Even though digital certificates are generally considered more secure than passwords, concerns persist within some organizations regarding the issuance of certificates to unauthorized parties. To mitigate this risk, certificate pinning has been implemented as a security strategy, akin to pinning a message in a chat, to establish an approved list of “pinned” certificates.
Certificate pinning has proven crucial in safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of data exchanged across networks. However, it’s essential to delve into what certificate pinning entails, its significance in ensuring secure connections, and whether it remains a viable practice in the present-day scenario.
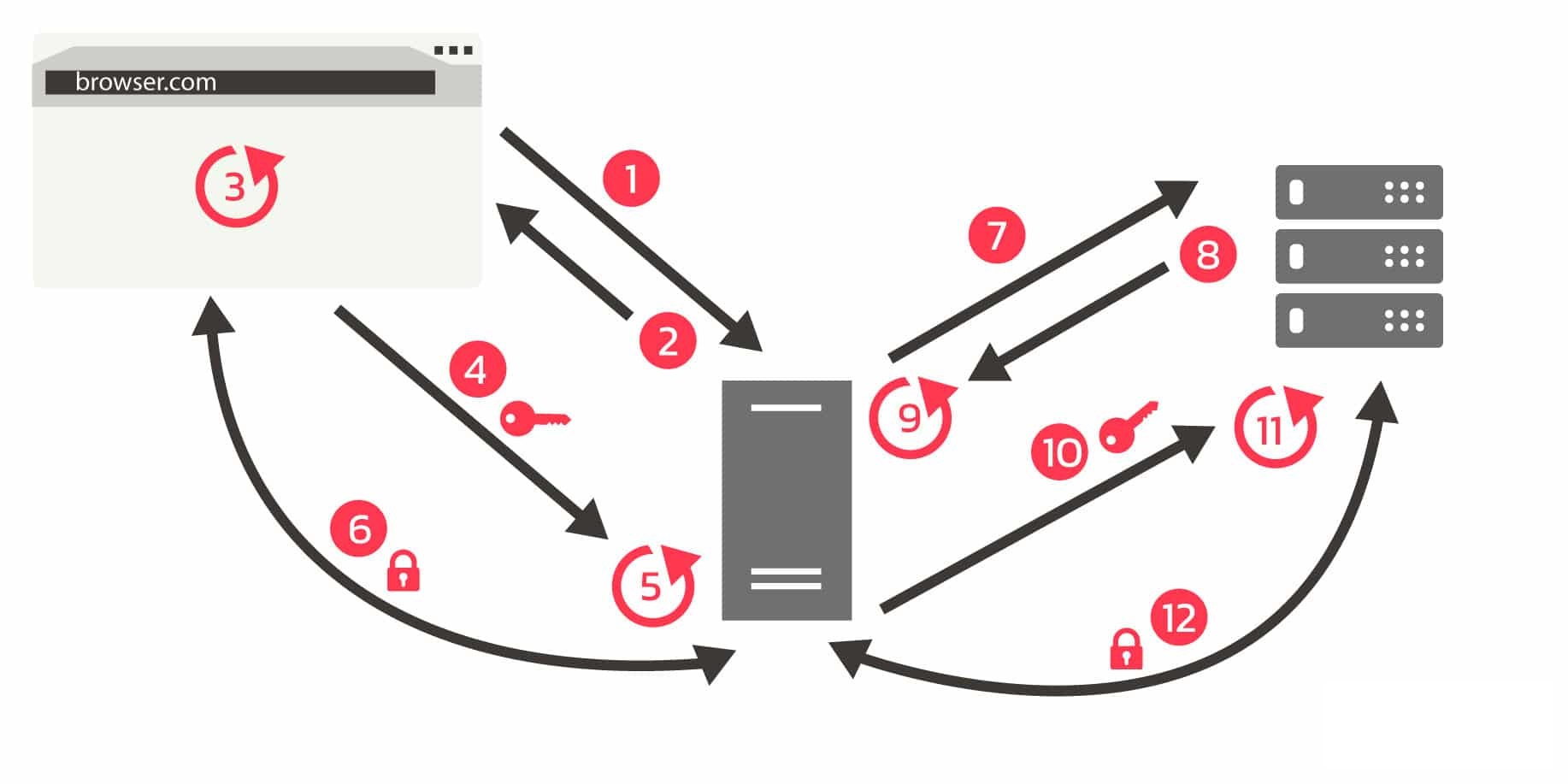
What is Certificate Pinning?
