What Is Cloud Integration?
Cloud integration is the process of linking data stored on local servers with data stored in remote SaaS (software as a service) applications and cloud services.
The process of merging multiple cloud-based technologies into a single cohesive entity is referred to as cloud integration. Additionally, the word may refer to the process of integrating on-premises systems with cloud-based ones. The ultimate objective of cloud integration is to combine the diverse aspects of various cloud resources and local resources into a unified, ubiquitous environment that enables administrators to access and administer applications, data, services, and systems in a seamless manner.
ad
The proliferation of public cloud computing has made it possible for businesses to access an extensive range of highly scalable resources and services on demand, as opposed to creating and managing these resources and services in-house. However, the entrance of these many resources and services has led to the formation of IT silos in certain firms. Administrators in these organizations are finding it difficult to manage and maintain the various cloud resources and data sets. Without cloud integration, IT managers are forced to do each integration activity individually and manually, which is not only a time-consuming process but also one that significantly increases the likelihood of making a mistake.
In this article, we’ll look at the main features (and benefits) of cloud integration and give you some helpful links if you’re thinking about a cloud, hybrid cloud, or multi-cloud integration strategy.
What an exact cloud integration is?
ad
Integration with the cloud has become increasingly popular among companies and organizations of all kinds in order to convert data into business intelligence. The explanation for this is quite straightforward: more and more business operations are taking place in hybrid cloud environments, or even fully cloud-to-cloud environments, and if the appropriate tools to manage data in the cloud are not utilized, then the data can become siloed, ignored, or even completely lost.
It acts as a conduit to highly effective data analytics platforms, customer relationship management (CRM) systems like Salesforce, and other applications hosted by third-party providers. These applications include data warehouses like Google BigQuery, Snowflake, Amazon Web Services, and Microsoft Azure.
How cloud integration works
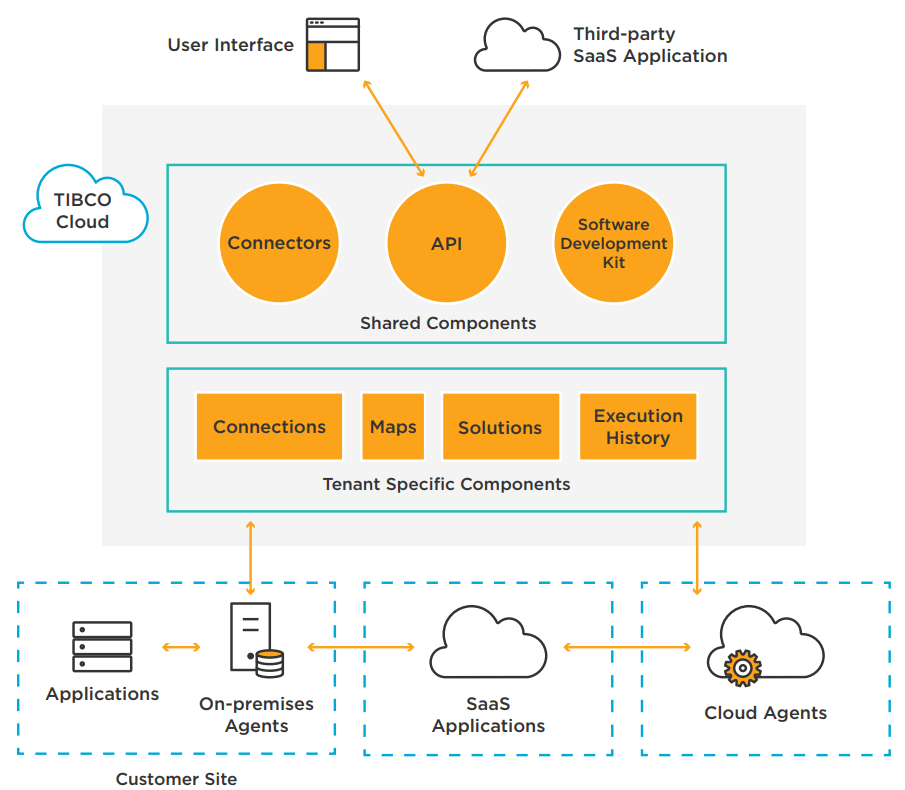
There is no one way to integrate the cloud, but there are several common ideas to think about.
