720p vs. 1080p vs. 1800p vs. 2160p (4K) vs. 4320p (8k) TV: difference explained
Buying a new TV can be both a fun and an agonizing experience. HDR, OLED, QLED, Full HD and 4K Ultra HD are all buzzwords in stores and online. That’s not clear. The latter two are resolutions, and they indicate the screen’s pixel count. In TV lingo, more pixels means better picture quality.
You’ll learn about the differences between 720p vs. 1080p vs. 1800p vs. 2160p (4K-Ultra HD) vs. 4320p (8K) in this article, so that you can make an informed decision before purchasing a new big-screen television.

Pixels Anatomy
The first thing you need to know about display resolutions is what the “p” stands for in 720p or 1080p. Electronic displays are made up of “pixels,” which are the smallest building blocks. The picture you see on a screen is made up of millions of these minuscule dots. You’ll only be able to see these pixels if you’re a few feet away from the screen.
The image on your screen is made up of thousands of them when viewed at the correct distance. It is the smallest pixel that can be accessed in a digital representation of a picture. Each pixel represents a portion of the original image, which can range from a few thousand to a few billion pixels.
There is a fixed number of pixels in each resolution, regardless of the screen size (well, some Ultrawide monitors do have different resolutions, but their pixel count is still set within that resolution).
To calculate the density of pixels, we only need to know the size of the pixel in order to know the number of pixels in each resolution. As a result, pixels on a television are much easier to discern. TVs, on the other hand, are safe thanks to the increased viewing distances.
We can plug in the numbers to see that a 18″ 720p display has 81.59 PPI, a 24″ 1080p display has 91.79 PPI, a 35″ 1800p display has 104.9 PPI while a 55″ 2160p display has 80.11 PPI, and a 70″ 4320p display has 125.13 PPI using something like this.
Here, we’ll explain what they mean and how they differ from one another. This year, we’ll examine whether 8K televisions are worth the extra cost in 2022.
Screen Resolution
When it comes to screen resolutions, even for those who are well-versed in technology, the lingo gets more and more confusing. The resolution is an important consideration when purchasing a new monitor. The most common resolution in use today is 1080p. Although 1440p and 4K are gaining popularity, the best graphics cards are needed to support them. We’ll be working with the following resolutions when purchasing a new monitor (or TV, if you’d rather play on the couch).
- 1280×720 — HD / 720p
- 1920×1080 — FHD (Full HD) / 1080p
- 2560×1440 — QHD/WQHD (Quad HD) / 1440p
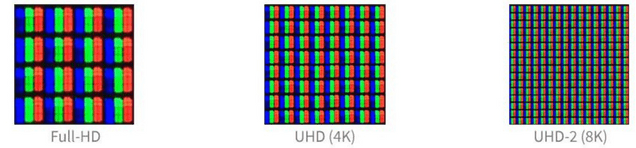
- 3840×2160 — UHD (Ultra HD) / 4K 2160p
- 7680×4320 — FUHD (Full Ultra HD) / 8K 4320p
720p
As the name implies, a 720p TV has 1,280 columns and 720 rows of pixels. To get 921,600 pixels, multiply the two numbers together. HDTV stands for “high definition television,” and this is the bare minimum required to qualify as such.
- You’re using an APU build
- You have no GPU power to spare
- You can’t achieve 60 FPS at 1080p
1080p (Full HD)
The term “Full HD” is frequently used to describe 1080p. There are 2,073,600 pixels in a 1080p TV, which is more than twice as many as there are in a 720p TV. A 1080p TV has 1,920 columns by 1,080 rows. In the high-definition display industry, 1080p has been the standard for a long time, and most content (such as television shows and movies) has been produced and distributed in this resolution.
- You want the best balance between performance and quality
- You want to more easily reach 144+ FPS in eSports titles
- You can’t achieve 60 FPS at 1440p
1800p QHD+ (Quad HD+)
1800p (3200 x 1800) has reemerged in the spotlight in the last year, after being forgotten for a long time. As a result, consoles like the Xbox One X frequently use it as a resolution from which to upscale to 4K after downscaling from 1440p.