Certificate pinning is a security measure used to authenticate client-server connections, especially in secure communications like HTTPS or other TLS protocols. Its main goal is to increase connection security by reducing the risk of man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, ensuring that the client only communicates with a trusted server.
History of Certificate Pinning
In 2011, Google introduced certificate pinning, directing Chrome to exclusively accept pinned certificates when connecting to google.com. This measure ensures that if an attacker attempts to mimic a trusted CA, Chrome will reject the certificate, thereby preventing the establishment of a connection. Following its implementation in Firefox and Chrome, certificate pinning gained adoption across various devices and technologies, including IoT devices, mobile apps, and other software applications. However, certificate pinning faced criticism due to its associated operational complexity. It could potentially lead to connectivity issues with applications and misconfiguration might result in website blocking.
How does Certificate Pinning Work?
- Conventional Certificate Validation: During a standard TLS handshake, upon connection, the server provides its digital certificate to the client. The client authenticates this certificate by confirming its issuance by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), as well as checking for expiry or revocation. Upon successful verification, the client establishes the secure connection.
- Enhanced Trust via Pinning: Certificate pinning extends trust verification beyond the CA system. Rather than solely depending on it, the client’s application or device maintains a predetermined catalog of public keys or certificates that it unequivocally trusts.
What are the Disadvantages of Certificate Pinning?
Certificate pinning presents challenges despite its potential in thwarting certain cyberattacks, as it brings its own drawbacks. In the subsequent section, we delve into the limitations of certificate pinning and explore alternative methods to tackle these issues.
- Maintenance Complexity: Implementing certificate pinning requires clients to maintain a roster of trusted certificates or public keys. However, this catalog must undergo continual updates to reflect alterations in server certificates. Since certificates have expiration dates and are regularly renewed, the process of keeping pinned certificates current can be laborious, susceptible to human error, and may cause service disruptions.
- Reduced Flexibility: In dynamic and cloud-based environments where server certificates undergo frequent changes (e.g., content delivery networks or microservices), certificate pinning can present operational hurdles. The rigidity of pinned certificates may impede seamless transitions during server updates and complicate certificate management.
- Risk of Connection Breakage: Associating a certificate with an application introduces the risk of losing connectivity if the pinned certificate is compromised or expires. This scenario could lead to service disruptions for users until the client application is updated with the new pinned certificate.
- Lack of Scalability: Certificate pinning may prove impractical for large-scale applications or services that interact with numerous servers, each possessing its unique certificate. Managing a multitude of pinned certificates becomes unwieldy and could undermine the very benefits of certificate pinning.
Which Certificates Can Be Pinned?
Application owners have the choice to implement pinning for all three types of certificates – root, intermediate, and leaf – instead of just one. Consequently, developers aim to pin all three certificates in the trust chain. The primary disadvantage of pinning only a single certificate is the potential for exploitation by a hacker who could utilize a certificate from the same CA, exploiting this vulnerability.
- Root Certificate: The Root CA issues a root certificate containing public and private keys and is constructed using standard hashing and cryptographic algorithms.
- Intermediate Certificate: An intermediate certificate resides between the root and leaf certificates, serving as a link within the certificate chain.
- Leaf Certificate: The leaf certificate, also known as an end-entity certificate, holds significant trust within the certificate chain. It requires timely updates and revocations by the CA.
Alternatives to Certificate Pinning
Various alternative methods can enhance the security of client-server connections while mitigating associated difficulties:
- Certificate Transparency (CT): CT maintains a public record of all issued certificates, ensuring transparency and accountability during issuance. Clients can monitor CT logs to identify unauthorized or fraudulent certificates. This approach supplements pinning by introducing an additional layer of trust verification, enabling clients to detect rogue certificates without the need for pinning-specific maintenance.
- Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Stapling: OCSP stapling enables servers to furnish clients with a digitally signed assertion regarding the status of their SSL/TLS certificates. By utilizing OCSP stapling, clients can verify the legitimacy of a server’s certificate without solely relying on CA trust. This dynamic approach obviates the necessity for pinning and mitigates risks associated with outdated certificates.
Conclusion
While certificate pinning is effective in bolstering connection security, its challenges such as maintenance complexity, reduced flexibility, connectivity risks, and scalability concerns necessitate consideration of alternative approaches like Certificate Transparency (CT) and Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Stapling. Balancing security, usability, and scalability is crucial for maintaining robust communication channels in cybersecurity.