For example, an IT team could use mediation or federation to connect the cloud. Mediation works between applications. When an event happens in one app, the cloud integration platform sees it and sends a response to another connected app.
In contrast, federation acts as a front end for two or more federated applications, where the cloud integration platform can catch and process events from outside of those applications and trigger actions. It is also possible to combine these two methods so that mediation handles actions between applications and federation handles actions from outside of the connected applications.
Depending on the type of communication going on, cloud integration can work either asynchronously or synchronously. Asynchronous cloud integration sends data and commands without waiting for a response from the application receiving them. This keeps data from being sent or created too slowly because the sending application doesn’t have to wait for the receiving application to respond. Synchronous cloud integration will wait for a response from the application it is talking to. This makes sure that both applications are in sync before moving on.
How long it takes to actually integrate the cloud can vary. Most of the time, integration tasks like automatic synchronization can be done quickly by IT. Other tasks may take hours or even days, especially if they involve a human workflow that needs to be synchronized.
Most cloud integration platforms use adapters or connectors, which are small pieces of software designed to work with certain business applications. So, a cloud integration platform can set up a central interface or broker that handles security and authentication, while specific adapters fit the applications being integrated. The communication and notifications are done by the connector.
Connectors can be made for specific applications, like SAP, or they can be vendor-neutral and use standard communication protocols, like simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP) message exchanges, simple object access protocol (SOAP) message exchanges, application programming interfaces (APIs), and the Java connector architecture (JCA).
Cloud integration platforms usually use an application-independent data format, like extensible markup language, for data integration (XML). Before it does any translations or conversions, each connector will change the specific format of the application to the independent format. Then, it can exchange common data with the receiving application.
Cloud integration platforms
In the past, growing a business relied on the specialized knowledge of experts in areas like warehousing, sales, marketing, finance, and others. This approach used people with a lot of knowledge, but important information ended up being locked away in data silos. Since each group’s data was kept in its own department, teams didn’t have many chances to share information or ideas. Because of this, the whole company was hurt.
But when business intelligence came along, companies wanted to mine, find, and share data across departments to improve their overall performance. By setting up APIs and connectors to make it easier for data to flow between silos, cloud integration helps with business intelligence projects and improves all kinds of important business processes.
With cloud integration platforms, a company can add important information from cloud applications to local data stored on-premises to make it better. This includes a lot of information that each department might not have access to, such as (but not limited to) the following:
- Network traffic patterns
- User behavior
- Security events, both external and in your environment
- Compliance information
- Errors and anomalies impacting performance data
- Resource usage
With cloud integration, teams from all over an organization can see all the important, and often very complicated, interactions in their business environment as a whole. With this new, much-needed access to data, they can use what they learn to gain and keep a competitive edge in their market.
Well, Integration platform as a service is one type of third-party integration tool that many companies choose (iPaaS). Tools for integrating the cloud include:
MuleSoft Anypoint Platform – includes various tools for developing, managing and testing application programming interfaces (APIs).
Dell Boomi – enables customers to design cloud-based integration processes called Atoms and transfer data between cloud and on-premises applications.
IBM App Connect – allows administrators to set up workflows that define how data is moved from one application to another.
Cleo Integration Cloud – provides digital integration agility across cloud and on-premise applications.
Microsoft Azure Logic Apps – allows administrators to automate workflows that integrate apps and data across cloud services and on-premises systems.
Apache Libcloud – this Python library allows administrators to manage different cloud resources through a unified application programming interface (API).
📚 Also Read: What is Cross Cloud?
Types of Cloud integration
Integration in the cloud can be cloud-to-cloud, cloud-to-on-premises, or a mix of the two. Integrations can cover many parts of a business, such as data integration and application integration.
Data integration is the process of keeping data in different places in sync. During data integration, data can be processed, moved, and/or changed. This link has nothing to do with anything but data.
Application integration connects different programs and makes sure they keep working and can talk to each other. It’s more than just sharing information. It involves sending requests and commands to start business processes or events.