Because it’s four times as high as HD+’s resolution of 1600 x 900, 1800p is referred to as QHD+. As a rare PC monitor resolution, this resolution was quickly replaced by the 1280 x 1024 and the 1920 x 1080 resolution monitors.
On a display with proper scaling, most people won’t be able to tell the difference between 1800p and 4K, at least in terms of resolution and quality.
- You have extra performance to spare at 1440p, but not enough for consistent FPS at 4K
- You want to be able to achieve 144+ FPS without reducing color settings
2160p/4k Ultra HD
4K, also known as “Ultra HD” or “UHD,” is the next step up from HD. A 4K TV has 3,840 columns and 2,160 rows of pixels, so the name “4K” is a bit misleading. This resolution is sometimes referred to as “2160p” instead. An 829,400-pixel display is four times larger than an HD 1080p display and nine times larger than a standard-definition display. This has a lot of pixels, so the pixel density is high.
- You don’t mind reducing color settings for 144 FPS, or you only intend to play at 60 FPS
- You have the setup to keep up with the graphical demands
- You want the absolute best image quality, on a screen large enough to justify it. (27 inches or more on PC, 50 inches or more on a TV.)
8k UHD-2
There are only a handful of high-end TVs that support this new high-resolution standard. A higher resolution than 4K, 8K refers to UHD-2 (UHD). A horizontal resolution of approximately 8,000 columns is provided by the 8K resolution. Or 7,680 x 4,320 pixels, which is four times more pixels than 4K and 16 times more pixels than Full HD, distributed over the respective display size in the classic 16:9 format.
It is possible to perceive an improvement in image quality in terms of depth and level of detail at 8K resolution. The 12 bit color depth also makes colors appear more vibrant. Color brilliance and detail can be perceived differently by different people.
For the past few years, all of the major consumer electronics companies have been introducing 8K TVs. UHD TVs have become more affordable in recent years, and as a result, studios have caved and are now pumping out 4K content like crazy. Nevertheless, 8K content is unlikely to enter the mainstream anytime soon due to the high costs associated with producing and distributing 8K content.
In addition, you’ll see a number of other consumer technology products boasting 4K as a major selling point. 4K will reign supreme until 8K is widely available, which isn’t expected for another decade or so. Only a small percentage of video content and very few games on consoles support native 4K resolution, but high-end GPUs like the RTX 2080 or Radeon VII can achieve it.
What’s the point of upgrading?
What does this all mean? Upgrade to a 65-inch UHD display from your beloved CRT television? To begin with, it simply appears to be a much better design. The quality of the lines, curves, and level of detail will all be improved. You can get closer to the screen and still not see the pixels if it has a higher resolution.
Size is also a factor to consider. If you’re looking to buy a 24-inch TV for your kitchen, for example, the difference between 720p and 1080p will be barely noticeable. Similar to this, if you buy a 32-inch bedroom TV, you won’t see many advantages from 4K resolution. That said, 4K is a no-brainer if you’re looking at a TV larger than 40 inches because it’s so inexpensive.
To top it all off, manufacturers these days are solely focused on producing high-quality 4K TVs, which means that they frequently feature improved technology, like color support for high dynamic range (HDR).
In the future
Afraid that the high-end 4K television you’ve had your eye on will be out of date within the next few years? Don’t get too excited just yet. While 8K is supposedly on the way, it’s prohibitively expensive for the time being. Because the difference between 4K and 8K isn’t as striking as that between 1080p and 4K, you’re safe for the time being with your current setup.
Our Thoughts
You’ll have a better time if you choose the right screen resolution, whether it’s for gaming, watching videos, or working. Reading up on topics like high-resolution gaming and live streaming will help you better understand your system’s capabilities. These screen resolutions also scale with your budget, so you know you’re getting the most bang for your buck.
I’ll remind you that more pixels doesn’t always mean better. Contrast and color are far more important aspects of picture quality than resolution.
Here’s the bottom line: Older TVs are 1080p. A 4K Ultra HD TV has four times the pixels of a 1080p TV. There will be an 8K or even 10K TV, but that is a long way off.
ad


Comments are closed.