differences between LAN and VLAN?
LANs involve devices connected via cables for data exchange within a specific geographic area, while VLANs logically separate a LAN into segments for more efficient communication, offering customization and eliminating the need for multiple switches.
What challenges and considerations arise with VLANs?
Challenges in VLAN implementation include misconfiguration, scalability concerns, inter-VLAN routing complexities, VLAN overlap, troubleshooting issues, device compatibility, and resource/change management. These challenges can be mitigated with careful planning, training, and documentation.
How can misconfiguration in VLANs be avoided?
Implement strict change control procedures, thoroughly document configurations, and regularly audit them to align with the network design. Training and certification programs can help ensure proficient VLAN management.
What is VLAN hopping, and how can it be prevented?
VLAN hopping is a security risk where attackers exploit misconfigured ports or trunk lines. Preventing it involves additional security controls, ensuring consistent VLAN configurations across devices, and maintaining vigilance in monitoring and troubleshooting.
How does VLAN overlap occur, and how can it be addressed?
VLAN overlap arises when VLAN IDs conflict in different parts of the network. Implementing a standardized VLAN numbering scheme and carefully documenting VLAN assignments can prevent overlap. Consistent VLAN IDs across devices are crucial.
Conclusion
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) offer indispensable benefits in network management, providing flexibility, enhanced security, and streamlined administration. The various VLAN types address specific needs, and efficient management involves careful configuration and proactive troubleshooting. While VLANs bring advantages like cost savings and increased flexibility, successful implementation requires thorough planning and ongoing training. Addressing challenges such as misconfiguration and compatibility issues demands best practices and vigilant monitoring. As organizations rely on complex networking systems, effective VLAN deployment remains crucial for secure and efficient communication.
ad


Comments are closed.