For cloud integrations, businesses can either build their own data integration solutions or use a third-party provider. But as the number of apps grows and cloud integrations get more complicated, it becomes much less scalable to build custom integrations in-house that must be rebuilt and updated for each project. Using a cloud integration platform gives organizations the ability to integrate both applications and data using a solution that is flexible, scalable, and can be used again and again.
Cloud integration benefits
Cloud-based integration has many benefits that all have to do with fixing the problems that data silos cause. These silos are separated data stores that are managed by one department and are not part of the organization-wide data management system. When you get rid of these data silos, you can use cloud integration to your advantage.
- Cost control. With all of these features, companies can finally keep track of how much they spend on the cloud and data management. As businesses learn which apps are used the most and how much storage space is needed, they can make changes and put their resources to the best use.
- Accessibility. Putting data in the cloud makes it much easier for everyone in the business to access it. Different departments can access all of the company’s data sets, making it easier for people to share information. This stops the problems mentioned above and makes sure that data flows smoothly.
- Flexibility. Also, there is a lot of flexibility in how data is shared, accessed, and analysed, so different ways of running the system may be used. So, the company is in charge of how the data is handled, what restrictions are put on it, and who can use it. The company is also in charge of how the tools are used.
- Scalability. Also, changes to how data is handled are easy to make in the cloud. This includes changes to both the amount of data and the software tools that are used.
- Visibility. With cloud integration, the teams in charge can always see what is going on and why, which apps are being used, and how the data is moving. This makes it easier to avoid errors or conflicts in data management that come up out of the blue and to fix problems quickly if they do happen.
- Maximized human capital: Even a crack team of IT experts wouldn’t be able to take in and make sense of all the data that flows through an organization with only human power. With the right integration tools and design, proper task automation, and full reporting options, your current resources can have a much bigger effect.
- Faster delivery. Business moves faster than ever these days. By moving integration flows and other important workflows to the cloud, your apps will be able to share real-time data instantly. Digital delivery helps you decide quickly on things that are important.
The last one is especially important: leaders in their fields are quickly adopting new methods like continuous delivery and DevOps. Both of these ideas call for delivery cycles that are close to real time, which can’t be done without a lot of automation. This will always require a complicated network of SaaS apps and cloud computing solutions. To solve for speed, you need to change your mind about what modern data integration means.
Challenges for businesses with cloud integration
Concerns about security are the main problems that come with integrating the cloud. When multiple clouds are used to store data, these worries are even more important because there are more places where cyberattacks could happen.
Here are some ideas and best practices for how to deal with these problems.
- Privacy and security of data. Almost every news cycle includes news of a new and major security breach. A growing number of online threats, such as theft, ransomware, and destruction of digital information, put big businesses, financial institutions, and even political institutions in danger. If a company doesn’t have the right security, it could face even worse problems than bad business intelligence. Cloud providers know that their businesses and reputations are on the line, so they are always improving their data security measures to keep up with new threats.
- Synchronizing policies and settings across providers. When multiple clouds are used for the same operations and data storage, the same security policies and rules should apply to all of them.
- Policies and settings should be different for each operation. When different operations and applications are used in different clouds, however, settings should also be different. This is because the initial level of security for each operation can be different. Since different numbers and types of users may be working with the same batch of data, different types of oversight may be needed. The security settings should be changed to account for this difference.
- Automation. Automation is the best way to prevent data breaches caused by human error or bad actors. Every job that can be done by a machine should be. For example, automated PKI saves you money on set-up costs, team resources, maintenance time, and compliance, among other things. Digital signing saves a lot of time that would be lost if the person had to be identified by hand. Digital Signatures save time, make work easier, and make it harder for unauthorized people to get into data.
When organizations try to integrate data more, the most important question to answer is about data security. So, experts in business data are always trying to find better ways to protect data in the cloud by using the best tools and management techniques.
Conclusion:
At this point, there’s no question: the cloud is the future of managing data. Even organizations with a lot of legacy on-premises infrastructure have to work with so many SaaS apps that they end up spending a lot of time in the cloud, whether they know it or not.
If you’re ready to see what the cloud can do for you, a data integration platform can help you move quickly and easily. The Talend Data Integration Platform gives you a complete set of tools that are easy to use and get your data where it needs to go without you having to do a lot of hand coding.
ad


Comments are closed.